Abstract
Background
Impaired cerebral autoregulation (CA) is increasingly recognized to contribute to sequelae after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). The current study characterizes the course of the dynamic autoregulation index (ARI) during the first 8 days after SAH and its coherence with angiographic vasospasm (VS) and clinical outcome.
Methods
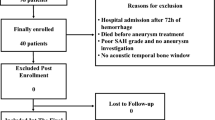
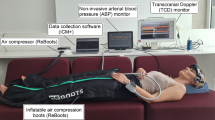
Fifty-one patients with SAH were prospectively included within 48 h after the ictus. The ARI was determined daily for each hemisphere with the thigh cuff test. The degree of cerebral VS was evaluated based on a baseline digital subtraction angiography (DSA) after the ictus and a follow-up DSA on day 8. The clinical outcome was determined by the Modified Rankin Scale (mRS), the Glasgow Outcome Scale Extended (GOSE), and the National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) at discharge from the intensive care unit.
Results
Impaired CA significantly correlated with unfavorable clinical outcome scores (mRS, p = 0.0021; GOSE, p = 0.0027; NIHSS, p = 0.0091). ARI-values of patients with a favorable clinical outcome (mRS 0–3) showed a significant improvement during the first 8 days (+0.1964/day; p = 0.0148) compared to a significant decrease of ARI-values in patients with an unfavorable clinical outcome (–0.2976/day; p = 0.0182). The degree of CA impairment significantly correlated with the severity of VS in the middle cerebral artery (p = 0.0184).
Conclusions
Early deterioration of CA significantly correlates with unfavorable clinical outcome and severity of angiographic vasospasm. Dynamic CA measurements might represent an important tool in stratifying therapy guidelines in patients after SAH.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Budohoski KP, Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, et al. Impairment of cerebral autoregulation predicts delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a prospective observational study. Stroke. 2012;43:3230–7.
Diedler J, Sykora M, Rupp A, et al. Impaired cerebral vasomotor activity in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 2009;40:815–9.
Saeed NP, Panerai RB, Horsfield MA, Robinson TG. Does stroke subtype and measurement technique influence estimation of cerebral autoregulation in acute ischaemic stroke? Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;35:257–61.
Buczek J, Karliński M, Kobayashi A, Białek P, Członkowska A. Hyperperfusion syndrome after carotid endarterectomy and carotid stenting. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;35:531–7.
Atkins ER, Brodie FG, Rafelt SE, Panerai RB, Robinson TG. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation is compromised acutely following mild ischaemic stroke but not transient ischaemic attack. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010;29:228–35.
Abstracts of the 18th Meeting of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics (ESNCH) and the 3rd Meeting of the Cerebral Autoregulation Network (CARNet).Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;35 Suppl 2:1–77. May 24–27, 2013 Porto, Portugal.
Aaslid R, Lindegaard KF, Sorteberg W, Nornes H. Cerebral autoregulation dynamics in humans. Stroke. 1989;20:45–52.
Barth M, Woitzik J, Weiss C, et al. Correlation of clinical outcome with pressure-, oxygen-, and flow-related indices of cerebrovascular reactivity in patients following aneurysmal SAH. Neurocrit Care. 2010;12:234–43.
Budohoski KP, Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, et al. Cerebral autoregulation after subarachnoid hemorrhage: comparison of three methods. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:449–56.
Christ M, Noack F, Schroeder T, et al. Continuous cerebral autoregulation monitoring by improved cross-correlation analysis: comparison with the cuff deflation test. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33:246–54 Epub 2006 Dec 2.
Tzeng YC, Ainslie PN, Cooke WH, et al. Assessment of cerebral autoregulation: the quandary of quantification. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;303:H658–71.
Jaeger M, Schuhmann MU, Soehle M, Nagel C, Meixensberger J. Continuous monitoring of cerebrovascular autoregulation after subarachnoid hemorrhage by brain tissue oxygen pressure reactivity and its relation to delayed cerebral infarction. Stroke. 2007;38:981–6.
Jaeger M, Soehle M, Schuhmann MU, Meixensberger J. Clinical significance of impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation after severe aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2012;43:2097–101.
Soehle M, Czosnyka M, Pickard JD, Kirkpatrick PJ. Continuous assessment of cerebral autoregulation in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anesth Analg 2004;98:1133–9, table of contents.
Raabe A, Beck J, Berkefeld J, et al. Recommendations for the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Zentralbl Neurochir. 2005;66:79–91.
Macdonald RL, Kassell NF, Mayer S, et al. Clazosentan to overcome neurological ischemia and infarction occurring after subarachnoid hemorrhage (CONSCIOUS-1): randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 dose-finding trial. Stroke. 2008;39:3015–21.
Hlatky R, Furuya Y, Valadka AB, et al. Dynamic autoregulatory response after severe head injury. J Neurosurg. 2002;97:1054–61.
Mahony PJ, Panerai RB, Deverson ST, Hayes PD, Evans DH. Assessment of the thigh cuff technique for measurement of dynamic cerebral autoregulation. Stroke. 2000;31:476–80.
Park CW, Sturzenegger M, Douville CM, Aaslid R, Newell DW. Autoregulatory response and CO2 reactivity of the basilar artery. Stroke. 2003;34:34–9.
Vavilala MS, Newell DW, Junger E, et al. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in healthy adolescents. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002;46:393–7.
Jünger EC, Newell DW, Grant GA, et al. Cerebral autoregulation following minor head injury. J Neurosurg. 1997;86:425–32.
Engelhard K, Werner C, Mollenberg O, Kochs E. Effects of remifentanil/propofol in comparison with isoflurane on dynamic cerebrovascular autoregulation in humans. Acta Anesthesiol Scand. 2001;45:971–6.
