Abstract
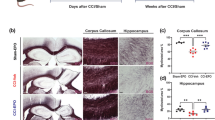
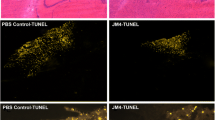
Erythropoietin (EPO) and granulocyte colonystimulating factor (G-CSF) are likely to play broad roles in the brain. We investigated the effects of combination therapy with EPO and G-CSF in hypoxicischemic brain injury during the acute, subacute, and chronic phases. A total of 79 C57BL/6 mice with hypoxic-ischemic brain injury were randomly assigned acute (days 1–5), subacute (days 11–15) and chronic (days 28–32) groups. All of them were treated with G-CSF (250 μg/kg) and EPO (5 000 U/kg) or saline daily for 5 consecutive days. Behavioral assessments and immunohistochemistry for angiogenesis, neurogenesis, and astrogliosis were performed with an 8-week follow-up. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) was also measured by Western blot analysis. The results showed that the combination therapy with EPO and G-CSF in the acute phase significantly improved rotarod performance and forelimb-use symmetry compared to the other groups, while subacute EPO and G-CSF therapy exhibited a modest improvement compared with the chronic saline controls. The acute treatment significantly increased the density of CD31+ (PECAM-1) and α-smooth muscle actin+ vessels in the frontal cortex and striatum, increased BrdU+/PSANCAM+ neurogenesis in the subventricular zone, and decreased astroglial density in the striatum. Furthermore, acute treatment significantly increased the HIF-1 expression in the cytosol and nucleus, whereas chronic treatment did not change the HIF-1 expression, consistent with the behavioral outcomes. These results indicate that the induction of HIF-1 expression by combination therapy with EPO and G-CSF synergistically enhances not only behavioral function but also neurogenesis and angiogenesis while decreasing the astroglial response in a timedependent manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasselblatt M, Jeibmann A, Riesmeier B, Maintz D, Schabitz WR. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) and G-CSF receptor expression in human ischemic stroke. Acta Neuropathol 2007, 113: 45–51.
Schlager GW, Griesmaier E, Wegleiter K, Neubauer V, Urbanek M, Kiechl-Kohlendorfer U, et al. Systemic G-CSF treatment does not improve long-term outcomes after neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury. Exp Neurol 2011, 230: 67–74.
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O. Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med 2002, 8: 963–970.
Sprigg N, Bath PMB. Colony stimulating factors (blood growth factors) are promising but unproven for treating stroke. Stroke 2007, 38: 1997–1998.
Digicaylioglu M. Erythropoietin in stroke: quo vadis. Expert Opin Biol 2010, 10: 937–949.
Siren AL, Fratelli M, Brines M, Goemans C, Casagrande S, Lewczuk P, et al. Erythropoietin prevents neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemia and metabolic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98: 4044–4049.
Leist M, Ghezzi P, Grasso G, Bianchi R, Villa P, Fratelli M, et al. Derivatives of erythropoietin that are tissue protective but not erythropoietic. Science 2004, 305: 239–242.
Wang L, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Zhang R, Chopp M. Treatment of stroke with erythropoietin enhances neurogenesis and angiogenesis and improves neurological function in rats Stroke 2004, 35: 1732–1737.
Ehrenreich H, Hasselblatt M, Dembowski C, Cepek L, Lewczuk P, Stiefel M, et al. Erythropoietin therapy for acute stroke is both safe and beneficial. Mol Med 2004, 8: 495–505.
Ehrenreich H, Weissenborn K, Prange H, Schneider D, Weimar C, Wartenberg K, et al; EPO Stroke Trial Group. Recombinant human erythropoietin in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2009, 40: e647–656.
Burgess AW, Metcalf D. Characterization of a serum factor stimulating the differentiation of myelomonocytic leukemic cells. Int J Cancer 1980, 26: 647–654.
Sachs L. The molecular control of blood cell development. Science 1987, 238: 1374–1379.
Cavallaro AM, Lilleby K, Majolino I, Storb R, Appelbaum FR, Rowley SD, et al. Three to six year follow-up of normal donors who received recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000, 25: 85–89.
Toth ZE, Leker RR, Shahar T, Pastorino S, Szalayova I, Asemenew B, et al. The combination of granulocyte colonystimulating factor and stem cell factor significantly increases the number of bone marrow-derived endothelial cells in brains of mice following cerebral ischemia. Blood 2008, 111: 5544–5552.
Beck H, Voswinckel R, Wagner S, Ziegelhoeffer T, Heil M, Helisch A, et al. Participation of bone marrow-derived cells in long-term repair processes after experimental stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2003, 23: 709–717.
Six I, Gasan G, Mura E, Bordet R. Beneficial effect of pharmacological mobilization of bone marrow in experimental cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol 2003, 458: 327–328.
Schneider A, Wysocki R, Pitzer C, Kruger C, Laage R, Schwab S, et al. An extended window of opportunity for G-CSF treatment in cerebral ischemia. BMC Biol 2006, 4: 36.
Sadamoto Y, Igase K, Sakanaka M, Sato K, Otsuka H, Sakaki S, et al. Erythropoietin prevents place navigation disability and cortical infarction in rats with permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998, 253: 26–32.
