Abstract
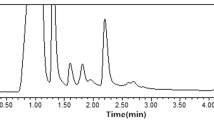
Preconcentration and determination of benzimidazole anthelmintics in egg samples has been successfully carried out using low-toxic organic solvent based ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction (UAEME) method coupled with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). A modified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe (QuEChERS) was used for precipitating protein and fat in egg samples before subjecting it to UAEME–HPLC. In UAEME, 1-octanol was used as extraction solvent and MeOH (chosen disperser solvent) under ultrasound radiation assisted. Under the optimum condition chosen (60 μl of octanol, 250 μl of MeOH, and 4-min ultrasonication), extraction efficiency was obtained in the range of 30–95, depending on the analytes. Limits of detection (LODs) of the studied benzimidazoles in egg samples were 7.2–14.4 μg/kg. Satisfied recoveries evaluated at the four-level spiked concentrations (i.e., 25, 50, 100, and 150 μg/kg) were obtained between 74.3 and 112.9 with the relative standard deviation (RSD) less than 11.5 %. Precisions comprising intra-day and inter-day measurements were obtained with RSD below 9.0 %. Less consumption of low toxic organic solvents, simple, and effective are beneficial of the demonstrated method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC guidelines for single laboratory validation of chemical methods for dietary supplements and botanicals (2002) http://www.aoac.org/Official_Methods/slv_guidelines.pdf. Accessed 1 Sep 2012
Bistoletti M, Moreno L, Alvarez L, Lanusse C (2011) Multiresidue HPLC method to measure benzimidazole anthelmintics in plasma and egg from laying hens. Evaluation of albendazole metabolites residue profiles. Food Chem 126:793–800
Chen D, Tao Y, Liu Z, Liu Z, Huang L, Wang Y, Pan Y, Peng D, Dai M, Yuan Z (2010) Development of a high-performance liquid chromatography method to monitor the residues of benzimidazoles in bovine milk. J Chromatogr B 878:2928–2932
Chen D, Tao Y, Zhang H, Pan Y, Liu Z, Huang L, Wang Y, Peng D, Wang X, Dai M, Yuan Z (2011) Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with pressurized liquid extraction method for the determination of benzimidazole residues in edible tissues. J Chromatogr B 879:1659–1667
Codex Alimentarius (1993) Residues of veterinary drugs in foods, Volume 3. 2nd Joint FAP/WHO Food Standards Programme, FAO, Rome Italy, p. 59
Danaher M, O’Keeffe M, Glennon JD (2003) Development and optimization of a method for the extraction of benzimidazoles from animal liver using supercritical carbon dioxide. Anal Chim Acta 483:313–324
Danaher M, Ruyck HD, Crooks SRH, Dowling G, O’Keeffe M (2007) Review of methodology for the determination of benzimidazole residues in biological matrices. J Chromatogr B 845:1–37
De Ruyck H, Van Renterghem R, De Ridder H, De Brabander D (2000) Determination of anthelmintic residues in milk by high performance liquid chromatography. Food Control 11:165–173
Dominguez-Alvarez J, Mateos-Vivas M, Garcia-Gomez D, Rodriguez-Gonzalo E, Carabias-Martinez R (2013) Capillary electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry for the determination of anthelmintic benzimidazoles in eggs using a QuEChERS with preconcentration as sample treatment. J Chromatogr A 1278:166–174
Frenich AG, Aguilera-Luiz MM, Vidal JLM, Romero-Gonzalez R (2010) Comparison of several extraction techniques for multiclass analysis of veterinary drugs in eggs using ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 661:150–160
Ghambarian M, Yamini Y, Esrafili A (2013) Liquid-phase microextraction based on solidified floating drops of organic solvents. Microchim Acta 180:519–535
Guo B, Huang Z, Wang M, Wang X, Zhang Y, Chen B, Li Y, Yan H, Yao S (2010) Simultaneous direct analysis of benzimidazole fungicides and relevant metabolites in agricultural products based on multifunction dispersive solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1217:4796–4807
Hu X-Z, Wang J-X, Feng Y-Q (2010) Determination of benzimidazole residues in edible animal food by polymer monolith microextraction combined with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 58:112–119
Huang K-J, Wei C-Y, Liu W-L, Xie W-Z, Zhang J-F, Wang W (2009) Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection for sensitive determination of biogenic amines in rice wine samples. J Chromatogr A 1216:6636–6641
Liang P, Wang F, Wan Q (2013) Ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of four fungicides in environmental water samples. Talanta 105:57–62
Moreno L, Imperiale F, Mottier L, Alvarez L, LanusseMoreno C (2005) Comparison of milk residue profiles after oral and subcutaneous administration of benzimidazole anthelmintics to dairy cows. Anal Chim Acta 536:91–99
Mottier L, Alvarez L, Lanusse C (2003) Quantitative chromatographic determination of several benzimidazole anthelmintic molecules in parasite material. J Chromatogr B 798:117–125
Official Journal of the European Communities (2002) Commission Decision of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation o f results (2002/657/EC).