Barth M, Moratin B, Dostal M, Kalenka A, Scharf J, Schmieder K. Correlation of clinical outcome and angiographic vasospasm with the dynamic autoregulatory response after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2012;114:157–60.
Jaeger M, Schuhmann MU, Soehle M, Meixensberger J. Continuous assessment of cerebrovascular autoregulation after traumatic brain injury using brain tissue oxygen pressure reactivity. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:1783–8.
Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Kirkpatrick P, Laing RJ, Menon D, Pickard JD. Continuous assessment of the cerebral vasomotor reactivity in head injury. Neurosurgery 1997;41:11–7; discussion 7–9.
Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Kirkpatrick P, Menon DK, Pickard JD. Monitoring of cerebral autoregulation in head-injured patients. Stroke. 1996;27:1829–34.
Dohmen C, Bosche B, Graf R, et al. Identification and clinical impact of impaired cerebrovascular autoregulation in patients with malignant middle cerebral artery infarction. Stroke. 2007;38:56–61.
Reinhard M, Gerds TA, Grabiak D, et al. Cerebral dysautoregulation and the risk of ischemic events in occlusive carotid artery disease. J Neurol. 2008;255:1182–9.
Schmieder K, Moller F, Engelhardt M, et al. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in patients with ruptured and unruptured aneurysms after induction of general anesthesia. Zentralbl Neurochir. 2006;67:81–7.
Frontera JA, Rundek T, Schmidt JM, et al. Cerebrovascular reactivity and vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a pilot study. Neurology. 2006;66:727–9.
Lam JM, Smielewski P, Czosnyka M, Pickard JD, Kirkpatrick PJ. Predicting delayed ischemic deficits after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage using a transient hyperemic response test of cerebral autoregulation. Neurosurgery. 2000;47:819–25.
Lang EW, Diehl RR, Mehdorn HM. Cerebral autoregulation testing after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the phase relationship between arterial blood pressure and cerebral blood flow velocity. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:158–63.
Ratsep T, Asser T. Cerebral hemodynamic impairment after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage as evaluated using transcranial doppler ultrasonography: relationship to delayed cerebral ischemia and clinical outcome. J Neurosurg. 2001;95:393–401.
Voldby B, Enevoldsen EM, Jensen FT. Cerebrovascular reactivity in patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1985;62:59–67.
Otite F, Mink S, Tan CO, et al. Impaired cerebral autoregulation is associated with vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2014;45:677–82.
Tiecks FP, Lam AM, Aaslid R, Newell DW. Comparison of static and dynamic cerebral autoregulation measurements. Stroke. 1995;26:1014–9.
Strebel S, Lam AM, Matta B, Mayberg TS, Aaslid R, Newell DW. Dynamic and static cerebral autoregulation during isoflurane, desflurane, and propofol anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1995;83:66–76.
van Lieshout JJ, Secher NH. Point:counterpoint: sympathetic activity does/does not influence cerebral blood flow. Point: sympathetic activity does influence cerebral blood flow. J Appl Physiol. 2008;105:1364–6.
Diehl RR, Linden D, Lucke D, Berlit P. Phase relationship between cerebral blood flow velocity and blood pressure. Clinical test of autoregulation. Stroke. 1995;26:1801–4.
Steinmeier R, Bauhuf C, Hubner U, et al. Slow rhythmic oscillations of blood pressure, intracranial pressure, microcirculation, and cerebral oxygenation. Dynamic interrelation and time course in humans. Stroke. 1996;27:2236–43.
Steinmeier R, Hofmann RP, Bauhuf C, Hubner U, Fahlbusch R. Continuous cerebral autoregulation monitoring by cross-correlation analysis. J Neurotrauma. 2002;19:1127–38.
Périard D, Rey MA, Casagrande D, Vesin JM, Carrera E, Hayoz D. The effect of valsartan versus non-RAAS treatment on autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;34:78–85.
Brodie FG, Atkins ER, Robinson TG, Panerai RB. Reliability of dynamic cerebral autoregulation measurement using spontaneous fluctuations in blood pressure. Clin sci (Lond). 2009;116:513–20.
Ramos EG, Simpson DM, Panerai RB, Nadal J, Lopes JM, Evans DH. Objective selection of signals for assessment of cerebral blood flow autoregulation in neonates. Physiol Meas. 2006;27:35–49.
Katsogridakis E, Bush G, Fan L, et al. Detection of impaired cerebral autoregulation improves by increasing arterial blood pressure variability. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:519–23.
Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Lavinio A, Pickard JD, Panerai RB. An assessment of dynamic autoregulation from spontaneous fluctuations of cerebral blood flow velocity: a comparison of two models, index of autoregulation and mean flow index. Anaesth Analg. 2008;106:234–9.
Piechnik SK, Yang X, Czosnyka M, et al. The continuous assessment of cerebrovascular reactivity: a validation of the method in healthy volunteers. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:944–9.
Vergouwen MD, Vermeulen M, van Gijn J, et al. Definition of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage as an outcome event in clinical trials and observational studies: proposal of a multidisciplinary research group. Stroke. 2010;41:2391–5.
Banks JL, Marotta CA. Outcomes validity and reliability of the modified Rankin scale: implications for stroke clinical trials: a literature review and synthesis. Stroke. 2007;38:1091–6.
Etminan N, Vergouwen MD, Ilodigwe D, Macdonald RL. Effect of pharmaceutical treatment on vasospasm, delayed cerebral ischemia, and clinical outcome in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011;31:1443–51.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fontana, J., Moratin, J., Ehrlich, G. et al. Dynamic Autoregulatory Response After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Its Relation to Angiographic Vasospasm and Clinical Outcome. Neurocrit Care 23, 355–363 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-014-0104-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-014-0104-7