Abstract
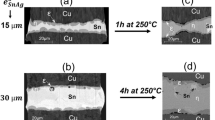
Three-dimensional (3D) integrated circuits (ICs) are the most important packaging technology for next-generation semiconductors. Cu-to-Cu throughsilicon via interconnections with micro-bumps are key components in the fabrication of 3D ICs. However, significant reliability concerns have been raised due to the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds in the entire 3D IC joints. This study proposes a Ga-based Cu-to-Cu bonding technology with Pt under bump metallurgy (UBM). A systematic analysis of reactive wetting between Ga solders and polycrystalline, single-crystalline, and Ptcoated Cu substrates was conducted. Pt UBM as a wetting layer was identified to be a key component for Ga-based Cu-to-Cu bonding. Pt-coated Cu substrates were bonded using Ga solders with various Ga-to-Pt ratios (n) at 300℃. When n ≥ 4, the Cu/Pt/Ga/Pt/Cu interface evolves to Cu/facecentered cubic (fcc)/γ1-Cu9Ga4/fcc/Cu, Cu/fcc/γ1-Cu9Ga4 + Ga7Pt3/fcc/Cu, and finally Cu/fcc + Ga7Pt3/Cu structures. The desired ductile solid solution joint formed with discrete Ga7Pt3 precipitates. When n ≤ 1, a Cu/Ga7Pt3/Cu joint formed without Cu actively participating in the reactions. The reaction mechanism and microstructure evolution were elaborated with the aid of CALPHAD thermodynamic modeling.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. H. Lau, Microelectron. Int. 28, 8 (2011).
M. Motoyoshi, P. IEEE 97, 43 (2009).
K. Chen, C. Tan, A. Fan, and R. Reif, Electrochem. Solid St. 7, 14 (2004).
E.-J. Jang, J.-W. Kim, B. Kim, T. Matthias, and Y.-B. Park, Met. Mater. Int. 17, 105 (2011).
C.-T. Ko and K.-N. Chen, Microelectron. Reliab. 50, 481 (2010).
Y.-S. Tang, Y.-J. Chang, and K.-N. Chen, Microelectron. Reliab. 52, 312 (2012).
R. Agarwal, W. Zhang, P. Limaye, and W. Ruythooren, Proc. IEEE Electronic Components and Technology Conference, p. 345, IEEE Inst. Elec. Electron. Eng. Inc., San Diego, USA (2009).
J. Li, P. Agyakwa, and C. Johnson, Acta Mater. 59, 1198 (2011).
G. Zeng, S. Xue, L. Zhang, and L. Gao, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 22, 565 (2011).
S.-K. Lin, C.-L. Cho, and H.-M. Chang, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 204 (2014).
G. O. Cook, and C. D. Sorensen, J. Mater. Sci. 46, 5305 (2011).
W. Cao, S.-L. Chen, F. Zhang, K. Wu, Y. Yang, Y. Chang, R. Schmid-Fetzer, and W. Oates, Calphad 33, 328 (2009).
J.-B. Li, L. Ji, J. Liang, Y. Zhang, J. Luo, C. Li, and G. Rao, Calphad 32, 447 (2008).
J. Wang, S. Jin, W. Zhu, H. Dong, X. Tao, H. Liu, and Z. Jin, Calphad 33, 561 (2009).
T. Abe, B. Sundman, and H. Onodera, J. Phase Equilib. Diff. 27, 5 (2006).
R. Picha, J. Vreštál, and A. Kroupa, Calphad 28, 141 (2004).
B. J. Keene, Int. Mater. Rev. 38, 157 (1993).
S.-P. Sun, D.-Q. Yi, and B. Zang, Chinese J. Nonferrous Metal. 20, 930 (2010).
K. Mukai, T. Matsushita, K. C. Mills, S. Seetharaman, and T. Furuzono, Metall. Mate. Trans. B 39, 561 (2008).
ASM Handbook: Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, USA (1992).
K. A. Narh, V. P. Dwivedi, and J. M. Grow, J. Mater. Sci. 33, 329 (1998).
Y.-G. Deng and J. Liu, Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 95, 907 (2009).
M. G. Nicolas and C. F. Old, J. Mater. Sci. 14, 1 (1979).
S. C. Hardy, J. Cryst. Growth 71, 602 (1985).
C. M. L. Wu, D. Q. Yu, C. M. T. Law, and L. Wang, Mat. Sci. Eng. R 44, 1 (2004).
S.-W. Chen, S.-W. Lee, and M. C. Yip, J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1284 (2003).
S. M. Hayes, N. Chawla, and D. R. Frear, Microelectron. Reliab. 49, 269 (2009).
J. W. Yoon, S. W. Kim, and S. B. Jung, Mater. Trans. 45, 727 (2004).
D. Swenson and B. Morosin, J. Alloy. Compd. 243, 173 (1996).
Y. Xu, M. Yamazaki, and P. Villars, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 50, 11–02 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Sk., Chang, Hm., Cho, Cl. et al. Formation of solid-solution Cu-to-Cu joints using Ga solder and Pt under bump metallurgy for three-dimensional integrated circuits. Electron. Mater. Lett. 11, 687–694 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-015-5015-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-015-5015-z