Ozcan S, Tor A, Aydin ME (2010) Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in waters by ultrasound-assisted emulsification–microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 665:193–199
Padró JM, Marsón ME, Mastrantonio GE, Altcheh J, García-Bournissen F, Reta M (2013) Development of an ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method for the determination of nifurtimox and benzimidazole in human plasma. Talanta 107:95–102
Picó Y (2013) Ultrasound-assisted extraction for food and environmental samples. Trends Anal Chem 43:84–99
Pirsaheb M, Fattahi N, Shamsipur M, Khodadadi T (2013) Application of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop for simultaneous determination of alachlor and atrazine in aqueous samples. J Sep Sci 36:684–689
Regueiro J, Llompart M, Garcia-Jares C, Garcia-Monteagudo JC, Cela R (2008) Ultrasound-assisted emulsification–microextraction of emergent contaminants and pesticides in environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1190:27–38
Santaladchaiyakit Y, Srijaranai S (2012) A simplified ultrasound-assisted cloud-point extraction method coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for residue analysis of benzimidazole anthelmintics in water and milk samples. Anal Methods 4:3864–3873
Santaladchaiyakit Y, Srijaranai S (2013a) Preconcentration and simultaneous analysis of benzimidazole anthelmintics in milk samples by ultrasound-assisted surfactant-enhanced emulsification microextraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal Methods 6:1551–1560
Santaladchaiyakit Y, Srijaranai S (2013b) Surfactant-solvents based quaternary component emulsification microextraction followed by high performance liquid chromatography for the simultaneous analysis of benzimidazole anthelmintics in milk samples. Food Anal Methods. doi:10.1007/s12161-013-9738-x
Suh JH, Lee YY, Lee HJ, Kang M, Hur Y, Lee SN, Yang D-H, Han SB (2013) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplets followed by high performance liquid chromatography for the determination of duloxetine in human plasma. J Pharm Biomed Anal 75(2013):214–219
Vázquez MMP, Vázquez PP, Galera MM, García MDG (2012) Determination of eight fluoroquinolones in groundwater samples with ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction prior to high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 748:20–27
Whelan M, Kinsella B, Furey A, Moloney M, Cantwell H, Lehotay SJ, Danaher M (2010) Determination of anthelmintic drug residues in milk using ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with rapid polarity switching. J Chromatogr A 1217:4612–4622
Wu Q, Li Y, Wang C, Liu Z, Zang X, Zhou X, Wang Z (2009) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection for the determination of carbandazim and thiabendazole in environmental samples. Anal Chim Acta 638:139–145
Xia X, Dong Y, Luo P, Wang X, Li X, Ding S, Shen J (2010) Determination of benzimidazole residues in bovine milk by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 878:3174–3180
Zhang Y, Lee HK (2012) Ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of ultraviolet filters in environmental water samples. Anal Chim Acta 750:120–126
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Thailand Research Fund (TRF), the Commission on Higher Education (CHE), and Rajamangala University of Technology Isan, Khon Kaen Campus through the TRF-CHE Research Grant for New Scholars under Grant No. MRG5480135. The authors would like to acknowledge Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Khon Kaen University for providing deionized water. The authors also thank Miss Namfon Jampaburee, Miss Witchunee Rachdusadee, Miss Sunisa Leykan, and Miss Wanida Sangsawang for their assistance in the laboratory.
Conflict of Interest
Yanawath Santaladchaiyakit declares that he has no conflict of interest. Supalax Srijaranai declares that she has no conflict of interest. Rodjana Burakham declares that she has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santaladchaiyakit, Y., Srijaranai, S. & Burakham, R. Low Toxic Organic Solvent-Based Ultrasound-Assisted Emulsification Microextraction for the Residue Analysis of Benzimidazole Anthelmintics in Egg Samples by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Anal. Methods 7, 1973–1981 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9838-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-9838-2