Abstract
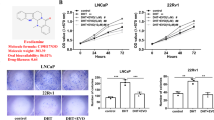
The androgen receptor(AR) signaling activated by dihydrotestosterone(DHT) plays critical roles in prostate cancer development and progression. Phytoestrogens, which are diphenolic compounds with estrogen and antiestrogen effects, can bind to estrogen receptors. However, their function on AR signaling has not been fully elucidated. In this study, dual-luciferase reporter assay, immunobloting, docking system test, MTT assay, immunofluorescence and chromatin immunoprecipitation(ChIP) assays were employed to examine the potential effects of three phytoestrogens(genistein, daidzein, flavone) on DHT-activated prostate specific antigen(PSA) activation, cell proliferation and AR transactivation in lymph node carcinoma of prostate(LNCaP) cells. Phytoestrogens were detected to down-regulate DHT-activated AR-mediated PSA promoter transactivation by dual-luciferase reporter system. Furthermore, three phytoestrogens, especially genistein, were demonstrated to significantly decrease AR-activated PSA protein expression by Western blotting analysis. MTT experiment proves that phytoestrogens, especially genistein, remarkably inhibits the DHT-induced cell proliferation in LNCaP cells. To provide reasonable explanations for experimental phenomena mentioned above, we did docking system test and detected phytoestrogens to share the same AR-binding site with DHT. To further prove the competition between phytoestrogen and DHT on AR binding, we examined the effects of phytoestrogens on DHT-activated AR nuclear translocation and immunofluorescence analysis which confirms that phytoestrogens, especially genistein, inhibit DHT-activated androgen receptor nuclear translocation. Results from ChIP show that phytoestrogens down-regulate DHT-induces AR binding to the androgen response elements(AREs, including AREI, AREII, and AREIII) in PSA promoter. Genistein remarkably down-regulates AR, binding to the AREI located in −250— −39 bp and AREIII in −4170— −3978 bp in the presence of DHT. In general, three phytoestrogens were identified to inhibit DHT-AR binding by competitively binding to AR and inhibit AR-mediated transactivation. And genistein shows the strongest effects among three phytoestrogens. Our findings confirm that phytoestrogens are AR antagonist in the regulation of AR-related PSA activation and cell proliferation, which provides valuable insights into the treatment of prostate cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J., Shin H. R., Bray F., Forman D., Mathers C., Parkin D. M., International Journal of Cancer, 2010, 127(12), 2893
Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T., Science, 1988, 240(4850), 324
Heinlein C. A., Chang C., Endocrine Reviews, 2004, 25(2), 276
Rahman M., Miyamoto H., Chang C., Clinical Cancer Research, 2004, 10(7), 2208
Vernon S. E., Williams W. D., The Journal of Urology, 1983, 130(1), 95
Reid K. J., Hendy S. C., Saito J., Sorensen P., Nelson C. C., Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(4), 2943
Shang Y., Myers M., Brown M., Molecular Cell, 2002, 11, 601
Wu J., Wei W., Yang N. Y., Shen X. Y., Tsuji I., Yamamura T., Li J., Li X. M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(3), 512
Ososki A. L., Kennelly E. J., Phytotherapy Research, 2003, 17(8), 845
Yildiz F., Phytoestrogens in Functional Foods, CRC Press Taylor & Francis Ltd., Boca Raton, 2005, 3
Chuu C. P., Chen R. Y., Kokontis J. M., Hiipakka R. A., Liao S., Cancer Letters, 2009, 275(1), 86
Keri R. A., Ho S. M., Hunt P. A., Knudsen K. E., Soto A. M., Prins G. S., Reproductive Toxicology, 2007, 24(2), 240
Trott O., Olson A. J., Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2010, 31, 455
Pereira de Jésus-Tran K., Côté P. L., Cantin L., Blanchet J., Labrie F., Breton R., Protein Science, 2006, 15, 987
Lill M. A., Winiger F., Vedani A., Ernst B., Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2005, 48, 5666
Li X. M., Xu Y., Tsuji I., Soybean and Prostate Cancer, InTech Publishiug, Rijeka, 2013, 265
Li X. M., Li J., Ichiro T., Naoki N., Yoshikazu N., Zhao X. J., Asian J. Androl., 2008, 10(4), 551
Wang B. F., Wang J. S., Lu J. F., Kao T. H., Chen B. H., Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(6), 2221
Miodini P., Fioravanti L., di Fronzo G., Cappelletti V., British Journal of Cancer, 1999, 80(8), 1150
Kohen F., Gayer B., Kulik T., Frydman V., Nevo N., Katzburg S., Limor R., Sharon O., Stern N., Somjen D., Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2007, 50, 6405
Kousidou O. C., Tzanakakis G. N., Karamanos N. K., Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry, 2006, 6(3), 331
Murata M., Midorikawa K., Koh M., Umezawa K., Kawanishi S., Biochemistry, 2004, 43(9), 2569
Manthey J. A., Guthrie N., Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2002, 50(21), 5837
Heemers H. V., Tindall D. J., Endocrine Reviews, 2007, 28(7), 778
Liu G. F., Gao L. Z., Yu Q., Zhang H. M., Wang Z. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(9), 1920
Xie J., Zhu J. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(7), 1532
Zhou J. R., Gugger E. T., Tanaka T., Guo Y., Blackburn G. L., Clinton S. K., The Journal of Nutrition, 1999, 129(9), 1628
Zhang L., Jiao M., Wu D., Wu K., Li X., Zhu G., Yang L., Wang X., Hsieh J. T., He D., Cancer Lett., 2012, 323(1), 48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China(No.2010DFA31430), the Project of the Ministry of Education of China(Nos.NCET-10-0316, 10SSXT147), the Project of the Jilin Provincial Science & Technology Department, China(Nos.20070719, 200905116) and the Project of the Changchun Science & Technology Department, China (No.2011114-11GH29).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Liu, S., Shen, Xy. et al. Phytoestrogens inhibiting androgen receptor signal and prostate cancer cell proliferation. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 29, 911–916 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-013-3123-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-013-3123-6