Abstract
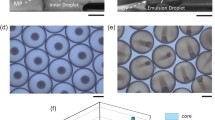
A facile and versatile route to prepare porous polymer microparticles with tunable pore size and density through the combination of phase separation and emulsion-solvent evaporation method is demonstrated. When volatile organic solvent (e.g., chloroform) diffuses through the aqueous phase containing poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and evaporates, n-hexadecane (HD) and polystyrene (PS) in oil-in-water emulsion droplets occur to phase separate due to the incompatibility between PS and HD, ultimately yielding microparticles with porous structures. Interestingly, density of the pores (pore number) on the shell of microparticles can be tailored from one to hundreds by simply varying the HD concentration and/ or the rate of solvent evaporation. Moreover, this versatile approach for preparing porous microparticles with tunable pore size and density can be applied to other types of hydrophobic polymers, organic solvents, and alkanes, which will find potential applications in the fields of pharmaceutical, catalyst carrier, separation, and diagnostics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, S.E., J.S. Son, K. Park, and D.K. Han, 2009, Fabrication of covered porous PLGA microspheres using hydrogen peroxide for controlled drug delivery and regenerative medicine, J. Control. Release 133, 37–43.
Chung, H.J., H.K. Kim, J.J. Yoon, and T.G. Park, 2006, Heparin immobilized porous PLGA microspheres for angiogenic growth factor delivery, Pharm. Res. 23, 1835–1841.
Deng, R.H., S.Q. Liu, J.Y. Li, Y.G. Liao, J. Tao, and J.T. Zhu, 2012, Mesoporous block copolymer nanoparticles with tailored structures by hydrogen-bonding-assisted self-assembly, Adv. Mater. 24, 1889–1893.
Ding, S.Y., J. Gao, Q. Wang, Y. Zhang, W.G. Song, C.Y. Su, and W. Wang, 2011, Construction of covalent organic framework for catalysis: Pd/COF-LZU1 in Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 19816–19822.
Durie, S., K. Jerabek, C. Mason, and D.C. Sherrington, 2002, One-pot synthesis of branched poly (styrene divinylbenzene) suspension polymerized resins, Macromolecules 35, 9665–9672.
Gokmen, M.T. and F.E. Du Prez, 2012, Porous polymer particles-A comprehensive guide to synthesis, characterization, functionalization and applications, Prog. Polym. Sci. 37, 365–405.
Gokmen, M.T., W. Van Camp, P.J. Colver, S. Bon, and F.E. Du Prez, 2009, Fabrication of porous “clickable” polymer beads and rods through generation of high internal phase emulsion (HIPE) droplets in a simple microfluidic device, Macromolecules 42, 9289–9294.
Gong, X., W. Wen, and P. Sheng, 2009, Microfluidic fabrication of porous polymer microspheres: dual reactions in single droplets, Langmuir 25, 7072–7077.
Hudson, D., 1999, Matrix assisted synthetic transformations: A mosaic of diverse contributions. I. The pattern emerges, J. Comb. Chem. 1, 333–360.
Jang, T.S., E.J. Lee, H.E. Kim, and Y.H. Koh, 2012, Hollow porous poly(epsilon-caprolactone) microspheres by emulsion solvent extraction, Mater. Lett. 72, 157–159.
Jose, A.J., S. Ogawa, and M. Bradley, 2005, Tuning the pore size and surface area of monodisperse Poly (Methyl Acrylate) beads via parallel seeded polymerization, Polymer 46, 2880–2888.
Kim, M.R., S. Lee, J.K. Park, and K.Y. Cho, 2010, Golf ballshaped PLGA microparticles with internal pores fabricated by simple O/W emulsion, Chem. Commun. 46, 7433–7435.
Klose, D., F. Siepmann, K. Elkharraz, S. Krenzlin, and J. Siepmann, 2006, How porosity and size affect the drug release mechanisms from PLGA-based microparticles, Int. J. Pharm. 314, 198–206.
Kong, S.F., X.F. Wen, P.H. Pi, J. Cheng, and Z.R. Yang, 2008, Preparation and characterization of magnetic porous γ-Fe2O3/P(St-DVD-MAA) polymer microspheres, Acta. Polym. Sin. 2, 168–173.
