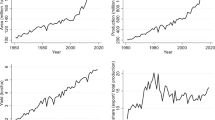
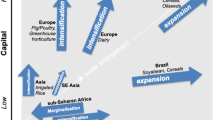
Abstract
Livestock keeping constitutes a traditional and important economic activity in the Arab region. This paper aims to assess the role of the Arab livestock sector in food and nutritional security in terms of demand, supply, national policies and trade in the light of major environmental constraints, with data illustrations from Morocco (Mediterranean country) and Saudi Arabia (oil-rich country). Demand for livestock products is increasing in the Arab region driven by the growing population with different degrees of increased urbanization and wealth. On the supply side, local livestock production is largely based on rainfed mixed and pastoral livestock systems making it vulnerable to the effects of climate change and water scarcity. Intensive systems, where present, are mostly dependent on feed imports with an important water footprint. Livestock production is further conditioned by a history of arbitrary national policies that had a particularly negative effect on small producers and contributed to the degradation of national resources. Arab countries rely on trade from the world market to fill their gap in animal feed and livestock products with varying trading power based on wealth and the availability of free trade agreements. Following analysis of the sector, the paper concludes with the proposition of a pro-poor policy framework for the development of a sustainable Arab livestock sector.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Hima: Grazing reserve for restricted use by a village community, clan or tribe, set aside to allow regeneration as part of a grazing management strategy (Kilani et al.: A Way of Life, IUCN West Asia Regional Office, Amman Jordan – SPNL Beirut, Lebanon, 2007:3).
See Plan Maroc Vert (2009), http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/FAO-countries/Maroc/plan_maroc_vert.pdf
References
Al Rowaily, S. L. R. (1999). Rangeland of Saudi Arabia and the “tragedy of commons. Rangelands, 21(3), 27–29.
Aljaloud, A. A., Yan, T., & Abdulkader, A. M. (2011). Development of a national methane emission inventory for domestic livestock in Saudi Arabia. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 166–167, 619–627.
Al-Obaid, A.A. (2010). “King Abdullah’s Initiative for Saudi Agricultural Investment Abroad: A Way of Enhancing Saudi Food Security”. http://www.isdb.org/irj/go/km/docs/documents/IDBDevelopments/Internet/English/IDB/CM/Publications/IDB_AnnualSymposium/20thSymposium/8-AbdullaAlobaid.pdf, Accessed March 2016.
Al-Saleh, M. A. (1992). Declining groundwater level of the Minjur aquifer, Tebrak area, Saudi Arabia. Geographical Journal, 215–222.
Al-Tkhais, A. (2014). Food security options in Saudi Arabia. In Arab Environment 7: Food security challenges and prospects (ed. A-K Sadik, M. El-Solh & N. Saab). p. 94. 2014 Report of the Arab Forum for Environment and Development, Beirut, Lebanon.
AOAD (Arab Organization for Agricultural Development) (2008), [Workshop on the Requirements for the Preparation of Agricultural Policies in the Arab Countries for the Establishment of an Arab Customs Union] (Arabic), AOAD, http://www.aoad.org/publications/CustomsUnion.pdf Accessed March 2016.
AOAD (Arab Organization for Agricultural Development) (2009), [Comprehensive Study for the Documentation of Agricultural Policies in Arab Countries During the First Decade of the Third Millennium] (Arabic), AOAD, http://www.aoad.org/agrPolicies.pdf Accessed March 2016
ARABSPATIAL. (2016). website: http://www.arabspatial.org/ Accessed March 2016.
Badran, M., & Laher, I. (2011). Obesity in Arabic-speaking countries. Journal of Obesity. doi:10.1155/2011/686430.
Banović, M., & Ševarlić, M. M. (2013). The EU Meat Market and the Doha Round at a Glance. Challenges for the Global Agricultural Trade Regime After Doha, 45.
Behnke, R. (2012). The economics of pastoral livestock production and its contributin to the wider economy of Sudan. Feinstein International Center working paper. Somerville, MA: Feinstein International Center.
