Abstract
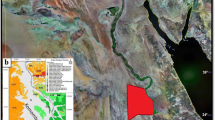
This study provides an evaluation of the subsurface oil contaminant flow in an oil production field at the Wadi Feiran fan, along the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. The 2D electrical resistivity tomography technique has been applied along four profiles surrounding the spill location of oil dump site. Theoretical soil resistivity response versus fluid resistivity for different cation exchange capacity values has been studied. Then, a physical model for the current situation of flowing the oil over the groundwater (sea invaded water) of saturated fluvial sediments has been introduced. It was supposed that the crude oil has higher resistivity values and turned to be conductive far away from the oil spill source under the effect of microbial biodegradation. Such conditions of contaminated distribution and its resistivity values have been considered during the inversion and interpretation of the acquired data sets. The processed 2D resistivity profiles reveal that oil plumes are accumulated in the seawater invasion direction, whereas it has low signatures along the profiles parallel to the shore line.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sayed EA, El-Qady G (2007) Evaluation of sea water intrusion using the electrical resistivity and transient electromagnetic survey: case study at fan of Wadi Feiran, Sinai, Egypt. EGM International Workshop. Innovation in EM, Grav, Mag Methods: a new Perspective for Exploration. Capri, Italy, 15–18 April 2007, pp. 1–4
Atekwana EA, Sauck WA, Werkema DD Jr (2000) Investigations of geoelectrical signatures at a hydrocarbon contaminated site. J Appl Geophys 44:167–180
Baedecker MJ, Cozzarelli IM, Eganhouse RP, Siegel DI, Benett PC (1993) Crude oil in a shallow sand in gravel aquifer—III. Appl Geochem 3:569–586
Barker RD (1980) Application of geophysics in groundwater investigations. Water Surv 84:489–492
Delgado Rodríguez O, Torres ML, Shevnin V, Ryjov A (2012) Estimation of soil petrophysical parameters based on electrical resistivity values obtained from lab and in-field measurements. Geofisc Int 51:5–15
Dey A, Morrison HF (1979) Resistivity modeling for arbitrarily shaped two-dimensional structures. Geophys Prospect 27:1020–1036
Godio A, Naldi M (2003) Two-dimensional electrical imaging for detection of hydrocarbon contaminants. Near Surf Geophys 1(3):131–137
Jiang Y, Li Y, Kang X, Zhou Q, Zhou X, Zhu Y (2012) Characteristics of leakage pollution of Longpan Road gas station and its enlightenment. J Environ Prot 3:49–54
Loke M, Barker R (1996) Rapid least squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections using a quasi Newton’s method. Geophys Prospect 44:131–152
Lssar A, Gat J (1981) Environmental isotopes as a tool in hydrogeological research in an Arid Basin. Ground Water 19:490–494
Said R (1962) The geology of Egypt. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 377
Sauck WA (2000) A model for the resistivity structure of LNAPL plumes and their environs in sandy sediments. J Appl Geophys 44:151–165
Sauck WA, Atekwana EA, Nash MS (1998) Elevated conductivities associated with an LNAPL plume imaged by integrated geophysical techniques. J Environ Eng Geophys 2:203–212
Shevnin V, Delgado-Rodrigues O, Fernandez-Linares L, Martinez AM, Ryjov A (2005) Geoelectrical characterization of an oil-contaminated site in Tabasco, Mexico. Geofisc Int 44:251–263
Urish DW, Frohlich RK (1990) Surface electrical resistivity in coastal groundwater exploration. Geoexploration 26:267–289
Waxman MH, Smits LJM (1968) Electrical conductivities in oil bearing sands. Soc Petrol Eng J 8:107–122
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the Geoelectricity and Geothermic Lab. at NRIAG, Egypt for helping to carry out the field work. The first author appreciates the College of Science Research Center at King Saud University for partially supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metwaly, M., Khalil, M.A., Al-Sayed, ES. et al. Tracing subsurface oil pollution leakage using 2D electrical resistivity tomography. Arab J Geosci 6, 3527–3533 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0600-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0600-z