Summary
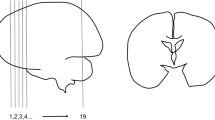
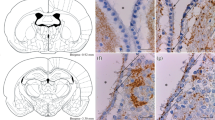
The lateral ventricles of the Pekin duck, Anas platyrhynchos, display characteristic ependymal and hypendymal specializations. Adjacent to the nucleus accumbens and the basal pole of the lateral septum the ventricular surface shows a highly folded pattern either with protrusions into the ventricular lumen or deep invaginations into the brain tissue. These medial and basal ependymal folds are found exclusively in a circumscribed region extending over a range of 600 μm in the rostrocaudal direction. Ependymal folds occurring in the lateral wall of the ventricles were traced up to the level of the interventricular foramen. Numerous capillaries are observed in the subependymal layer of these folds.
By means of immunocytochemistry with antibodies against chicken vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) an aggregation of classical cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons is shown in the region of the nucleus accumbens and the lateral septum. These neurons are closely related to the ependymal folds. Additional VIP-immunoreactive neurons are scattered in deeper layers of the lateral septum and the nucleus accumbens. The latter are richly innervated by VIP-immunoreactive nerve fibers.
The results of the present study are discussed with particular reference to the hypothesis of Kuenzel and van Tienhoven (1982) that ependymal specializations demonstrated in the lateral ventricles of the domestic fowl might represent a new circumventricular organ (“lateral septal organ”).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akert K (1967) Das Subfornikalorgan. Morphologische Untersuchungen mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der cholinergen Innervation und der neurosekretorischen Aktivität. Schweiz Arch Neurol Neurochir Psychiatr 100:1–15
Andres KH (1965) Ependymkanälchen im Subfornikalorgan vom Hund. Naturwissenschaften 52:433
Besson J, Rotsztejn WH, Bataile D (1982) Involvement of VIP in neuroendocrine functions. In: Said I (ed) Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Raven Press, New York, pp 253–262
Blähser S, Vigh-Teichmann I, Ueck M (1982) Cerebrospinal fluidcontacting neurons and other somatostatin-immunoreactive perikarya in brains of tadpoles of Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res 224:693–697
Coates PW (1977) The third ventricle of monkeys. Scanning electron microscopy of surface features in mature males and females. Cell Tissue Res 177:307–316
Deutsch H, Simon E (1980) Intracerebroventricular osmosensitivity in the Pekin duck. Pfluegers Arch 387:1–7
Dimaline R, Dockray GJ (1982) Molecular forms of VIP in normal tissue. In: Said SI (ed) Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Raven Press, New York, pp 23–33
Dimaline R, Vaillant C, Dockray GJ (1980) The use of region specific antibodies in the characterization and location of vasoactive polypeptide-like substances in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Regul Peptides 1:1–15
Fahrenkrug J (1982) VIP as a neurotransmitter in the peripheral nervous system. In: Said SI (ed) Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Raven Press, New York, pp 361–372
Ferraz de Carvalho CA (1970) Considerations on the ependyma of the encephalic ventricles of Tropidonotus natrix, Alligator mississippiensis and Testudo graeca. Acta Anat (Basel) 76:352–380
Ferraz de Carvalho CA, Costacurta L, de Carvalho Filho JR (1975) Histological and histochemical study on the ependyma of Bradypus tridactylus. Acta Anat (Basel) 92:424–442
Flament-Durand J (1978) Etude par la microscopie électronique a transmission et a balayage du revêtement épendymaire du troisieme ventricule chez l'homme et chez le rat Bull Mem Acad R Med Belg 133:88–102
Fleischhauer K (1960) Fluoreszenzmikroskopische Untersuchungen an der Faserglia. I. Beobachtungen an den Wandungen der Hirnventrikel der Katze (Seitenventrikel, III. Ventrikel). Z Zellforsch 51:467–496
Fleischhauer K (1970) Über die postnatale Entwicklung des Stratum subcallosum im Vorderhorn des Seitenventrikels der Katze. Z Anat Entwickl Gesch 132:1–17
Friede RL (1961) Surface structures of the aqueduct and the ventricular walls: a morphologic, comparative and histochemical study. J Comp Neurol 116:229–247
