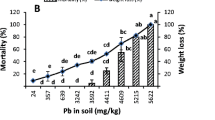
The effects of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc on survival, growth, cocoon production and cocoon viability of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny) were determined in three experiments. In experiment 1, worms were exposed to single metals in standard artificial soil. For experiment 2, worms were maintained in contaminated soils collected from sites at different distances from a smelting works situated at Avonmouth, south-west England. In experiment 3, worms were exposed to mixtures of metals in artificial soil at the same concentrations as those present in the field soils. A survey of earthworm populations was carried out also. Population densities and species diversities of earthworms declined with proximity to the smelting works. No earthworms were found within 1 km of the factory. Comparison of toxicity values for the metals determined in the experiments indicated that zinc is most likely to be limiting earthworm populations in the vicinity of the works. Zinc was at least ten times more toxic to E. fetida in artificial soil than in contaminated soils collected from the field. This difference was probably due to the greater bioavailability of zinc in the artificial soil. The results are discussed in the context of setting ‘protection levels’ for metals in soils based on laboratory toxicity data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bengtsson, G. and Rundgren, S. (1988) The Gusum case: a brass mill and the distribution of soil Collembola. Can. J. Zool. 66, 1518–26.
Bengtsson, G., Gunnarson, T. and Rundgren, S. (1986) Effects of metal pollution on the earthworm Dendrobaena rubida (Sav) in acidified soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 28, 361–83.
Berger, B., Dallinger, R., Felder, E. and Moser, J. (1993) Budgeting the flow of zinc through the terrestrial gastropod Helix pomatia L. In Dallinger, R. and Rainbow, P.S. eds. Ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates, pp. 291–313. Chelsea, USA: Lewis Publishers.
Beyer, W.N., Hensler, G. and Moore, J. (1987) Relation of pH and other soil variables to concentrations of Pb, Cu, Zn and Se in earthworms. Pedobiologia 30, 167–72.
Callahan, C.A., Russell, L.K. and Peterson, S.A. (1985) A comparison of three earthworm bioassay procedures for the assessment of environmental samples containing hazardous wastes. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1, 195–200.
Corp, N. and Morgan, A.J. (1991) Accumulation of heavy metals from polluted soils by the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus: can laboratory exposure of control worms reduce biomonitoring problems? Environ. Pollut. 74, 39–52.
Edwards, C.A. (1983) Development of a standardised laboratory method for assessing the toxicity of chemical substances to earthworms. Report of the Commission of European Communities, EUR.
EEC (1985) Methods for the Determination of Ecotoxicity. Level I. C(II)4: Toxicity for Earth-worms. Artificial Soil Test. EEC Directive 79.831. ???.
Goats, G.C. and Edwards, C.A. (1988) Tge prediction of field toxicity of chemicals to earthworms by laboratory methods. In Edwards, C.A. and Neuhauser, E. eds. Earthworms in waste and environmental management, pp. 283–94. The Hague: SPB Academic Publishing.
Greig-Smith, P.W. (1992) Recommendations of an international workshop on ecotoxicology of earthworms. In Becker, H., Greig-Smith, P.W., Edwards, P.J. and Heimbach, F. eds. Ecotoxicology of earthworms, pp. 247–62. Andover, UK: Intercept.
Heimbach, F. (1992) Effects of pesticides on earthworm populations: comparison of results from laboratory and field tests. In Becker, H., Greig-Smith, P.W., Edwards, P.J. and Heimbach, F. eds. Ecotoxicology of earthworms, pp. 100–6. Hants, UK: Intercept.
Heimbach, F. (1993) Correlation between data from laboratory and field tests for investigating the toxicity of pesticides to earthworms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 24, 1749–53.
Hoekstra, J.A. and Van Ewijk, P.H. (1993a) Alternatives for the no-observed effect level. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12, 187–94.
Hoekstra, J.A. and Van Ewijk, P.H. (1993b) The bounded effect concentration as an alternative for the NOEC. Sci. Total Environ. Suppl. (1), 705–12.
