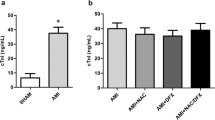
Abstract
The ability of an iron chelator, desferrioxamine, to inhibit the infarct size in in vivo rat heart was assessed. Anaesthetised rats were subjected to coronary artery ligation (CAL) for 72 hr and infarct size was measured macroscopically using TTC staining. Systolic blood pressure and ECG were monitored. Desferrioxamine (10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg i.v.) administered half an hour after CAL markedly reduced the infarct size. However, drug treatment did not alter the systolic blood pressure of animals. In addition, desferrioxamine in vitro and in vivo demonstrated an inhibition of rat PMN-evoked and luminol-enhanced chemiluminiscence. The capacity of desferrioxamine to impair the generation or to scavenge directly oxygen free radicals may be responsible for its beneficial effect on myocardial infarct size in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosio G, Weisfeldt ML, Jacobus WE, Flaherty JT: Evidence for a reversible oxygen radical-mediated component of reperfusion injury; reduction by recombinant human superoxide dismutase administered at the time of reflow. Circulation 75: 282–291, 1987
Chambers DJ, Braimbridge MV, Hearse DJ: Free radicals and cardioplegia: free radical scavengers improve post-ischemic function of the rat myocardium. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1: 37–45, 1987
Stewart JR, Blackwell WH, Crute SL, Loughlin V, Greenfield LJ, Hess ML: Inhibition of surgically induced ischemia/reperfusion injury by oxygen free radical scavengers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 86: 262–272, 1983
Prezyklenk K, Kloner RA: ‘Reperfusion injury’ by oxygen-derived free radicals? Effect of superoxide dismutase plus catalase, given at the time of reperfusion, on myocardial infarct size, contractile function, coronary micro vasculature and regional myocardial blood flow. Circ Res 64: 86–96, 1989
Nejima J, Knight DR, Fallon JT, Uemura N, Manders T, Canfield DR, Cohen MV, Vatner SF: Superoxide dismutase reduces reperfusion arrhythmias but fails to salvage regional function or myocardium at risk in conscious dogs. Circulation 79: 143–153, 1989
Aust SD, White BC: Iron chelation prevents tissue injury following ischemia. Adv Free Rad Biol Med 1: 1–17, 1985
Halliwell B: Superoxide — dependent formation of hydroxyl radicals in the presence of iron salts is a feasible source of hydroxyl radicals in vivo. Biochem J 205: 461–470, 1982
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC: Oxygen free radicals and iron in relation to biology and medicine: Some problems and concepts. Arch Biochem Biophys 246: 501–514, 1986
Holt S, Gunderson KJ, Nayini NR: Myocardial tissue iron depletion and evidence for lipid peroxidation after two hours of ischemia (abstr). Ann Emerg Med 14: 499, 1985
Kerbele H: The biochemistry of desferrioxamine and its relation to iron metabolism. Ann NY Acad Sci 119: 758–768, 1964
Willis ED: Lipid peroxide formation of microsomes: the role of non-haem iron. Biochem J 113: 325–332, 1969
Bolli R, Patel BS, Zhu W, O'Neil PG, Hartley CJ, Charlat ML, Roberts R: The iron chelator desferrioxamine attenuates postischemic ventricular dysfunction. Am J Physiol 253: H1372-H1380, 1987
Bernier M, Hearse DJ, Manning AS: Reperfusion-induced arrhythmias and oxygen-derived free radicals: studies with ‘antifree radical’ interventions and a free radical-generating system in the isolated perfused rat heart. Circ Res 58: 331–340, 1986
Reddy BR, Kloner RA, Prezyklenk K: Early treatment with desferrioxamine limits myocardial ischemic/reperfusion injury. Free Radical Biol Med 7: 45–52, 1989
Lesnefsky EJ, Repine JE, Horwitz LD: Deferoxamine pretreatment reduces canine infarct size and oxidative injury. J Pharm Exp Ther 253: 1103–1109, 1990
Maxwell MP, Hearse DJ, Yellon DM: Inability of desferrioxamine to limit tissue injury in the ischemic and reperfused rabbit heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 13: 608–615, 1989
Myers CL, Weiss SJ, Kirsh MM, Sheafer M: Involvement of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical in the ‘oxygen paradox’: reduction of creative kinase release by catalase, allopurinol or deferoxamine, but not by superoxide dismutase. J Mol Cell Cardiol 17: 675–684, 1985
Selye H, Bausz E, Grasso S, Mendell P: Simple techniques for the surgical occlusion of coronary vessels in the rat. Angiology 2: 398–407, 1960
Mittleman R, Szabo S, Heinsimar J, Reynolds ES: Macroscopic histochemical detection of myocardial necrosis in the heart autopsy by TTC technique (abstr.). Clin Res 23: 198A, 1975
Banka N, Anand IS, Chakravarti RN, Sharma PL, Wahi PL: Macroscopic measurements of experimental myocardial infarct size in rhesus monkey-A comparison of two methods. Bull PGI 15: 147–150, 1981
Boyum A: Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Scan J Clin Lab Invest 21, Suppl 97: 77–89, 1968
Cheung K, Archibald AC, Robinson MF: Luminol dependent Chemiluminiscence produced by PMN's stimulated by immune complex. Aust J Expt Biol Med Sci 62: 403–419, 1984
Kumar C, Singh M: Pharmacological interventions and myocardial infarct size in rat. Eur J Pharmacol 109; 117–120, 1985
Schaper W: Experimental infarcts and the Microcirculation. In: DJ Hearse and DM Yellon (eds.) Therapeutic approaches to myocardial infarct size limitation. Raven Press, New York, 79–90, 1984
Hearse DJ, Yellon DM: Why are we still in doubt about myocardial infarct size limitation? The experimentalist's viewpoint. In: Therapeutic approaches to myocardial infarct size limitation. Raven Press, New York 17–42, 1984
Borg DC, Schaich KM: Prooxidant action of desferrioxamine: Fenton-like production of hydroxyl radicals by reduced ferrioxamine. J Free Radic Biol Med 2: 237–243, 1986
Graf E, Mahoney JR, Bryant RG, Eaton JW: Iron-catalyzed hydroxyl radical formation. J Biol Chem 259: 3620–3624, 1984
Uraizee A, Reimer KA, Murry CE, Jennings RB: Failure of superoxide dismutase to limit size of myocardial infarction after 40 minutes of ischemia and 4 days of reperfusion in dogs. Circulation 75: 1237–1248, 1987
Mehta J, Nichols WW, Mehta P: Neutrophils as potential participants in acute myocardial ischemia. J Am Coll Cardiol 11: 1309–1316, 1988
Lucchesi BR: Role of neutrophils in ischemic heart disease. Cardiovase Clin 18: 3325–3348, 1987
Lucchesi BR, Mullane KM: Do leukocytes influence infarct size. In: DJ Hearse and DM Yellon (eds). Therapeutic approaches to myocardial infarct size limitation. Raven Press, New York, 219–248, 1984
Romson J, Hook B, Kunkel S, Abrans G, Schort MA, Lucchesi BR: Reduction of the extent of ischemic myocardial injury by neutrophil depletion in the dog. Circulation 67: 1016–1023, 1983
Halliwell B: Use of desferrioxamine as a probe for iron-dependent formation of OH. Biochem Pharmacol 34: 229–233, 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chopra, K., Singh, M., Kaul, N. et al. Decrease of myocardial infarct size with desferrioxamine: possible role of oxygen free radicals in its ameliorative effect. Mol Cell Biochem 113, 71–76 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230887
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230887