Abstract
Background
Total knee arthroplasty with the use of a tourniquet during the entire operation has not been shown to improve the performance of the operation and may increase the risk of complications.
Questions/purposes
We asked whether the limited use of a tourniquet for cementation only would affect (1) surgical time; (2) postoperative pain and motion of the knee; (3) blood loss; or (4) complications such as risk of nerve injuries, quadriceps dysfunction, and drainage compared with use of a tourniquet throughout the procedure.
Methods
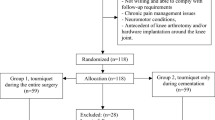
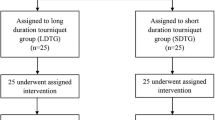
Seventy-one patients (79 knees) were randomized to either use of a tourniquet from the incision through cementation of the implants and deflated for closure (operative tourniquet group) or tourniquet use only during cementation (cementation tourniquet group). The initial study population was a minimum of 30 knees in each group as suggested for randomized studies by American Society for Testing and Materials standards; termination of the study was determined by power analysis performed after 40 knees in each group showed any statistical solution to our questions would require a minimum of 260 more cases. Patients were excluded who were considered in previous randomized studies as high risk for complications, which might be attributed to the tourniquet.
Results
There were no differences in terms of surgical time, pain scores, pain medicine requirements, range of motion, hemoglobin change, or total blood loss. One major complication (compartmental syndrome) occurred in a patient with tourniquet inflation until closure. No other complications were attributed to the use of a tourniquet.
Conclusions
With the numbers available, our results suggest that there are no important clinical differences between patients who had a tourniquet inflated throughout the procedure compared with those who had it inflated only during cementation. Tourniquet inflation for cementation only provides the benefit of bloodless bone for fixation and may eliminate the risks associated with prolonged tourniquet use.
Level of Evidence
Level I, therapeutic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Salam A, Eyres KS. Effects of tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty. A prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77:250–253.
Aglietti P, Baldini A, Vena LM, Abbate R, Fedi S, Falciani M. Effect of tourniquet use on activation of coagulation in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;371:169–177.
Alcelik I, Pollock RD, Sukeik M, Bettany-Saltikov J, Armstrong PM, Fismer P. A comparison of outcomes with and without a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27:331–340.
Dorr LD, Gendelman V, Maheshwari AV, Boutary M, Wan Z, Long WT. Multimodal thromboprophylaxis for total hip and knee arthroplasty based on risk assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:2648–2657.
Dorr LD, Raya J, Long WT, Boutary M, Sirianni LE. Multimodal analgesia without parenteral narcotics for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:502–508.
Fisher DA, Trimble SM, Breedlove K. The medial trivector approach in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 1998;21:53–56.
Gielen M. Cardiac arrest after tourniquet release. Can J Anaesth. 1991;38:541.
Horlocker TT, Hebl JR, Gali B, Jankowski CJ, Burkle CM, Berry DJ, Zepeda FA, Stevens SR, Schroeder DR. Anesthetic, patient, and surgical risk factors for neurologic complications after prolonged total tourniquet time during total knee arthroplasty. Anesth Analg. 2006;102:950–955.
Insall JN. Surgery of the Knee. New York, NY, USA: Churchill Livingstone; 1993.
Kageyama K, Nakajima Y, Shibasaki M, Hashimoto S, Mizobe T. Increased platelet, leukocyte, and endothelial cell activity are associated with increased coagulability in patients after total knee arthroplasty. J Thromb Hemost. 2007;5:738–745.
Kang HJ, Han CD, Jahng JS, Ko SO. Blood gas and electrolyte changes after tourniquet application in total knee replacement surgery. Yonsei Med J. 1992;33:153–158.
Kato N, Nakanishi K, Yoshino S, Ogawa R. Abnormal echogenic findings detected by transesophageal echocardiography and cardiorespiratory impairment during total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet. Anesthesiology. 2002;97:1123–1128.
Kumar SN, Chapman JA, Rawlins I. Vascular injuries in total knee arthroplasty. A review of the problem with special reference to the possible effects of the tourniquet. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13:211–216.
Li B, Qian QR, Wu HS, Zhao H, Lin XB, Zhu J, Weng WF. [The use of a pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized study] [in Chinese]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008;46:1054–1057.
Matziolis G, Drahn T, Schroder JH, Krocker D, Tuischer J, Perka C. Endothelin-1 is secreted after total knee arthroplasty regardless of the use of a tourniquet. J Orthop Res. 2005;23:392–396.
Medical Research Council. Aids to the Examination of the Peripheral Nervous System, Memorandum No. 45. London, UK: Her Majesty’s Stationery Office; 1981.
Nercessian OA, Ugwonali OF, Park S. Peroneal nerve palsy after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20:1068–1073.
O’Leary AM, Veall G, Butler P, Anderson GH. Acute pulmonary oedema after tourniquet release. Can J Anaesth. 1990;37:826–827.
Ochoa J, Fowler TJ, Gilliatt RW. Anatomical changes in peripheral nerves compressed by a pneumatic tourniquet. J Anat. 1972;113:433–455.
Rush JH, Vidovich JD, Johnson MA. Arterial complications of total knee replacement. The Australian experience. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69:400–402.
Saunders KC, Louis DL, Weingarden SI, Waylonis GW. Effect of tourniquet time on postoperative quadriceps function. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;143:194–199.
Sharma S, Iorio R, Specht LM, Davies-Lepie S, Healy WL. Complications of femoral nerve block for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:135–140.
Tai TW, Chang CW, Lai KA, Lin CJ, Yang CY. Effects of tourniquet use on blood loss and soft-tissue damage in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:2209–2215.
Tai TW, Lin CJ, Jou IM, Chang CW, Lai KA, Yang CY. Tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthroscopy. 2011;19:1121–1130.
Tetro AM, Rudan JF. The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg. 2001;44:33–38.
Vandenbussche E, Duranthon LD, Couturier M, Pidhorz L, Augereau B. The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2002;26:306–309.
Wakai A, Winter DC, Street JT, Redmond PH. Pneumatic tourniquets in extremity surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001;9:345–351.
Wakankar HM, Nicholl JE, Koka R, D’Arcy JC. The tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81:30–33.
Yang ZG, Chen WP, Wu LD. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94:1153–1159.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jennifer Okuno PT, and Don Shimabukuro PT, who provided the physical therapy on all of these patients.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funding was provided by Good Samaritan Hospital, Los Angeles, CA, USA (LDD, ZW, WTL).
All ICMJE Conflict of Interest Forms for authors and Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research editors and board members are on file with the publication and can be viewed on request.
Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research neither advocates nor endorses the use of any treatment, drug, or device. Readers are encouraged to always seek additional information, including FDA-approval status, of any drug or device prior to clinical use.
Each author certifies that his or her institution approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained.
About this article
Cite this article
Tarwala, R., Dorr, L.D., Gilbert, P.K. et al. Tourniquet Use During Cementation Only During Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472, 169–174 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3124-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3124-2