Hopkin, S.P. (1989) Ecophysiology of Metals in Terrestrial Invertebrates. London: Elsevier Applied Science.
Hopkin, S.P. (1990) Species specific differences in the net assimilation of zinc, cadmium, lead, copper and iron by the terrestrial Isopods Oniscus asellus and Porcellio scaber. J. Appl. Ecol. 27, 460–74.
Hopkin, S.P. (1993) Ecological implications of ‘95% protection levels’ for metals in soils. Oikos 66, 137–41.
Hopkin, S.P., Watson, K.M., Martin, M.H. and Mould, M.L. (1985) The assimilation of heavy metals by Lithobius variegatus and Glomeris marginata (Chilopoda; Diplopoda). Bijdragen tot de Dierkunde 55, 88–94.
Hopkin, S.P., Jones, D.T. and Dietrich, D. (1993) The terrestrial isopod Porcellio scaber as a monitor of the bioavailability of metals: towards a global ‘woodlouse watch’ scheme. Sci. Total Environ. Suppl. (1), 357–65.
Jones, D.T. (1991) Biological monitoring of metal pollution in terrestrial ecosystems. PhD thesis, University of Reading.
Jones, D.T. and Hopkin, S.P. (1991) Biological monitoring of metal pollution in terrestrial ecosystems. In Ravera, O. ed. Terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems perturbation and recovery, pp. 148–52. London, UK, Ellis Horwood.
Kraak, M.H.S., Schoon, H., Peeters, W.H.M. and Van Straalen, N.M. (1993) Chronic ecotoxicity of mixtures of Cu, Zn, and Cd to the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 25, 315–27.
Ma, W.C. (1983) Regenwormen als Bio-indicators van Bodemverontreiniging. Bodembescherming 15. The Hague: Staatsuitgeverij.
Ma, W.C. (1984) Sublethal toxic effects of copper on growth reproduction and litter breakdown activity in the earthworm Lumbricus rubellus, with observations on the influence of temperature and soil pH. Environ. Pollut. (Ser. A) 33, 207–19.
Ma, W.C. (1988) Toxicity of copper to Lumbricid earthworms in sandy agricultural soils amended with Cu-enriched organic waste materials. Ecol. Bull. (Copenhagen) 39, 53–6.
Martin, M.H. and Bullock, R.J. (1994) The impact and fate of heavy metals in an oak woodland ecosystem. In Ross, S.M. ed. Toxic metals in soil-plant systems, pp. 321–65. Chichester: John Wiley.
Morgan, J.E. and Morgan, A.J. (1988) Earthworms as biological monitors of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in metalliferous soils. Environ. Pollut. 54, 123–38.
Morgan, J.E. and Morgan, A.J. (1991) Differences in the accumulated metal concentration in two epigeic earthworm species (L. rubellus and D. rubidus) living in contaminated soils. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 47, 289–301.
Morgan, A.J., Morgan, J.E., Turner, M., Winters, C. and Yarwood, A. (1993) Metal relationships of earthworms. In Dallinger, R. and Rainbow, P.S. eds. Ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates, pp. 333–58. Chelsea, USA: Lewis Publisher.
Neuhauser, E.F., Loehr, R.C., Milligan, D.L. and Malecki, M.R. (1985) Toxicity of metals to the earthworm Eisenia foetida. Biol. Fertility Soils 1, 149–52.
OECD (1984) Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals No. 207 Earthworm Acute Toxicity Tests. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Reinecke, A.J. (1992) A review of ecotoxicological test methods using earthworms. In Becker, H., Greig-Smith, P.W., Edwards, P.J. and Heimbach, F. eds. Ecotoxicology of earthworms, pp. 7–19. Andover, UK Intercept.
Sims, R.W. and Gerard, B.M. (1985) Earthworms. London: The Linnean Society of London and the Estuarine and Brackish-Water Sciences Association, E.J. Brill/W. Backhuys.
