Abstract
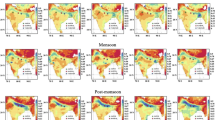
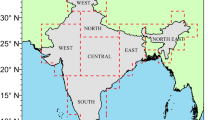
Spectral aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements, carried out regularly from a network of observatories spread over the Indian mainland and adjoining islands in the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea, are used to examine the spatio-temporal and spectral variations during the period of ICARB (March to May 2006). The AODs and the derived Ångström parameters showed considerable variations across India during the above period. While at the southern peninsular stations the AODs decreased towards May after a peak in April, in the north Indian regions they increased continuously from March to May. The Ångström coefficients suggested enhanced coarse mode loading in the north Indian regions, compared to southern India. Nevertheless, as months progressed from March to May, the dominance of coarse mode aerosols increased in the columnar aerosol size spectrum over the entire Indian mainland, maintaining the regional distinctiveness. Compared to the above, the island stations showed considerably low AODs, so too the northeastern station Dibrugarh, indicating the prevalence of cleaner environment. Long-range transport of aerosols from tshe adjoining regions leads to remarkable changes in the magnitude of the AODs and their wavelength dependencies during March to May. HYSPLIT back-trajectory analysis shows that enhanced long-range transport of aerosols, particularly from the west Asia and northwest coastal India, contributed significantly to the enhancement of AOD and in the flattening of the spectra over entire regions; if it is the peninsular regions and the island Minicoy are more impacted in April, the north Indian regions including the Indo Gangetic Plain get affected the most during May, with the AODs soaring as high as 1.0 at 500 nm. Over the islands, the Ångström exponent (α) remained significantly lower (∼1) over the Arabian Sea compared to Bay of Bengal (BoB) (∼1.4) as revealed by the data respectively from Minicoy and Port Blair. Occurrences of higher values of α, showing dominance of accumulation mode aerosols, over BoB are associated well with the advection, above the boundary layer, of fine particles from the east Asian region during March and April. The change in the airmass to marine in May results in a rapid decrease in α over the BoB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht B A 1989 Aerosols, cloud microphysics and fractional cloudiness; Science 245 1227–1230.
Ångström A 1964 Techniques of determining the turbidity of the atmosphere; Tellus 13 214.
Asnani G C 1993 Tropical Meteorology 1 603. Indian Inst. of Trop. Meteorol., Pune.
Babu S S and Moorthy K K 2002 Aerosol black carbon over a tropical coastal station in India; Geophys. Res Lett. 29(23) 2098, doi:10.1029/2002GL015662, 13-1 to 13-4.
Charlson R J 1992 Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols; Science 255 423–430.
Chinnam N, Dey S, Tripathi S N and Sharma M 2006 Dust events in Kanpur, Northern India: Chemical evidence for source and implications to radiative forcing; Geophys. Res. Lett. 33 L08803, doi:10.1029/2005GL025278.
Dey S, Tripathi S N, Singh R P and Holben B 2004 Influence of dust storm on the aerosol parameters over the Indo-Gangetic Basin; J. Geophys. Res. 109 D20211, doi:10.1029/2004JD004924.
Holben B N, Eck T F, Slutsker I, Tanre D, Buis J P, Setzer S, Vermote E, Reagan J A, Kaufman Y J, Nakajima T, Lavenu F, Jankowiak I and Smirnov A 1998 AERONET — A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization; Rem. Sens. Environ. 66 1–s16.
Hoppel W A, Frick G M, Larson R E and Mack E J 1990 Aerosol size distributions and optical properties found in the marine boundary layer over the Atlantic Ocean; J. Geophys. Res. 95 3659–3686.
Ichoku, Charles, Robert Levy and Kaufman Y J et al 2002 Analysis of the performance characteristics of the five-channel Microtops II Sun Photometer for measuring aerosol optical thickness and perceptible water vapor; J. Geophys. Res. 107(D13) 10.1029/2001JD00130.
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 2001; Climate change 1994: Radiative Forcing of Climate, report to IPCC from the Scientific Assessment Group (WGI) (New York: Cambridge Univ. Press).