Fuxe K, Hökfelt T, Said SI, Mutt V (1977) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and the nervous system: immunohistochemical evidence for localization in central and peripheral neurons, particularly intracortical neurons of the cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 5:241–246
Gerstberger R (1983) Zentralnervöse Kontrollmechanismen im Salzund Wasserhaushalt der Pekingente (Anas platyrhynchos). Inaugural-Dissertation. Fachbereich Biologie, Universität Hohenheim
Hartwig HG (1975) Neurobiologische Studien an photoneuroendokrinen Systemen. Habilitationsschrift, Fachbereich Humanmedizin, Universität Giessen
Hökfelt T, Schultzberg M, Lundberg JM, Fuxe K, Mutt V, Fahrenkrug J, Said SI (1982) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the central and peripheral nervous system as revealed by immunocytochemistry. In: Said SI (ed) Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Raven Press, New York, pp 65–90
Hofer H (1959) Zur Morphologie der circumventrikulären Organe des Zwischenhirns der Säugetiere. Zool Anz 22:202–251
Hofer H (1965) Circumventrikuläre Organe des Zwischenhirns. In: Hofer H, Schultz AH, Starck D (eds) Primatologia Bd II/2/13. Karger, Basel New York, pp 1–104
Karten HJ, Hodos W (1967) A stereotaxic atlas of the brain of the pigeon. John Hopkins Press, Baltimore, pp 1–193
Kirsche W (1967) Über postembryonale Matrixzonen im Gehirn verschiedener Vertebraten und deren Beziehung zur Hirnbauplanlehre. Z mikrosk anat Forsch 77:313–406
Korf HW, Simon-Oppermann Ch, Simon E (1982) Afferent connections of physiologically identified neuronal complexes in the paraventricular nucleus of conscious Pekin ducks involved in regulation of saltand water-balance. Cell Tissue Res 226:275–300
Korf HW, Viglietti-Panzica C, Panzica GC (1983) A Golgi study on the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the Pekin duck. Cell Tissue Res 228:149–163
Kuenzel WJ, van Tienhoven A (1982) Nomenclature and location of avian hypothalamic nuclei and associated circumventricular organs. J Comp Neurol 206:293–313
Kuhlenbeck H (1977) The central nervous system of vertebrates. Derivatives of the prosencephalon: diencephalon and telencephalon. Vol. 5, Part I. Karger, Basel, pp 1–888
Kusche P (1966) Über Ependym und Gliafasern in der Epiphyse der erwachsenen Katze. Z Zellforsch 71:405–414
Larsson LI (1982) Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: a critical appraisal. In: Said SI (ed) Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Raven Press, New York, pp 51–64
Leonhardt H (1980) Ependym und circumventriculäre Organe. In: Oksche A (ed) Neuroglia I. Hdbh mikr Anat Mensch. Vol IV/10. Springer, Berling Heidelberg New York, pp 177–666
Lorén I, Emson PC, Fahrenkrug J, Björklund A, Alumets J, Hakanson P, Sundler F (1979) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat and mouse brain. Neuroscience 4:1953–1976
Marley P, Emson P (1982) VIP as a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. In: Said SI (ed) Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Raven Press, New York, pp 341–360
Merker G (1968) Licht-und elektronenmikroskopische Studien über die Fasergliastruktur der Epiphysen-Subcommissuralregion der Primaten. Z Zellforsch 92:232–255
Merker G (1970) Fasergliastruktur der dorsalen Wand des Aquaeductus cerebri bei einigen Primaten. Z Zellforsch 107:564–585
Mikami S, Yamada S (1983) Localization of immunoreactive neurotensin, VIP, and somatostatin in the hypothalamus of the Japanese quail. In: Mikami S, Homma K, Wada M (eds) Avian endocrinology. Jap Sci Soc Press, Tokyo and Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 25–38
Möller W (1976) Paraffinum liquidum in einer Intermediumkombination für die Paraffineinbettung. Mikroskopie 32:100–104
Møller M, Glistrup OV, Olsen W (1983) Contrast enhancement of the brownish horseradish peroxidase-activated 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride reaction product in black and white photomicrography by the use of interference filters. J Histochem Cytochem (in press)
Mutt V (1982) Isolation and structure of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide from various species. In: Said SI (ed) Vasoactive intestinal peptide. Raven Press, New York, pp 1–10