Li, B.Y., X. Huang, L.Y. Liang, and B.E. Tan, 2010, Synthesis of uniform microporous polymer nanoparticles and their applications for hydrogen storage, J. Mater. Chem. 20, 7444–7450.
Liu, S.Q., R.H. Deng, W.K. Li, and J.T. Zhu, 2012, Polymer microparticles with controllable surface textures generated through interfacial instabilities of emulsion droplets, Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 1692–1697.
Loxley, A. and B. Vincent, 1998, Preparation of poly (methylmethacrylate) microcapsules with liquid cores, J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 208, 49–62.
Okubo, M., T. Fujibayashi, and A. Terada, 2005, Synthesis of micron-sized, monodisperse polymer particles of disc-like and polyhedral shapes by seeded dispersion polymerization, Colloid Polym. Sci. 283, 793–798.
Rao, T.P., R.S. Praveen, and S. Daniel, 2004, Styrene-divinyl benzene copolymers: synthesis, characterization, and their role in inorganic trace analysis, Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 34, 177–193.
Shi, X.D., L. Sun, and Z.H. Gan, 2011, Formation mechanism of solvent-induced porous PLA microspheres, Acta. Polym. Sin. 8, 866–873.
Sing, K.S.W., D.H. Everett, R.A.W. Haul, L. Moscou, R.A. Pierotti, J. Rouquerol, and T. Siemieniewska, 1985, Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity, Pure Appl. Chem. 57, 603–619.
Slater, M., M. Snauko, F. Svec, and J.M. Fréchet, 2006, “Click chemistry” in the preparation of porous polymer-based particulate stationary phases for μ-HPLC separation of peptides and proteins, Anal. Chem. 78, 4969–4975.
Svec, F. and J.M. Fréchet, 1996, New designs of macroporous polymers and supports: from separation to biocatalysis, Science 273, 205–211.
Tanaka, T., Y. Komatsu, T. Fujibayashi, H. Minami, and M. Okubo, 2010, A novel approach for preparation of micrometersized, monodisperse dimple and hemispherical polystyrene particles, Langmuir 26, 3848–3853.
Wang, N.X., Y.G. Liao, R.H. Deng, S.Q. Liu, N. Cao, B.E. Tan, J.T. Zhu, and X.L. Xie, 2012, Polymer-inorganic hybrid microparticles with hierarchical structures formed by interfacial instabilities of emulsion droplets, Soft Matter 8, 2697–2704.
Watanabe, T., T. Ono, and Y. Kimura, 2011, Continuous fabrication of monodisperse polylactide microspheres by droplet-to-particle technology using microfluidic emulsification and emulsion-solvent diffusion, Soft Matter 7, 9894–9897.
Wood, C.D., B.E. Tan, A. Trewin, F. Su, M.J. Rosseinsky, D. Bradshaw, Y. Sun, L. Zhou, and A.I. Cooper, 2008, Microporous organic polymers for methane storage, Adv. Mater. 20, 1916–1921.
Wu, D.C., F. Xu, B. Sun, R.W. Fu, H.K. He, and K. Matyjaszewski, 2012, Design and preparation of porous polymers, Chem. Rev. 112, 3959–4015.
Yabu, H., T. Higuchi, K. Ijiro, and M. Shimomura, 2005, Spontaneous formation of polymer nanoparticles by goodsolvent evaporation as a nonequilibrium process, Chaos 15, 047505.
Yow, H.N., and A.F. Routh, 2008, Colloidal buckets formed via internal phase separation, Soft Matter 4, 2080–2085.
Zou, S.W., H. Liu, Y. Yang, Z.J. Wei, and C.Y. Wang, 2013, Multihollow nanocomposite microspheres with tunable pore structures by templating Pickering double emulsions, React. Funct. Polym. 73, 1231–1241.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Cai, M., Deng, R. et al. Fabrication of porous polymer microparticles with tunable pore size and density through the combination of phase separation and emulsion-solvent evaporation approach. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 26, 63–71 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-014-0007-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-014-0007-3