Abstract
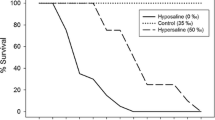
Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) post-smolts exposed to 1.23‰ hydrogen peroxide for 20 min at 13.5 ‡C suffered an acute toxicity resulting in a 35% mortality within 2 h. Under similar conditions at 10 ‡C no mortalities were observed with Atlantic salmon or goldsinny wrasse (Ctenolabrus rupestris). No histological changes were noted in tissues from exposed fish. Thirty-three per cent of adult and pre-adult sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) were immobilized or killed following exposure to 0.5‰ hydrogen peroxide at 10 ‡C, rising to 98% at 2‰. Some lice were able to recover and regained normal swimming movements. Gas bubbles within the haemolymph caused affected lice to float on the water surface. A delay in the toxicity of hydrogen peroxide to copepodites occurred, with a 10% mortality following a 20 min exposure to 1.25‰ at 10 ‡C rising to 100% mortality at 19 h post treatment.
Dilute hydrogen peroxide was stable over the 20 min treatment period. Aeration and higher temperatures increased the long-term breakdown of a working concentration of hydrogen peroxide in seawater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjordal, ÅA. (1988) Cleaning symbiosis between wrasses (Labridae) and lice infested salmon (Salmo salar) in mariculture. International Council for the Exploration of the Sea 1988/F:17, 8 pp.
Darwall, W., Costello, M. and Lysaght, S. (1992) Wrasse — how well do they work? Aquaculture Ireland 50, 26–29.
Egidius, E. and Møster, B. (1987) Effect of Neguvon® and Nuvan® treatment on crabs (Cancer pagurus, C. maenas), lobster (Homarus gammarus) and blue mussel (Mytilus edulis). Aquaculture 60, 165–168.
Grayson, T.H., Jenkins, P.G., Wrathmell, A.B. and Harris, J.E. (1991) Serum responses to the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Krøyer, 1838), in naturally infected salmonids and immunised rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), and rabbits. Fish and Shellfish Immunology 1, 141–155.
Jaworski, A. and Holm, J.C. (1992) The distribution and structure of the population of sea lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis Krøyer) on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) under typical rearing conditions. Aquaculture and Fisheries Management 23, 577–589.
Jones, M.W., Sommerville, C. and Wootten, R. (1992) Reduced sensitivity of the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, to the organophosphate dichlorvos. Journal of Fish Diseases 15, 197–202.
Pike, A.W. (1989) Sea lice — major pathogens of farmed Atlantic salmon. Parasitology Today 5, 291–297.
Ross, A. and Horsmam, P.V. (1988) The use of Nuvan 500EC in the salmon farming industry. Marine Conservation Society, Herefordshire, 24 pp.
Smed, J. (1951) Monthly anomalies of the surface temperature in areas of the northern North Atlantic in 1951. Annals Biologiques No. VIII, 19–20.
Thomassen, J.M. (1993) A new method for control of salmon lice. In: Fish Farming Technology (eds H. Reinertsen, L.A. Dahle, L. Jørgensen and K. Tvinnereim) Balkema: Rotterdam, pp. 233–236.
Treasurer, J. (1993) More facts on the role of wrasse in louse control. Fish Farmer Jan/Feb, 37–38.
Tully, O. (1989) The succession of generations and growth of the caligid copepods Caligus elongatus and Lepeophtheirus salmonis parasitising farmed Atlantic salmon smolts (Salmo salar). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 69, 279–287.
Vogel, A.I. (1978) Vogel's Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis. Longman: England 4th edition, 355 pp.
Wootten, R., Smith, J.W. and Needham, E.A. (1982) Aspects of the biology of the parasitic copepods Lepeophtheirus salmonis and Caligus elongatus on farmed salmonids, and their treatment. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh 81B, 185–197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruno, D.W., Raynard, R.S. Studies on the use of hydrogen peroxide as a method for the control of sea lice on Atlantic salmon. Aquacult Int 2, 10–18 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00118529
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00118529