Abstract
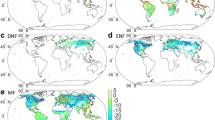
The effects in climate models of changes in albedo and soil moisture which are expected to follow from tropical deforestation are reviewed. The major results from experiments with tropical forest regions (a) forested (‘Experiment F’) and (b) grass-covered (‘Experiment G’) are compared over South America and Central Africa. Then, Experiment F is compared with ‘Experiment 2’ which has constant snowfree albedo of 0.2, close to that of grassland; in both South America and Zaire regions, the albedo changes for (G-F) and (2-F) are similar and, as Experiment 2 is an eight year run, assessments of the statistical significance can be made.
The results for December to February and March to May show a decrease of rainfall over the Amazon region and also to the southeast outside the area which has changed albedos in (G-F). These decreases are common to both (G-F) and (2-F) and are statistically significant in the comparison with the eight year record for Experiment 2. Deforestation in the Zaire regions is associated with similar changes, which, though less extensive, are generally larger in relation to the albedo changes. In June to August, changes are small south of the equator because the rainbelt has moved north; in South America larger, significant decreases are obtained north of the equator.
The drying with increased albedo is due to decreases in both evaporation and moisture convergence. The decreases in evaporation result both from a reduction in absorbed energy at the surface and an increase in surface resistance to evaporation due to greater soil moisture deficits arising from earlier decreases in rainfall.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carson, D. J.: 1982, ‘Current Parameterization of Land-Surface Processes in Atmospheric General Circulation Models’, in Eagleson, P. S. (ed.), Land Surface Processes in Atmospheric General Circulation Models, Cambridge University Press, pp. 67–108.
Carson, D. J. and Sangster, A. B.: 1981, ‘The Influence of Land Surface Albedo and Soil Moisture on General Circulation Model Simulations’, Rutherford, I. D. (ed.), GARP/WCRP: Research Activities in Atmospheric and Oceanic Modelling, Numerical Experimental Programme Report 2, pp. 5.14–5.21.
Charney, J. G.: 1975, ‘Dynamics of Deserts and Drought in the Sahel’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 101, 193–202.
Charney, J. G., Quirk, W. J., Chew, S. M., and Kornfield, J.: 1977, ‘A Comparative Study of the Effects of Albedo Change on Drought in Semi-Arid Regions’, J. Atmos. Sci. 34, 1360–1388.
Chervin, R. M.: 1979, ‘Response of the NCAR General Circulation Model to Changed Land Surface Albedo’, Report of the JOC Study Conference on Climate Models: Performance, Intercomparison and Sensitivity Studies, Vol. 1, 563–581.
Clarke, R. H.: 1970, ‘Recommended Methods for the Treatment of the Boundary Layer in Numerical Models’, Aust. Met. Mag. 18, 51–73.
Cunnington, W. M. and Rowntree, P. R.: 1986, ‘Simulations of the Saharan Atmosphere-Dependence on Moisture and Albedo’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 112, 971–999.
Dickinson, R. E. and Henderson-Sellers, A.: 1988, ‘Modelling Tropical Deforestation: A Study of GCM Land-Surface Parameterizations’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 114, 439–462.
Henderson-Sellers, A. and Gornitz, V.: 1984, ‘Possible Climatic Impacts of Land Cover Transformation, with Particular Emphasis on Tropical Deforestation’, Climatic Change 6, 231–257.
Henderson-Sellers, A. and Wilson, M. F.: 1983, ‘Surface Albedo Data for Climatic Modelling’, Rev. Geoph. Space Phys. 21, 1743–1778.
Ingram, W. J.: 1985, A Comparison of the Time Mean Fields of the AGCM with Observational Data Meteorological Office, Met 0 20 Internal note 42.
Jaeger, L.: 1976, ‘Monatskarten des Niederschlags für die Ganze Erde’, Bericht Deutsche Wetterdienst 18, No 139.
Kurbatkin, G. P., Manabe, S., and Hahn, D. G.: 1979, ‘The Moisture Content of the Continents and the Intensity of the Summer Monsoon Circulation’, Soviet Meteorology and Hydrology 11, 1–6.