Liu SP, Lee SD, Lee HT, Liu DD, Wang HJ, Liu RS, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor activating HIF-1alpha acts synergistically with erythropoietin to promote tissue plasticity. PLoS One 2010, 5: e10093.
Levesque JP, Hendy J, Takamatsu Y, Williams B, Winkler IG, Simmons PJ. Mobilization by either cyclophosphamide or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor transforms the bone marrow into a highly proteolytic environment. Exp Hematol 2002, 30: 440–449.
Levesque JP, Takamatsu Y, Nilsson SK, Haylock DN, Simmons PJ. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD106) is cleaved by neutrophil proteases in the bone marrow following hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood 2001, 98: 1289–1297.
Ke Q, Costa M. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol 2006, 70: 1469–1480.
Pierelli L, Perillo A, Greggi S, Salerno G, Panici PB, Menichella G, et al. Erythropoietin addition to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor abrogates life-threatening neutropenia and increases peripheral-blood progenitorcell mobilization after epirubicin, paclitaxel, and cisplatin combination chemotherapy: results of a randomized comparison. J Clin Oncol 1999, 17: 1288.
Olivieri A, Offidani M, Cantori I, Ciniero L, Ombrosi L, Masia MC, et al. Addition of erythropoietin to granulocyte colonystimulating factor after priming chemotherapy enhances hemopoietic progenitor mobilization. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995, 16: 765–770.
Pierelli L, Menichella G, Scambia G, Teofili L, Iovino S, Serafini R, et al. In vitro and In vitro effects of recombinant human erythropoietin plus recombinant human G-CSF on human haemopoietic progenitor cells. Bone Marrow Transplant 1994, 14: 23–30.
Brines ML, Ghezzi P, Keenan S, Agnello D, de Lanerolle NC, Cerami C, et al. Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97: 10526–10531.
Cheer SM, Wagstaff AJ. Epoetin Beta: a review of its clinical use in the treatment of anaemia in patients with cancer. Drugs 2004, 64: 323–346.
Im SH, Yu JH, Park ES, Lee JE, Kim HO, Park KI, et al. Induction of striatal neurogenesis enhances functional recovery in an adult animal model of neonatal hypoxicischemic brain injury. Neuroscience 2010, 169: 259–268.
MacLellan CL, Auriat AM, McGie SC, Yan R, Huynh HD, De Butte MF, et al. Gauging recovery after hemorrhagic stroke in rats: implications for cytoprotection studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2006, 26: 1031–1042.
Ribatti D, Presta M, Vacca A, Ria R, Giuliani R, Dell’Era P, et al. Human erythropoietin induces a pro-angiogenic phenotype in cultured endothelial cells and stimulates neovascularization in vivo. Blood 1999, 93: 2627–2636.
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Ko SY, Kim EH, Sinn DI, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 2005, 1058: 120–128.
Sugiyama Y, Yagita Y, Oyama N, Terasaki Y, Omura-Matsuoka E, Sasaki T, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances arteriogenesis and ameliorates cerebral damage in a mouse model of ischemic stroke. Stroke 2011, 42: 770–775.
Zaidi AU, Bessert DA, Ong JE, Xu H, Barks JD, Silverstein FS, et al. New oligodendrocytes are generated after neonatal hypoxicischemic brain injury in rodents. Glia 2004, 46: 380–390.
Gonzalez FF, McQuillen P, Mu D, Chang Y, Wendland M, Vexler Z, et al. Erythropoietin enhances long-term neuroprotection and neurogenesis in neonatal stroke. Dev Neurosci 2007, 29: 321–330.
Pekny M, Nilsson M. Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Glia 2005, 50: 427–434.
Askalan R, Deveber G, Ho M, Ma J, Hawkins C. Astrocyticinducible nitric oxide synthase in the ischemic developing human brain. Pediatr Res 2006, 60: 687–692.
Bush TG, Puvanachandra N, Horner CH, Polito A, Ostenfeld T, Svendsen CN, et al. Leukocyte infiltration, neuronal degeneration, and neurite outgrowth after ablation of scarforming, reactive astrocytes in adult transgenic mice. Neuron 1999, 23: 297–308.
Silver J, Miller JH. Regeneration beyond the glial scar. Nat Rev Neurosci 2004, 5: 146–156.
Sofroniew MV. Reactive astrocytes in neural repair and protection. Neuroscientist 2005, 11: 400–407.
Vangeison G, Rempe DA. The Janus-faced effects of hypoxia on astrocyte function. Neuroscientist 2009, 15: 597–588.
Desclaux M, Teigell M, Amar L, Vogel R, Gimenez YRM, Privat A, et al. A novel and efficient gene transfer strategy reduces glial reactivity and improves neuronal survival and axonal growth in vitro. PLoS One 2009, 4: e6227.
Jelkmann W, Effects of erythropoietin on brain function. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2005, 6: 65–79.
Chen ZY, Warin R, Noguchi CT. Erythropoietin and normal brain development: receptor expression determines multitissue response. Neurodegener Dis 2006, 3: 68–75.
Buemi M, Cavallaro E, Floccari F, Sturiale A, Aloisi C, Trimarchi M, et al. The pleiotropic effects of erythropoietin in the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2003, 62: 228–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J.H., Seo, J.H., Lee, J.E. et al. Time-dependent effect of combination therapy with erythropoietin and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in a mouse model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Neurosci. Bull. 30, 107–117 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1397-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1397-9