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 2007 Climate change — 2007, Changes in Atmospheric Constituents and in radiative Forcing, Contribution of Working group to the Fourth Assessment report of the IPCC (New York: Cambridge Univ. Press).
Jacobson M Z 2001 Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols; Nature 409 695–697.
Jaenicke R 1984 Aerosols and their climatic effects; A Deepak Publishing, Virginia, USA.
Li F and Ramanathan V 2002 Winter to summer monsoon variation of aerosol optical depth over tropical Indian Ocean; J. Geophys. Res. 107 doi:10.1029/2001JD000949.
Moorthy K K and Satheesh S K 2000 Characteristics of aerosols over a remote island, Minicoy in the Arabian Sea: optical properties and retrieved size characteristics; Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 126 81–109.
Moorthy K K, Satheesh S K and Murthy B V K 1997 Investigations of marine aerosols over the tropical Indian Ocean; J. Geophys. Res. 102 18,827–18,842.
Moorthy K K, Niranjan K, Narasimha Murthy B N, Agashe V V and Murthy B V K 1999 Aerosol Climatology over India; 1 — ISRO GBP MWR Network and Database, ISRO GBP, ISRO GBP SR-03-99, Indian Space Research Organisation, Bangalore.
Moorthy K K, Babu S S and Satheesh S K 2003 Aerosol spectral optical depths over the Bay of Bengal: Role of transport; Geophys. Res. Lett. 30(5) 1249, doi:10.1029/2002GL016520.
Moorthy K K, Babu S S and Satheesh S K 2005 Aerosol characteristics and radiative impacts over the Arabian Sea during the intermonsoon season: Results from ARMEX field campaign; J. Atmos. Sci. 62 192–206.
Moorthy K K, Satheesh S K and Babu S S 2006 ICARB: An integrated campaign for Aerosols, gases and radiation budget; Proc. of SPIE 6408 64080P, 0277-786X/06/$15 · doi:10.1117/12.696110.
Moorthy K K, Babu S S, Satheesh S K, Srinivasan J and Dutt C B S 2007 Dust Absorption over the “Great Indian Desert” inferred using ground-based and satellite remote sensing; J. Geophys. Res. 112 D09206, doi:10.1029/2006JD007690.
Morys M, Mims F M, Hagerup S, Anderson S E, Baker A, Kia J and Walkup T 2001 Design, calibration and performance of MICROTOPS II hand-held ozone monitor and Sun Photometer; J. Geophys. Res. 106(D13) 14,573–14,582.
Porter, John N, Mark Miller, Chritophe Pietras and Craig Motell 2001 Ship-Based Sun Photometer Measurements Using Microtops Sun Photometer; J. Atmos. Ocea. Tech. 18 765–774.
Rosefield D 2000 Suppression of rain and snow by urban and industrial air pollution; Science 287 1793–1796.
Saha A and Moorthy K K 2005 Interannual Variations of Aerosol Optical Depth over Coastal India: Relation to Synoptic Meteorology; J. Appl. Meteorol. 44 1066–1077.
Shaw G E, Regan R A and Herman B M 1973 Investigations of atmospheric extinctions using direct solar radiation measurements made with a multiple wavelength radiometer; J. Appl. Meteorol. 12 374–380.
Singh R P, Dey S, Tripathi S N and Tare V 2004 Variability of aerosol parameters over Kanpur, northern India; J. Geophys. Res. 109 D23206, doi:10.1029/2004JD004966.
Tare V et al 2006 Measurement of atmospheric parameters during ISRO-GBP Land Campaign II at a typical location in the Ganga Basin: 2. Chemical properties; J. Geophys. Res. 111 D23210, doi:10.1029/2006JD007279.
Twomey S A 1977 The influence of pollution on the short-wave albedo of clouds; J. Atmos. Sci. 34 1149–1152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beegum, S.N., Moorthy, K.K., Nair, V.S. et al. Characteristics of spectral aerosol optical depths over India during ICARB. J Earth Syst Sci 117 (Suppl 1), 303–313 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-008-0033-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-008-0033-y