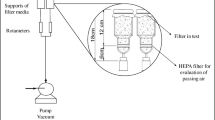
Abstract
This paper reports the installation of a carbon fiber ionizer in front of a fibrous medium filter to enhance the removal of submicron aerosol particles and bioaerosols. Test particles (KCl) were classified with a size range of 50–600 nm using a differential mobility analyzer (DMA). The number concentration of the test particles was measured using a condensation particle counter (CPC). The average charge per particle was estimated by current measurements using an aerosol electrometer. At the face velocity of 0.5 m/s, the particle removal efficiency was 31.4% (for dp=100 nm) when the ionizers were not operating but increased to 35.7% and 46.9% at 1.6×1011ions/s and 6.4×1012ions/s with the ionizers, respectively. For the antibacterial tests, the test bioaerosols (E. coli) were aerosolized using a nebulizer and were deposited on the filter media for 5 minutes. After the deposited bioaerosols were exposed to unipolar air ions, they were incubated for 12 hours. The survival efficiency of E. coli was measured using a colony counting method. The survival fractions of E. coli exposed to positive air ions for 1, 5 and 10 minutes were 61.7%, 45.4% and 25.2%, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Mitsakou, C. Housiadas, K. Eleftheriadis, S. Vratolis, C. Helmis and D. Asimakopoulos, Lung deposition of fine and ultrafine particles outdoors and indoors during a cooking event and a no activity period, Indoor Air, 17 (2007) 143–152.
W. C. Hinds, Aerosol technology: Properties, behavior, and measurement of airborne particles, Second ed. Wiley-Interscience, NewYork, USA, (1999).
H. Schleibinger and H. Rüden. Air filters from HVAC systems as possible source of volatile organic compounds (VOC) — laboratory and field assays, Atmospheric Environment, 33 (1999) 4571–4577.
B. U. Lee, M. Yermakov and S. A. Grinshpun, Unipolar ion emission enhances respiratory protection against fine and ultrafine particles, J. Aerosol Sci., 35 (2004) 1359–1368.
I. E. Agranovski, R. Huang, O. V. Pyankov, I. S. Altman and S. A. Grinshpun, Enhancement of the performance of low-efficiency HVAC filters due to continuous unipolar emission, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 40 (2006) 963–968.
R. Huang, I. E. Agranovski, O. V. Pyankov and S. A. Grinshpun, Removal of viable bioaerosol particles with a low-efficiency HVAC filter enhanced by continuous emission of unipolar air ions, Indoor Air, 18 (2008) 106–112.
L. A. Fletcher, L. F. Gaunt, C. B. Beggs, S. J. Shepherd, P. A. Sleigh, C. J. Noakes and K. G. Kerr, Bactericidal action of positive and negative ions in air BMC Microbiology, 7(32) (2007) 10.1186/1471-2180-7-32.
B. Han, H. J. Kim, Y. J. Kim and C. Sioutas, Unipolar charging of fine and ultra-fine particles using carbon fiber ionizers, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 42 (2008) 793–800.
ANSI/ASHRAE 52.2-2007, Method of Testing General Ventilation Air Cleaning Devices for Removal Efficiency by Particle Size, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Atlanta, G.A., USA (2007).
ISO 14698-1:2003, Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments-biocontamination control: Part 1: General principles and methods, International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland (2003)
K. W. Lee and B. Y. H. Liu, Theoretical study of aerosol filtration by fibrous filters, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 1 (1982) 147–161.
H. Landahl and K. Hermann, Sampling of liquid aerosols by wires, cylinders, and slides, and the efficiency of impaction of the droplets, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 4 (1949) 103–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jungho Hwang received his B.S. and M.S. degree in Department of Mechanical Engineering from Seoul National University, South Korea, in 1983 and 1985, respectively. He received his Ph.D. degree from UC Berkeley in 1991. Dr. Hwang is currently a Professor at the School of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University in Seoul, Korea. Dr. Hwang’s research interests include aerosols, air cleaning and thermal environmental engineering.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JH., Yoon, KY., Kim, YS. et al. Removal of submicron aerosol particles and bioaerosols using carbon fiber ionizer assisted fibrous medium filter media. J Mech Sci Technol 23, 1846–1851 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0613-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0613-z