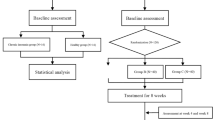Abstract
Objective
To observe the effects of comprehensive therapy (CT) with electroacupuncture (EA) in combination with psycho-intervention (PI) on the cognitive function and event-related potentials (ERP), P300 and mismatch negativity (MMN), in patients with internet addiction (IA) for a preliminary exploration of the possible mechanism of the therapy.
Methods
One hundred and twenty patients with IA were randomly divided into three groups, and a total of 112 subjects reached the final analysis of the trial, the EA group (39 patients), the PI group (36 patients) and the CT group (37 patients). EA was applied at acupoints Baihui (GV20), Sishencong (EX-HN1), Hegu (LI4), Neiguan (PC6), Taichong (LR3) and Sanyinjiao (SP6), once every other day; PI with the cognitionbehavior mode was implemented every 4 days; both EA and PI were used in the CT group. The treatment course for all patients was 40 days. Changes before and after treatment in terms of scoring by the IA self-rating scale, short-term memory capacity, short-term memory span, and the latency and amplitude of P300 and MMN in patients were observed.
Results
After treatment, in all groups, the IA score was lowered significantly (P <0.05) and scores of short-term memory capacity and short-term memory span increased significantly (P <0.05), while the decreased IA score in the CT group was more significant than that in the other two groups (P <0.05). ERP measurements showed that P300 latency was depressed and its amplitude raised in the EA group; MMN amplitude increased in the CT group (all P<0.05).
Conclusion
The EA in combination with PI could improve the cognitive function of IA patients, and its mechanism might be related to the speedup of cerebral discrimination on external stimulus and the enhancement of effective resource mobilization during information processing of the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young KS. Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder. Cyberpsychol Behav 1998;1:237–244.
Shi JG, ed. Addictive medicine. Beijing: Science Press; 2002:197–205.
Luo QH, Meng QH, Fu YX, Du L, Du XD, Yang H, et al. A case-control study of cognitive function of internet addicts. Chin Ment Health J (Chin) 2007;21:237–239.
Jiang NN, Guo PF. Foreign research on internet addiction disorder. Psychol Sci (Chin) 2003;26:178.
Zhu YH ed. Recovery Evaluation And Assessment. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Press 2008: 192.
Laura W, Mary M. The psychometric properties of the internet addiction test. Cyber Psychol Behavior 2004;7:443–450.
Su H, Jiang KD, Lou FY, Chen XS, Liang JH. Changes of P300 and mismatch negativity in the treatment of first episode depression. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Med Sci, Chin) 2006;26:356–358.
Lin XH, Yan GG. Internet addiction disorder, online behavior and personality. Chin Ment Health J (Chin) 2004;20:111–113.
The report of China youth internet addition disorder. China Youth Internet Association 2009. Available from: URL: http://www.zqwx.youth.cn/web/zuizhong.jsp?id=907
Cui LH, Shi JX, Zhou XD, Luo KY. The explaination of schizophrenia with collateral disease theory and the method of choosing acupuncture point. Chin J Inf Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2008;15(12):9–10.
Zhu TM, Jin RJ, Zhong XM, Chen J, Li H. Clinical effect of electroacupuncture combined with psychologic interference on patient with internet addiction disorder. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2009;29:212–214.
Ungerleider LG, Couney SM, Haxby JV. A neural system for human visual working memo. Proc Natl Acad Sc USA 1998;95:883–890.
Zhang MD, Chen XS, eds. Brain evoked potentials. 2nd ed. Shanghai: Shanghai Science Technology and Education Press; 1997: 225–244.
Rugg MD, Coles MGH. Electrophysiology of mind: eventrelated brain potentials and cognition. New York: Oxford University Press; 1996:74–89.
Naatanen R, Paavilainen P, Titinen H, Jiang D, Alho K. Attention and mismatch negativity. Psychophysiology 1993;30:436–450.
Kathmann N, Wagner M, Rendtorff N, Engel R. Delayed peak latency of the mismatch negativity in schizophrenics and alcoholics. Biol Psychiatry 1995;37:754–757.
Shen YC, ed. Chinese encyclopaedic series of modern sciences, medicince, psychiatry. Changchun: Changchun Press; 2000:78–91.
Liu MS, ed. Neurology. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press; 2000:237–243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81072852); Fund of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Special Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. 06-07LQ04); and Scientific Research Fund of Sichuan Provincial Education Department (No. 11ZA059)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Tm., Li, H., Jin, Rj. et al. Effects of electroacupuncture combined psycho-intervention on cognitive function and event-related potentials P300 and mismatch negativity in patients with internet addiction. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 146–151 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-0990-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-0990-5