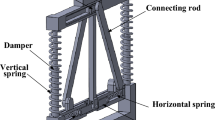
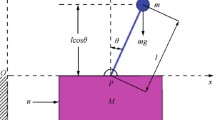
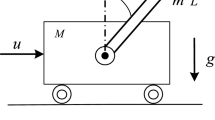
Abstract
This is a study of the design procedure establishment for an autonomous surveillance robot control system under continuous impulses. The purpose of the control system is to minimize vibration and misaiming when firing at a moving object from a gun installed on a surveillance robot. The surveillance robot was modeled using multi-body dynamic software (ADAMS and NASTRAN). In order to eliminate disturbances, the control system was designed by applying a disturbance observer. The designed control system effectively reduced 11Hz vibrations, and examined a control system required in high speed and high precision tracking. The simulation of the control algorithm used Matlab/Simulink. To examine whether the control results of the simulation and real control system program were the same, the inter-link of Matlab/Simulink and DSP is performed. Results of the disturbance observer function were satisfactory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Athans, W. B. Daverport, Jr., E. R. Ducot, and R. R. Tenney, “Surveillance and target tracking,” Proceeding of 4th MIT/ONR Workshop on Command-Communication (C3) Problem, Oct. 1981.
M. H. Lee, “On the C3I and stochastic control,” J. of Korean Institute of Electrical Engineers, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 14–25, 1981.
H. S. Lee and M. Tomizuka, “Robust motion controller design for high-accuracy positioning systems,” IEEE Trans. Industrial Electronics, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 42–45, Feb. 1996.
B. K. Kim and W. K. Chung, “Advanced disturbance observer design for mechanical positioning systems,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 50, no. 6, 2003.
M. H. Lee, Disturbance Absorber to Active Control and Gun Stabilization (Final Report), Pusan National University, Jan. 2006.
W. H. Chen, D. J. Balance, P. J. Gawthrop, J. J. Gribble, and J. O’Reilly, “A nonlinear disturbance observer for two link robotic manipulators,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 932–938, Aug. 2000.
W. H. Chen, “Nonlinear disturbance observer-enhanced dynamic inversion control of missiles,” J. Guid., Contr., Dynam., vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 161–166, 2003.
X. Chen, C. Y. Su, and T. Fukuda, “A nonlinear disturbance observer for multivariable systems and its application to magnetic bearing systems,” IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol., vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 569–577, Jul. 2004.
J. Jiang, S. Wang, and W. Song, “Design of observer with integrators for linear system with unknown input disturbances,” Electron. Lett., pp. 1168–1169, 2000.
S. Katsura, Y. Matsumoto, and K. Ohnishi, “Modeling of force sensing and validation of disturbance observer for force control,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 530–538, Feb. 2007.
K. S. Kim, “Analysis of optical data storage systems — tracking performance with eccentricity,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 1056–1062, Aug. 2005.
C. S. Liu and H. Peng, “Disturbance observer based tracking control,” Trans. ASME, vol. 122, pp. 332–335, 2000.
Q. C. Zhong and J. E. Normey-Rico, “Control of integral processes with dead time part I: a disturbance observer-based 2DOF control scheme,” IEE Proc.-Contr. Theory Appl., vol. 149, no. 4, pp. 285–290, 2002.
T. Umeno and Y. Hori, “Robust DC servosystem design based on the parameterization of two degrees of freedom control systems,” Industrial Electronics Society, IECON’ 89., 15th Annual Conference of IEEE, vol. 2, pp. 313–318, Nov. 1989.
Texas Instrument, TMS320R2811, TMS320F2812 Digital Signal Processors Data Manual (SPRS257B), Feb. 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Editor Jae Weon Choi.