Belghazi, S. (2013), “Scenarios for the Agricultural Sector in the Southern and Eastern Mediterranean”, MEDPRO Report No. 4 (March), http://www.medpro-foresight.eu/system/files/MEDPRO%20Rep%20No%204%20WP5%20Belghazi.pdf Accessed March 2016.
Bourn, D. (2003). Livestock Dynamics in the Arabian Peninsula: A Regional Review of National Livestock Resources and International Livestock Trade. FAO. http://brookfarmberrington.org/ergo2005/LivestockDynamicsinArabPen.pdf Accessed March 2016.
Brown, O., Crawford, A. (2009). Rising Temperatures, Rising Tensions: Climate change and the risk of violent conflict in the Middle East. International Institute for Sustainable Development, Manitoba, Canada.
Chapagain, A.K., Hoekstra, A.Y. (2003). Virtual water flows between nations in relation to trade in livestock and livestock products. Value of Water Research Report Series, No. 13, UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education, the Netherlands.
CURIA. (2015). Arrêt du tribunal (huitième chambre), dans l’affaire T-512/12, 10 Décembre, 2015. http://curia.europa.eu/juris/document/document.jsf?text=&docid=172870&pageIndex=0&doclang=FR&mode=lst&dir=&occ=first&part=1&cid=164110. [Accessed March, 2016].
De Chatel, F. (2014). The role of drought and climate change in the Syrian uprising: untangling the triggers of the revolution. Middle Eastern. Studies, 50, 521–535.
Dixon J., Gulliver, A., Gibbon, D. (2001). Farming Systems and Poverty: Improving Farmers’ Livelihoods in a Changing World. FAO and World Bank, Rome and Washington DC.
EC. (2015). European Neighbourhood policy and enlargement negotiations: Morocco. http://ec.europa.eu/enlargement/neighbourhood/countries/morocco/index_en.htm Accessed March 2016.
EC. (2016). EU Cereals Trade 2015/16 Marketing Year July – March. AGRI C 4 Committee for the Common Organisation of Agricultural Markets 26 May 2016. http://ec.europa.eu/agriculture/cereals/trade/cereals/2015-2016_en.pdf. Accessed March 2016.
EC Trade Statistics. (2015). http://ec.europa.eu/trade/policy/countries-and-regions/statistics/index_en.htm Accessed March 2016
Elasha, B.O. (2010). Mapping of Climate Change Threats and Human Development Impacts in the Arab Region. UNDP -Arab Human Development Report, Research paper series. http://www.arab-hdr.org/publications/other/ahdrps/paper02-en.pdf. Accessed March 2016.
Elzak, R. M., Elbushra, A. A., Ahmed, S. E. H., & Mubarak, A. M. (2011). The role of livestock production on food security in Sudan: The White Nile state. Online Journal of Feed and Animal Research, 1(6), 439–443.
EU Neighbourhood Info Centre. (2016). Morocco: EU to appeal Court ruling on trade agreement and strengthen cooperation. http://www.enpi-info.eu/medportal/news/latest/43106/Morocco:-EU-to-appeal-Court-ruling-on-trade-agreement-and-strengthen-cooperation. Accessed March 2016.
FAO (2003). World Agriculture: Towards 2015/2030. An FAO perspective. Economic and Social Development Department. http://www.fao.org/docrep/005/y4252e/y4252e05b.htm Accessed March 2016
FAO (2010a). Pro-Poor Livestock Policy Initiative. http://www.fao.org/ag/againfo/programmes/en/pplpi/about.html Accessed March 2016.
FAO (2010b), Livestock Sector Policies and Programmes in Developing Countries: A Menu for Practitioners, Rome, http://www.fao.org/docrep/012/i1520e/i1520e00.pdf
FAOSTAT (2016) website. http://faostat.fao.org/ Accessed March.
FEWS (Famine Early Warning Systems Network). (2010). Cross-border Livestock Trade Assessment Report: Impacts of lifting the livestock import ban on food security in Somalia, Ethiopia, and the Djibouti borderland. USAID funded. http://www.fews.net/sites/default/files/documents/reports/east_Cross%20border_2010_10_final.pdf Accessed March 2016.