Mutt V, Said SI (1974) Structure of the porcine vasoactive intestinal octacosapeptide. The amino acid sequence, use of kallikrein in its determination. Eur J Biochem 42:581–589
Nilsson A (1974) Isolation, amino acid composition and terminal amino acid residues of the vasoactive octacosapeptide from chicken intestine. Partial purification of chicken secretin. FEBS Lett 47:284–289
Nilsson A (1975) Structure of the vasoactive intestinal octacosapeptide from chicken intestine: the amino acid sequence. FEBS Lett 60:322–325
Oksche A (1982) Neuroglia: retrospect and prospect. Acta Morphol Neerl-Scand 20:225–235
Panzica GC, Viglietti-Panzica C (1983) A Golgi study of the parvocellular neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the domestic fowl. Cell Tissue Res 231:603–613
Pfenninger K (1969) Subfornikalorgan and Liquor cerebrospinalis. In: Sterba G (ed) Zirkumventrikuläre Organe und Liquor. G. Fischer, Jena, pp 103–106
Ritter U (1983) Studien an der Epiphysis cerebri und am Subkommissuralorgan der Primaten. Inaugural-Dissertation, Fachbereich Humanmedizin, Giessen
Rodríguez EM (1976) The cerebrospinal fluid as a pathway in neuroendocrine integration. J Endocrinol 71:407–443
Rodríguez EM, Pena P, Rodríguez S, Aguado LI (1982) Evidence for the participation of the CSF and periventricular structures in certain neuroendocrine mechanisms. Front Horm Res 9:142–158
Romeis B (1968) Mikroskopische Technik. Oldenbourg, München, Wien
Said SI, Rosenberg RN (1976) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: abundant immunoreactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science 192:907–908
Simon E (1982) The osmoregulatory system of birds with salt glands. Comp Biochem Physiol A 71:547–556
Simon E, Hammel HT, Oksche A (1977) Thermosensitivity of single units in the hypothalamus of conscious ducks. J Neurobiol 8:523–535
Sims KB, Hoffman DL, Said SI, Zimmerman EA (1980) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in mouse and rat brain: an immunocytochemical study. Brain Res 186:165–183
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry John Wiley-Sons, New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto
Vigh B (1971) Das Paraventrikularorgan und das zirkumventriku-läre System. Stud Biol Hung. Vol X. Akad Kiadó, Budapest
Vigh B, Majorossy K (1968) The nucleus of the paraventricular organ and its fibre connections in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung 19:181–192
Vigh B, Vigh-Teichmann I (1973) Comparative ultrastructure of the CSF-contacting neurons. Int Rev Cytol 35:189–251
Vigh-Teichmann I, Vigh B (1974) The infundibular cerebrospinal fluid contacting neurons. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 50/2:1–91
Vigh-Teichmann I, Vigh B (1983) The system of cerebrospinal fluid-contacting neurons. Arch Histol Jpn 46:427–468
Vigh-Teichmann I, Vigh B, Aros B (1971) Liquorkontaktneurone im Nucleus infundibularis des Kükens. Z Zellforsch 112:188–200
Vigh-Teichmann I, Vigh B, Korf HW, Oksche A (1983) CSF-contacting and other neurons in the brains of Anguilla anguilla, Phoxinus phoxinus and Salmo gairdneri (Teleostei). Cell Tissue Res 233:319–334
Viglietti-Panzica C, Panzica GC, Korf HW (1983) Morphological interrelationships between the avian paraventricular nucleus and the cerebrospinal fluid. Anat Anz (in press)
Weindl A, Sofroniew MV (1982) Peptide neurohormones and circumventricular organs in the pigeon. Front Horm Res 9:88–104
Wenger T, Törö I (1971) Studies on the organon vasculosum laminae terminalis. IV. Fine structure of the organon vasculosum laminae terminalis in man. Acta Biol Acad Sci Hung 22:331–342
Yamada S, Mikami S, Yanaihara N (1982) Immunohistochemical localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP)-containing neurons in the hypothalamus of the Japanese quail, Coturnix coturnix. Cell Tissue Res 226:13–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are greatly indebted to Professor A. Oksche for stimulating discussions
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Ko 758/2-2; 2-3) and the P. Carl Petersen Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korf, H.W., Fahrenkrug, J. Ependymal and neuronal specializations in the lateral ventricle of the Pekin duck, Anas platyrhynchos . Cell Tissue Res. 236, 217–227 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216534
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216534