Man Hyung Lee was born in Korea in 1946. He received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Electrical Engineering from Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, in 1969 and 1971, respectively, and his Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering from Oregon State University, Corvallis, in 1983. From 1971 to 1974, he was an Instructor with the Department of Electronics Engineering, Korea Military Academy, Seoul. From 1974 to 1978, he was an Assistant Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University. From 1978 to 1983, he held positions as a Teaching Assistant, Research Assistant, and Postdoctoral Fellow with Oregon State University. Since 1983, he has been a Professor in the College of Engineering, Pusan National University, where he was a Pohang Iron and Steel Co., Pohang, Korea, (POSCO) Chair Professor in the School of Mechanical Engineering from 1997 to 2003 and was Dean of the College of Engineering from March 2002 to February 2004. He is the author of more than 750 technical papers. His research interests include estimation, identification, stochastic processes, bilinear systems, mechatronics, micromachine automation, and robotics. Dr. Lee was Program Chair of the 1998 4th ICASE Annual Conference, General Cochairman of the 2001 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), and is a General Cochairman of the 30th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON ’04). He was president of ICROS from 2009 to 2010.
Hyung Gyu Park was born in Korea, on August 15, 1980. He received his B.S. degree in Automotive Engineering from Daegu University, Daegu, Korea in 2006, and his M.S. degree from the Department of Mechanical and Intelligent Systems Engineering at Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, in 2008. He is currently participating in the Ph.D. course of the Department of Mechanical and Intelligent Systems Engineering at Pusan National University. His research interests are in estimation, identification and robotics.
Won Bok Lee was born in Korea in 1967. He received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Chemical Engineering and Electronic Communication Engineering from Korea Military Academy in Seoul, Korea in 1990 and 1998, respectively, and his Ph.D. degree in Mechanical Engineering from the Pusan National University in Busan, Korea, in 2011. His research interests include estimation, mechatronics, automation and robotics.
Kil Soo Lee was born in Korea in 1980. He received his B.S. degree in Automotive Engineering from Silla University, Busan, Korea in 2005, and his M.S. degree from the Department of Mechanical and Intelligent Systems Engineering at Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, in 2007. He is currently a Ph.D. candidate of the Graduate School of Mechanical Engineering at the Pusan National University. His research interests are in pseudolite ultrasonic systems (PUS), automotive navigation, automation and estimation.
Weui Bong Jeong received his B.S. degree from Seoul National University in 1978. He then went on to receive his M.S. and Ph.D. degrees from KAIST in 1980 and from the Tokyo Institute of Technology in 1990, respectively. Dr. Jeong is currently a Professor at the Mechanical Engineering at Pusan National University in Busan, Korea.
Kang Sup Yoon received his B.S., M.S., and Ph.D. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, in 1986, 1988, and 1997, respectively. From Aug. 1991 to Aug. 1997, he was a Researcher in the Research Institute of Mechanical Technology, Pusan National University. From Sept. 1997 to Feb. 2000, he was a Postdoctorial Fellow in the Institute of Industrial Science, Tokyo University, Tokyo, Japan. He has been with the Division of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, Daegu University, Gyeongsan, Korea, since Apr. 2000. His current research interests include ITS, mechatronics, robotics, and predictive control.
Ho Hwan Chun received his B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees in Ship and Ocean Engineering from Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, in 1983 and 1985, respectively, and his Ph.D. degree in Naval Architecture from Glasgow University, Glasgow, U.K., in 1988. He was a Yard Research Fellow with Glasgow University from 1988 to 1990 and a Principal Researcher with Hyundai Maritime Research Institute, Ulsan, Korea, from 1991 to 1993. Since 1994, he has served as a Professor with the Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Pusan National University. He had been a Director of the Advanced Ship Engineering Research Center (ASERC), as designated by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Korea, from 2002 to 2011. In 2011, he became the Director of the Global Core Research Center for Ships and Offshore Plants, as designated by the National Research Foundation of Korea. His main research area is hydrodynamics, such as hull-form design, hull and structure interactions with waves, the sing-in-ground effect, drag reduction, etc.
Keun Kug Choi received his B.S., M.S., and Ph.D. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from Pusan National University, Busan, Korea, in 1981, 1987, and 2000, respectively. He has been with Samsung Techwin Co., Ltd, Changwon, Korea, since 1991. His research interests include estimation, fire control systems and surveillance robots.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.H., Park, H.G., Lee, W.B. et al. On the design of a disturbance observer for moving target tracking of an autonomous surveillance robot. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 10, 117–125 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-012-0113-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-012-0113-2