Lean, J. and Warrilow, D. A.: 1989, ‘Simulation of the Regional Impact of Amazon Deforestation’, Nature 342, 411–413.
Miller, D. B. and Feddes, R. G.: 1971, Global Atlas of Relative Cloud Cover 1967–1970, Based on photographic signals from meteorological satellites, U.S. Dept. of Commerce, NOAA/USAF Air Weath. Service, ETAC, Washington, D.C.
Mintz, Y.: 1984, ‘The Sensitivity of Numerically Simulated Climates to Land Surface Boundary Conditions’, in Houghton, J. T. (ed.), Global Climate, Cambridge University Press, pp. 79–105.
Planton, S.: 1986, Sensitivity of the Annual Cycle Simulated by a GCM to Change in Land Surface Albedo, Noordwijk: ESA SP-248, pp. 135–142.
Poore, D.: 1976, ‘The Value of Tropical Moist Forest Ecosystems and the Environmental Consequences of Their Removal’, Unasylva 28, 127–145.
Potter, G. L., Elsaesser, H. W., MacCracken, M. C., and Luther, F. M.: 1975, ‘Possible Impact of Tropical Deforestation’, Nature 258, 697–698.
Rowntree, P. R.: 1988, ‘Review of General Circulation Models as a Basis for Predicting the Effects of Vegetation Change on Climate’, in Reynolds, E. R. C. and Thompson, F. B. (eds.), Forests, Climate and Hydrology - Regional Impacts, Proceedings of United Nations University Workshop, Oxford, March 1984, pp. 162–193.
Rowntree, P. R. and Bolton, J. A.: 1983, ‘Simulation of the Atmospheric Response to Soil Moisture Anomalies over Europe’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 109, 501–526.
Salati, E. and Vose, P. B.: 1983, ‘Depletion of Tropical Rain Forests’, Ambio 12, 67–71.
Shukla, J. and Mintz, Y.: 1982, ‘Influence of Land-Surface Evapotranspiration on the Earth's Climate’, Science 215, 1498–1501.
Shukla, J., Nobre, C., and Sellers, P.: 1990, ‘Amazon Deforestation and Climate Change’, Science 247, 1322–1325.
Shuttleworth, W. J.: 1988, ‘Evaporation from the Amazon Rain Forest’, Proc. Royal Soc. of London B 233, 321–346.
Slingo, A.: 1985, Handbook of the Meteorological Office 11-Layer Atmospheric General Circulation Model, Volume 1: Model Description, Dynamical Climatology Technical Note DCTN 29, Meteorological Office, Bracknell, UK.
Slingo, A. and Pearson, D. W.: 1987, ‘A Comparison of the Impact of an Envelope Orography and of a Parameterization of Orographic Gravity Wave Dragon Model Simulations’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 113, 847–870.
Slingo, A. and Wilderspin, R. C.: 1986, ‘Development of a Revised Longwave Radiation Scheme for an Atmospheric General Circulation Model’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 112, 371–386.
Sud, Y. C. and Fennessy, M.: 1982, ‘A Study of the Influence of Surface Albedo on July Circulation in Semi Arid Regions Using the GLAS GCM’, J. Clim. 2, 105–125.
Sud, Y. C. and Fennessy, M.: 1984, ‘A Numerical Study of the Influence of Evaporation in Semi-Arid Regions on the July Circulation’, J. Clim. 4, 383–398.
Wilson, M. F.: 1984, The Construction and Use of Land Surface Information in a General Circulation Climate Model, PhD Thesis, University of Liverpool.
Wilson, M. F. and Henderson-Sellers, A.: 1985, ‘A Global Archive of Land Cover and Soils Data for Use in General Circulation Climate Models’, J. Clim. 5, 119–143.
Yeh, T. C., Wetherald, R. T., and Manabe, S.: 1984, ‘The Effect of Soil Moisture on the Short Term Climate and Hydrology Change - A Numerical Experiment’, Mon. Weather. Rev. 112, 474–490.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mylne, M.F., Rowntree, P.R. Modelling the effects of albedo change associated with tropical deforestation. Climatic Change 21, 317–343 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00139730
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00139730