Abstract.
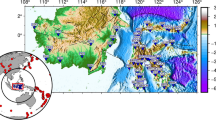
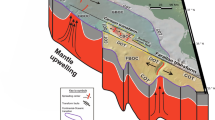
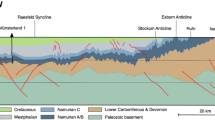
Krishna–Godavari offshore basin, a part of the eastern continental margin of India is a proven petroliferous basin. Recent drilling in this area in search of gas hydrates reveals that the upper ∼300 m thick Quaternary–Recent strata comprised of nannofossil bearing rich clays and, fractures/faults are the suitable zones for gas hydrates accumulation. Therefore, the knowledge about the shallow geological environments and its architecture are significantly important in assessing the gas hydrates potential of this area. In order to enhance the geological understanding, the newly acquired high resolution seismic (HRS) reflection data in this gas hydrates prone area is interpreted. The processed seismic sections show a maximum penetration of 562 ms TWT (∼450 m) underneath the seabed with high resolution stratification. An attempt has been made to: (i) deduce the shallow geological environment from the reflection characteristics, and, (ii) assign tentative ages under the constraints of drilling/coring results. We further explained the observed folded structures on the surface and subsurface through a mechanism linked to shale tectonism and neotectonic activity.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastia R 2004 Deposition model and reservoir architecture of tertiary deep water sedimentation, Krishna–Godavari offshore basin, India; J. Geol. Soc. India 64 11–20.
Bastia R and Nayak P 2006 Tectonostratigraphy and depositional patterns in Krishna offshore basin, Bay of Bengal; The Leading Edge 25(7) 839–845.
Bastia R, Singh P and Nayak P 2006 Linking shelf delta to deep water: Krishna–Godavari Basin; Geol. Soc. India 167 618–628.
Bastia R, Radhakrishna M, Srinivas T, Satyabrata Nayak, Nathanial D M and Biswal T K 2010 Structural and tectonic interpretation of geophysical data along the eastern continental margin of India with a special reference to deep water petroliferous basins; J. Asian Earth Sci. 39 608–619.
Chatterjee R, Mukhopadhyay M and Paul S 2010 Overpressure zone under the Krishna–Godavari offshore basin: Geophysical implications for natural hazard in deeper-water drilling; Nat. Hazards, doi:10.1007/s11069-010-9659-6.
Collett T S, Riedel M, Cochran J R, Boswell R, Presley J, Sibal V, Kumar P, Sathe A, Sethi A and Lall M 2008 The National Gas Hydrates Program Expedition 01 Initial reports, Directorate General of Hydrocarbons, Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, New Delhi.
Curray J R, Emmel F J, Moore D G and Raitt R W 1982 Structure, tectonics and geological history of the northeastern Indian Ocean; In: The Ocean basins and margins (eds) Nairn A E and Stehli F G (New York: Plenum Press) 6 399–450.
Dewangan P, Ramprasad T, Ramana M V, Mazumdar A, Desa M and Badesab F K 2010 Seabed morphology and gas venting features in the continental slope region of Krishna–Godavari basin, Bay of Bengal: Implications in gas–hydrate exploration; Mar. Petrol. Geol. 27(7) 1628–1641.
Dewangan P, Sriram G, Ramprasad T, Ramana M V and Jaiswal P 2011 Fault system and thermal regime in the vicinity of site NGHP-01-10, Krishna–Godavari basin, Bay of Bengal; Mar. Petrol. Geol. 28 1899–1914.
Gupta S K 2006 Basin architecture and petroleum system of Krishna Godavari basin, east coast of India; The Leading Edge 25(7) 830–837.
Kvenvolden K A 1993 Gas hydrates as a potential energy resource – a review of their methane content; In: The Future of Energy Gases (ed.) Howell D G, US Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper 1570 555–561.
Krishna K S, Ramana M V, Gopala Rao D, Murthy K S R, Malleswara Rao M M, Subrahmanyam V and Sarma K V L N S 1998 Periodic deformation of oceanic crust in the central Indian Ocean; J. Geophys. Res. 103 17,859–17,875.
Mazumdar A, Dewangan P, Joao H M, Peketi A, Khosla V R, Kocherla M, Badesab F K, Joshi R K, Roxanne P, Ramamurty P B, Karisiddaiah S M, Patil D J, Dayal A M, Ramprasad T, Hawkesworthn C J and Avanzinelli R 2009 Evidence of paleo-cold seep activity from the Bay of Bengal, offshore India; Geochem. Geophys. Geosys. 10(6) 15, doi:10.1029/2008GC002337.
Mazumdar A, Peketi A, Dewangan P, Kocherla M, Joshi R K and Ramprasad T 2012 Geochemical and geological constraints on the composition of marine sediment pore fluid: Possible link to gas hydrate deposits; Mar. Petrol. Geol. 38 35–52.
