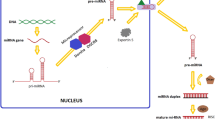
Abstract
This study was set to determine the expression of microRNA-449a in cancer tissue and serum of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and explore the underlying mechanisms of its tumor suppressor functions. We selected 50 NSCLC patients in our hospital as the lung cancer group and 50 healthy volunteers as the control group. RT-PCR was performed to detect the expression levels of microRNA-449a in NSCLC tissue and the plasma of NSCLC patients. Further, we transfected microRNA-449a mimic and inhibitor in lung cancer cell line A549, and used western blot to determine the expression level of apoptosis-related molecules Bcl-2 and p53. Compared with the surrounding tissue, microRNA-449a exhibited significantly reduced mRNA expression, which was statistically different (P < 0.05). microRNA-449a exhibited significantly lower expression in NSCLC patients’ plasma than the healthy volunteers, which was statistically different (P < 0.05). Spearman correlation analysis showed that microRNA-449a expression levels in NSCLC tissue and plasma of NSCLC patients were reversely correlated with lung cancer differentiation (P < 0.05). But microRNA-449a expression in the surrounding tissue was not significantly correlated with lung cancer differentiation (P > 0.05). Compared with negative control, cell proliferation and p53 and Bcl-2 expression significantly decreased after microRNA-449a mimic transfection (P < 0.05). However, after transfection of microRNA-449a inhibitor, cell proliferation and p53 and Bcl-2 expression significantly increased after microRNA-449a mimic transfection (P < 0.05). microRNA-449a expression levels in NSCLC are significantly lower than those in the surrounding tissue, and its expression levels in NSCLC patients are also lower than those in healthy volunteers. The tumor suppression role of microRNA-449a could be due to its promotion of tumor cell proliferation and its inhibition of tumor cell apoptosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal, A., Bray, F., Center, M. M., Ferlay, J., Ward, E., & Forman, D. (2011). Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 61, 69–90.
Boffetta, P., & Nyberg, F. (2003). Contribution of environmental factors to cancer risk. British Medical Bulletin, 68, 71–94.
Didkowska, J., Manczuk, M., McNeill, A., Powles, J., & Zatonski, W. (2005). Lung cancer mortality at ages 35-54 in the European Union: Ecological study of evolving tobacco epidemics. BMJ, 331, 189–191.
Ridge, C. A., McErlean, A. M., & Ginsberg, M. S. (2013). Epidemiology of lung cancer. Seminars in Interventional Radiology, 30, 93–98.
Paliogiannis, P., Attene, F., Cossu, A., Budroni, M., Cesaraccio, R., Tanda, F., et al. (2013). Lung cancer epidemiology in North Sardinia, Italy. Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine, 8, 45.
Lu, J., Getz, G., Miska, E. A., Alvarez-Saavedra, E., Lamb, J., Peck, D., et al. (2005). MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature, 435, 834–838.
Mishra, P. J., & Merlino, G. (2009). MicroRNA reexpression as differentiation therapy in cancer. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 119, 2119–2123.
Schmittgen, T. D. (2008). Regulation of microRNA processing in development, differentiation and cancer. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 12, 1811–1819.
Tsuchiya, S., Okuno, Y., & Tsujimoto, G. (2006). MicroRNA: Biogenetic and functional mechanisms and involvements in cell differentiation and cancer. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 101, 267–270.
Noonan, E. J., Place, R. F., Pookot, D., Basak, S., Whitson, J. M., Hirata, H., et al. (2009). miR-449a targets HDAC-1 and induces growth arrest in prostate cancer. Oncogene, 28, 1714–1724.
Ren, X. S., Yin, M. H., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Feng, S. P., Wang, G. X., et al. (2014). Tumor-suppressive microRNA-449a induces growth arrest and senescence by targeting E2F3 in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Letters, 344, 195–203.
Chen, H., Lin, Y. W., Mao, Y. Q., Wu, J., Liu, Y. F., Zheng, X. Y., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-449a acts as a tumor suppressor in human bladder cancer through the regulation of pocket proteins. Cancer Letters, 320, 40–47.
Luo, W., Huang, B., Li, Z., Li, H., Sun, L., Zhang, Q., et al. (2013). MicroRNA-449a is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and inhibits migration and invasion by targeting c-Met. PLoS ONE, 8, e64759.
Celli, B. R. (2012). Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung cancer: common pathogenesis, shared clinical challenges. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society, 9, 74–79.
Jiang, J., Gusev, Y., Aderca, I., Mettler, T. A., Nagorney, D. M., Brackett, D. J., et al. (2008). Association of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clinical Cancer Research, 14, 419–427.
Yamada, N., Noguchi, S., Mori, T., Naoe, T., Maruo, K., & Akao, Y. (2013). Tumor-suppressive microRNA-145 targets catenin delta-1 to regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Letters, 335, 332–342.
Braconi, C., Kogure, T., Valeri, N., Huang, N., Nuovo, G., Costinean, S., et al. (2011). microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene, 30, 4750–4756.
Iliopoulos, D. (2014). MicroRNA circuits regulate the cancer-inflammation link. Science Signaling, 7, pe8.
Noonan, E. J., Place, R. F., Basak, S., Pookot, D., & Li, L. C. (2010). miR-449a causes Rb-dependent cell cycle arrest and senescence in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget, 1, 349–358.
Bou Kheir, T., Futoma-Kazmierczak, E., Jacobsen, A., Krogh, A., Bardram, L., Hother, C., et al. (2011). miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and is down-regulated in gastric cancer. Molecular Cancer, 10, 29.
Wei, B., Song, Y., Zhang, Y., & Hu, M. (2013). microRNA-449a functions as a tumor-suppressor in gastric adenocarcinoma by targeting Bcl-2. Oncology Letters, 6, 1713–1718.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ming Ding and Tie-feng Qiu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, M., Qiu, Tf. & Zhou, Pg. microRNA-449a Suppresses Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys 71, 1255–1259 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0339-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0339-0