Haddad, N., Duwayri, M., Oweis, T., Bishaw, Z., Rischkowsky, B., AwHassan, A., & Granda, S. (2011). The potential of small-scale rainfed agriculture to strengthen food security in Arab countries. Food Security, 3(Suppl. 1), S163–S173.
Hamadeh, S. (2014). “Livestock and food security”. In Arab Environment 7: Food security challenges and prospects (ed. A-K Sadik, M. El-Solh & N. Saab). p. 156. 2014 Report of the Arab Forum for Environment and Development, Beirut, Lebanon.
Hamadeh, S., Jaber, L. & Diehl, K. (2015). “Livestock and food security in the Arab region: policy impact within the Euro-Mediterranean framework. In Building Sustainable Agriculture for Food-Security in the Euro-Mediterranean Area: Challenges and Policy Pptions (ed. M.C. Paciello). p. 61. Edizioni Nuova Cultura, Rome, Italy.
Harrigan, J. 2014. The Political Economy of Arab Food Sovereignty, Basingstoke; New York, Palgrave Macmillan.
Hassane, H. (2013). The Promotion of the Livestock Industry for Food Security in Africa and Arab countries. Arab/Africa- Economic Forum, Beyond Promises: Moving forward towards an effective Arab/Africa Partnership, Kuwait.
Keulertz, M., & Woertz, E. (2015). States as Actors in International Agro-Investments. International Development Policy| Revue internationale de politique de développement, (6.1). https://poldev.revues.org/2023. Accessed March 2016.
Lampietti, J. A., Micheals, S., Magnan, N., McCalla, A. F., Saade, M., & Khoury, N. (2011). A strategic framework for improving food security in Arab countries. Food Security, 3(Suppl. 1), S7-S22.
Mankor, A. (2013). Promoting intra-Africa trade in animals and animal products”. OIE Regional Commission for. Africa, 1–6.
Mirkin, B. (2010). Population levels, trends and policies in the Arab Region: challenges and opportunities. United Nations Development Programme, regional bureau for Arab States, Arab human development report, research paper series. http://www.arab-hdr.org/publications/other/ahdrps/paper01-en.pdf. Accessed March 2016.
Musaiger, A. O., Hassan, A. S., & Obaid, O. (2011). The paradox of nutrition-related diseasesin the Arab countries: the need for action. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 8, 3637–3671.
Nowshirvani, V. (1987). The Yellow Brick Road: Self-Sufficiency or Self-Enrichment in Saudi Agriculture? MERIP Middle East Report, 145, 7–13.
Oram, P. (1998). “The influence of government policies on livestock production and the environment in West Asia and North Africa (WANA)”. In Proceedings of the Livestock and the Environment International Conference, 16–20 June, 1997, Wageningen, the Netherlands (ed. A.J. Nell). p. 146. International Agricultural Center, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Otte, J., Costales, A., Dijkman, J., Pica-Ciamarra, U., Robinson, T., Ahuja, V., Ly, C. & Roland-Host, D. (2012). Livestock sector development for poverty reduction: an economic and policy perspective – Livestock’s many virtues. FAO, Rome.
Parra, M.D., Martinez-Zarzoso, I. & Suárez-Burguet, C. (2016). The impact of FTAs on MENA trade in agricultural and industrial products. Applied Economics, online: doi:10.1080/00036846.2015.1119792
Peacock, J. M., Ferguson, M. E., Alhadrami, G. A., McCann, I. R., AL Hajoj, A., Saleh, A., & Karnik, R. (2003). Conservation through utilization: a case study of the indigenous forage grasses of the Arabian peninsula. Journal of Arid Environments, 54, 15–28.
Perry, B., Nin Pratt, A., Sones, K. & Stevens, C. (2005). An Appropriate level of risk: Balancing the need for safe livestock products with fair market access for the poor. Pro-Poor Livestock Policy Initiative. International Livestock Research Institute, Rome, Italy.
Plan Maroc Vert (2009). http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/FAO-countries/Maroc/plan_maroc_vert.pdf. Accessed March 2016.
