Abstract
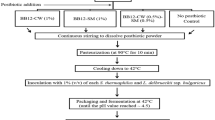
Increasing demand of low calorie and high fibre containing products give impetus to dairy industry for development of a well palatable low calorie dairy products like paneer. The objective of the present study was to develop low-fat fibre-supplemented paneer. The ingredients were chosen for low-fat fibre- supplemented paneer to reduce the cost and calorie content besides providing the functional benefits. Optimization of ingredients was carried out in terms of independent variables viz wheat bran (0.4–0.8 %), maltodextrin (1–5 %), coagulation temperature (60–80 °C) and amount of citric acid solution (150–210 ml). Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was used to design the experiments and to select the optimum levels of ingredients. Paneer was made by using different levels of ingredients by coagulating hot milk using citric acid solution followed by pressing and dipping in chilled water for texturization. These parameters were evaluated in terms of physico-chemical parameters viz water activity, pH and acidity. Instrumental texture profile analysis (TPA) of paneer during optimization trials was done using TAXT 2i Texture Analyzer. The textural responses namely hardness, adhesiveness, springiness, cohesiveness, gumminess and chewiness were measured via Texture Analyzer. The sensory properties namely flavor, appearance, body and texture, mouth feel and overall acceptability of paneer samples were evaluated by a semi-trained panel of judges using 9-point hedonic scale. Full second order polynomial was developed to predict each response. All the textural and sensory responses were statistically analysed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (American Association of Cereal Chemists) (1999) Joint workshop held at Institute of Food Technologist’s, North America
Anantakrishnan CP, Srinivasan MR (1964) Milk products of India. I.C.A.R, New Delhi
Bhattacharya DC, Mathur ON, Srinivasan MR, Samlik OL (1971) Studies on the method of production and shelf-life of paneer (cooking type of acid coagulated cottage cheese). J Food Sci Technol 8(5):117–120
Jagannath A, Ramesh MN, Varadaraj MC (2001) Response surface model for predicting the behavior of yersinia enterocolitica in paneer—a heat and acid coagulated milk product of India. Acta Hortic 566:487–491
Kanawjia SK, Singh S (2000) Technological advances in paneer making. Indian Dairyman 52(10):45–50
Nayak SK, Pattnaik P, Mohanty AK (2000) Dietary fiber: a low calorie dairy adjunct. Indian Food Ind 19(4):268–271
Patel AA, Arora SK (2005) Fiber fortification of dairy products. National Workshop on Entrepreneurship Development in Dairy and Food Industry. NDRI, Karnal 89–94
Rao KVSS, Zanjad PN, Mathur BN (1992) Paneer technology: a review. Indian J Dairy Sc 45(6):281–291
Schmidl MK, Labuza TP (1994) Medical foods. In: Goldberg I (ed) Functional foods. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 151–179
Stody JA, White A, West LG (1982) Adsorption of bile acids by components of alfalfa and wheat bran. J Food Sci 47:1276–1279
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G., Kumar, A., Kumbhar, B.K. et al. Optimization of processing parameters and ingredients for development of low-fat fibre-supplemented paneer . J Food Sci Technol 52, 709–719 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1049-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1049-0