Spurgeon, D.J., Hopkin, S.P. and Jones, D.T. (1994) Effects of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc on growth, reproduction and survival of the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Savigny): assessing the environmental impact of point-source metal contamination in terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 84, 123–30.
Tranvik, L. and Eijsackers, H. (1989) On the advantage of Folsomia fimetarioides over Isotomiella minor (Collembola) in a metal polluted soil. Oecologia 80, 195–200.
Tranvik, L., Bengtsson, G. and Rundgren, S. (1993) Relative abundance and resistance traits of two Collembola species under metal stress. J. Appl. Ecol. 30, 43–52.
Van Gestel, C.A.M. (1992) Validation of earthworm toxicity tests by comparison with field studies: a review of benomyl, carbendazim, carbofuran and carbaryl. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 23, 221–36.
Van Gestel, C.A.M. and Van Dis, W.A. (1988) The influence of soil characteristics on the toxicity of four chemicals to the earthworm Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta). Biol. Fertil. Soils 6, 262–5.
Van Gestel, C.A.M., Van Dis, W.A., Van Breemen, E.M. and Sparenburg, P.M. (1988) Comparison of two methods for determining the viability of cocoons produced in earthworm toxicity experiments. Pedobiologia 32, 367–71.
Van Gestel, C.A.M., Van Dis, W.A., Van Breemen, E.M. and Sparenburg, P.M. (1989) Development of a standardized reproduction toxicity test with the earthworm species Eisenia andrei using copper, pentachlorophenol and 2,4-dichloroaniline. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 18, 305–12.
Van Gestel, C.A.M., Van Dis, W.A., Dirven-Van Breemen, E.M., Sparenburg, P.M. and Baerselem, R. (1991) Influence of cadmium, copper and pentachlorophenol on growth and sexual development of Eisenia andrei (Oligochaete: Annelida). Biol. Fertil. Soils 12, 117–21.
Van Gestel, C.A.M., Dirven-Van Breemen, E.M. and Baerselman, R. (1992a) Influence of environmental conditions on the growth and reproduction of the earthworm Eisenia andrei in an artificial soil substrate. Pedobiologia 36, 109–20.
Van Gestel, C.A.M., Dirven-Van Breemen, E.M., Baerselman, R., Emans, H.J.B., Janssen, J.A.M., Postuma, R. and Van Vliet, P.J.M. (1992b) Comparison of sublethal and lethal criteria for nine different chemicals in standardized toxicity tests using the earthworm Eisenia andrei. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 23, 206–20.
Van Straalen, N.M. (1993) Soil and sediment quality criteria derived from invertebrate toxicity data. In Dallinger, R. and Rainbow, P.S. eds. Ecotoxicology of metals in invertebrates, pp. 427–41. Chelsea, USA: Lewis Publishers.
Van Straalen, N.M. and Denneman, C.A.J. (1989) Ecotoxicological evaluation of soil quality criteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 18, 241–51.
Van Straalen, N.M. and Ernst, W.H.O. (1991) Metal biomagnification may endanger species in critical pathways. Oikos 62, 255–6.
Van Straalen, N.M., Leeuwangh, P. and Stortelder, P.B.M. (1994) Progressing limits for soil ecotoxicological risk assessment. In Donker, M.H., Eijsackers, H. and Heimbach, F. eds. Ecotoxicology of soil organisms, pp. 397–409. Chelsea, USA: Lewis Publishers.
Wagner, C. and Løkke, H. (1991) Estimation of ecotoxicological protection levels from NOEC toxicity data. Water Res. 10, 1237–42.
Williams, D.A. (1971) A test for differences between treatment means when several dose levels are compared with a zero dose control. Biometrics 21, 103–17.
Williams, D.A. (1972) The comparison of several dose levels with a zero dose control. Biometrics 28, 519–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spurgeon, D.J., Hopkin, S.P. Extrapolation of the laboratory-based OECD earthworm toxicity test to metal-contaminated field sites. Ecotoxicology 4, 190–205 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116481
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116481