Raboy, D. G., Basher, S. A., Hossain, I., & Kaitibie, S. (2013). More efficient production subsidies for emerging agriculture in arab micro-states: a conceptual model. Review of Middle East Economics and Finance, 9(3), 293–319.
Rahman, I. A. (2011, January). Agricultural policies for reducing poverty in rural areas in the syrian arab republic. In the research institute for agriculture economy and rural development. international symposium. agrarian economy and rural development: realities and perspectives for romania. proceedings (p. 269). The research institute for agriculture economy and rural development.
Rota, A., & Thieme, O. (2009). The livestock challenge. Rural 21. The International Journal for Rural Development, 43(6), 8–11.
Shideed, K. (2011). Informing policy development for sustainable and productive food production systems in dry areas. International center for agricultural research in the dry areas (ICARDA), Aleppo, Syria.
Shideed, K., Mazid, A., Oweis, T. & van Ginkel, M. (2014). “Potential of rainfed Agriculture and Smallholder farmers in food self-sufficiency”. In Arab Environment 7: Food security challenges and prospects (ed. A-K Sadik, M. El-Solh & N. Saab). p. 74. 2014 Report of the Arab Forum for Environment and Development, Beirut, Lebanon.
Smith, J., Sones, K., Grace, D., MacMillan, S., Tarawali, S., & Herrero, M. (2013). Beyond milk, meat and eggs: Livestock’s role in food and nutrition security. Animal Frontiers, 3(1), 6–13.
Sulser, T. B., Nestorova, B., Rosegrant, M. W., & van Rheenen, T. (2011). The future role of agriculture in the Arab region’s food security. Food Security,, 3(Suppl. 1), S23–S48.
Tanyeri-Abur, A., & Elamin, N. H. (2011). International investments in Agriculture in Arab Countries: an overview and implications for policy. Food Security, 3(1), 115–127.
Taskiridou, E., Somwaru, A., & Mattas, K. (2010). Middle East and North Africa countries’ agricultural export potentials under trade reforms. Applied Economics, 42(12), 1591–1599.
UNEP (2012). The critical role of global food consumption patterns in achieving sustainable food systems and food for all. United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) discussion paper. http://www.unep.org/resourceefficiency/Portals/24147/scp/agri-food/pdf/Role_of_Global_Food_Consumption_Patterns_A_UNEP_Discussion_Paper.pdf Accessed March 2016.
USDA. (2015). Saudi Arabia Grain and Feed Annual Report. USDA Foreign Agricultural Service http://gain.fas.usda.gov/Recent%20GAIN%20Publications/Grain%20and%20Feed%20Annual_Riyadh_Saudi%20Arabia_5-14-2015.pdf Accessed March, 2016
USDA. (2016). Morocco Grain and Feed Update-January 2016. USDA Foreign Agricultural Service http://gain.fas.usda.gov/Recent%20GAIN%20Publications/Grain%20and%20Feed%20Update%20-%20January%202016_Rabat_Morocco_1-22-2016.pdf Accessed March 2016.
Vanzetti, D., & Peters, R. (2010). Impact of tariff reductions in nama and agriculture wto negotiations on gcc common external tariffs (No. 59175). Australian agricultural and resource economics society.
Verhoeven, H. (2011). Climate change, conflict and development in Sudan: global neo-Malthusian narratives and local power struggles. Development and Change, 42, 679–707.
Woertz, E. 2013. Oil for food. The global food crisis and the Middle East, Oxford; New York, Oxford University Press.
World Bank, FAO, IFAD (2009). Improving food security in arab countries. The World Bank, Washington DC.
Zurayk, R., Chaaban, J., & Sabra, A. (2011). Ensuring that potential Gulf farmland investments in developing countries are pro-poor and sustainable. Food Security, 3(Suppl. 1), S129–S137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaber, L.S., Diehl, K.E. & Hamadeh, S.K. Livestock and food security in the Arab region: policy framework. Food Sec. 8, 899–908 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-016-0608-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-016-0608-4