Murthy K S R, Subrahmanyam V, Subrahmanyam A S, Murty G P S and Sarma K V L N S 2010 Land–ocean tectonics (LOTs) and the associated seismic hazard over the Eastern Continental Margin of India (ECMI); Nat. Hazards 55 167–175, doi:10.1007/s11069-010-9523-8.
NIO 1997 Gas hydrates resource map of India; No. NIO/SP-25/97, National Institute of Oceanography, Dona Paula, Goa.
NIO 2001 Reprocessing of multichannel seismic data of ONGC; No. NIO/CON/3-2001, National Institute of Oceanography, Dona Paula, Goa.
NIO 2005 Geoscientific investigations of shallow sediments in KG offshore, East Coast; NIO/TR-13/2003, National Institute of Oceanography, Dona Paula, Goa.
Pateria M L, Rangaraju M K and Raiverman V 1992 A note on the structure and stratigraphy of Bay of Bengal sediments; In: Recent Geoscientific Studies in the Bay of Bengal and the Andaman Sea; Geol. Surv. India Spec. Publ. 29 21–23.
Raju D S N, Ravindran C N, Mishra P K, Chidambaram L and Saxena R K 1994 Stratigraphy and Paleoenvironments of the Godavari clay in the Krishna–Godavari basin, India; Indian J. Petrol. Geol. 3(2) 33–43.
Ramana M V, Nair R R, Sarma K V L N S, Ramprasad T, Krishna K S, Subrahmanyam V, Maria D’Cruz, Subrahmanyam C, Paul J, Subrahmanyam A S and Chandra Sekhar D V 1994 Mesozoic anomalies in the Bay of Bengal; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 121 469–475.
Ramana M V, Ramprasad T, Desa M, Sathe A V and Sethi A K 2006 Gas hydrates-related proxies inferred from multidisciplinary investigations in the Indian offshore areas; Curr. Sci. 91(2) 183–189.
Ramana M V, Ramprasad T, Paropkari A L, Borole D V, Ramalingeswara Rao B, Karisiddaiah S M, Desa M, Kocherla M, Joao H M, Loka-bharathi P, Gonsalves Maria-Judith, Pattan J N, Khadge N H, Prakash Babu C, Sathe A V, Kumar P and Sethi A K 2009 Multidisciplinary investigations exploring indicators of gas hydrates occurrence in the Krishna–Godavari basin offshore, east coast of India; Geo-Mar. Lett. 29(1) 25–38.
Ramprasad T, Dewangan P, Ramana M V, Mazumdar A, Karisiddaiah S M, Ramya E R and Sriram G 2011 Evidence of slumping/sliding in Krishna Godavari offshore basin due to gas/fluid movements; Mar. Petrol. Geol. 28 1806–1816.
Rao G N 2001 Sedimentation, stratigraphy, and petroleum potential of Krishna–Godavari basin, east coast of India; Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull. 85(9) 1623–1643.
Rao G N, Mani K S 1993 A study on generation of abnormal pressures in Krishna–Godavari Basin, India; Indian J. Petrol. Geol. 2(1) 20–30.
Sahu J N 2005 Deep water Krishna–Godavari basin and its potential; Petromin (Asia’s Exploration and Production Business magazine) 31 26–34.
Satyanarayana K, Rao G N, Bhavana P R, Sinha H R and Banerjee A N 1996 Miocene sedimentation in subsurface of Godavari Delta; Bull. ONGC 33(1) 77–92.
Shanmugam G 2009 Slides, slumps, debris flows, and turbidity currents; In: Encyclopaedia of Ocean Sciences (eds) Steele J H, Turekian K K and Thorpe S A, 2nd edn, Elsevier, pp. 447–467.
Shanmugam G, Shrivastava S K and Das B 2009 Sandy debrites and tidalites of pliocene reservoir sands in upper-slope canyon environments, offshore Krishna–Godavari basin (India): Implications; J. Sedim. Res. 79(9) 736–756.
Sloan E D 1990 Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank Director, National Institute of Oceanography, Goa for granting necessary permission to publish this manuscript. G Anitha (SRF) would like to thank Smt. Vimalabai (Jiji) Neelkanth Jatar Charitable Trust (VNJCT) for the financial support through institution of fellowships for the award of Ph.D. in gas hydrates studies. M V Ramana like to thank CSIR-Emeritus scientist scheme for financial assistance. This is NIO Contribution No. 5455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ANITHA, G., RAMANA, M.V., RAMPRASAD, T. et al. Shallow geological environment of Krishna–Godavari offshore, eastern continental margin of India as inferred from the interpretation of high resolution sparker data. J Earth Syst Sci 123, 329–342 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0399-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0399-3