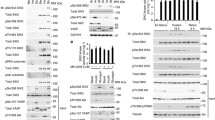
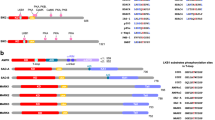
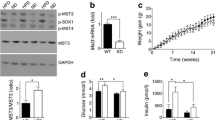
Abstract
In fasting mammals, the liver is the primary source of glucose production for maintenance of normoglycemia. In this setting, circulating peptide hormones and catecholamines cause hepatic glucose output by stimulating glycogen breakdown as well as de novo glucose production through gluconeogenesis. Fasting gluconeogenesis is regulated by a complex transcriptional cascade culminating in elevated expression of hepatic enzymes that promote gluconeogenesis and glucose export to the blood. The cAMP response element binding protein CREB and its co-activator CRTC2 play crucial roles in signal-dependent transcriptional regulation of gluconeogenesis. Recent work has identified a family of serine/threonine kinases, the salt inducible kinases (SIKs), which are subject to hormonal control and constrain gluconeogenic and lipogenic gene expression in liver. As normal regulation of gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis is disrupted in diabetic states, SIK kinases are poised to serve as therapeutic targets to modulate metabolic disturbances in diabetic patients. The purpose of this review is to 1) describe the identification of CRTCs CREB co-activators and their regulation by SIKs, 2) discuss recent progress toward understanding regulation and function of SIKs in metabolism and 3) examine the potential clinical impact of therapeutics that target SIK kinase function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altarejos J Y, Goebel N, Conkright M D, Inoue H, Xie J, Arias C M, Sawchenko P E, Montminy M (2008). The Creb1 coactivator Crtc1 is required for energy balance and fertility. Nat Med, 14(10): 1112–1117
Altarejos J Y, Montminy M (2011). CREB and the CRTC co-activators: sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 12(3): 141–151
Argaud D, Zhang Q, Pan W, Maitra S, Pilkis S J, Lange A J (1996). Regulation of rat liver glucose-6-phosphatase gene expression in different nutritional and hormonal states: gene structure and 5′-flanking sequence. Diabetes, 45(11): 1563–1571
Berdeaux R, Goebel N, Banaszynski L, Takemori H, Wandless T, Shelton G D, Montminy M (2007). SIK1 is a class II HDAC kinase that promotes survival of skeletal myocytes. Nat Med, 13(5): 597–603
Bonni A, Ginty D D, Dudek H, Greenberg M E (1995). Serine 133-phosphorylated CREB induces transcription via a cooperative mechanism that may confer specificity to neurotrophin signals. Mol Cell Neurosci, 6(2): 168–183
Bricambert J, Miranda J, Benhamed F, Girard J, Postic C, Dentin R (2010). Salt-inducible kinase 2 links transcriptional coactivator p300 phosphorylation to the prevention of ChREBP-dependent hepatic steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest, 120(12): 4316–4331
Bright N J, Thornton C, Carling D (2009). The regulation and function of mammalian AMPK-related kinases. Acta Physiol (Oxf), 196(1): 15–26
Brindle P, Nakajima T, Montminy M (1995). Multiple protein kinase Aregulated events are required for transcriptional induction by cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 92(23): 10521–10525
Cheng H, Liu P, Wang Z C, Zou L, Santiago S, Garbitt V, Gjoerup O V, Iglehart J D, Miron A, Richardson A L, Hahn W C, Zhao J J (2009). SIK1 couples LKB1 to p53-dependent anoikis and suppresses metastasis. Sci Signal, 2(80): ra35
Cheng J, Uchida M, Zhang W, Grafe MR, Herson P S, Hurn P D (2011). Role of salt-induced kinase 1 in androgen neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 31(1): 339–350
Choi S, Kim W, Chung J (2011). Drosophila salt-inducible kinase (SIK) regulates starvation resistance through cAMP-response elementbinding protein (CREB)-regulated transcription coactivator (CRTC). J Biol Chem, 286(4): 2658–2664
Conkright M D, Canettieri G, Screaton R, Guzman E, Miraglia L, Hogenesch J B, Montminy M (2003). TORCs: transducers of regulated CREB activity. Mol Cell, 12(2): 413–423
Dentin R, Hedrick S, Xie J, Yates J 3rd, Montminy M (2008). Hepatic glucose sensing via the CREB coactivator CRTC2. Science, 319(5868): 1402–1405
Dentin R, Liu Y, Koo S H, Hedrick S, Vargas T, Heredia J, Yates J 3rd, Montminy M (2007). Insulin modulates gluconeogenesis by inhibition of the coactivator TORC2. Nature, 449(7160): 366–369
Dentin R, Pégorier J P, Benhamed F, Foufelle F, Ferré P, Fauveau V, Magnuson M A, Girard J, Postic C (2004). Hepatic glucokinase is required for the synergistic action of ChREBP and SREBP-1c on glycolytic and lipogenic gene expression. J Biol Chem, 279(19): 20314–20326
Doi J, Takemori H, Lin X Z, Horike N, Katoh Y, Okamoto M (2002). Salt-inducible kinase represses cAMP-dependent protein kinasemediated activation of human cholesterol side chain cleavage cytochrome P450 promoter through the CREB basic leucine zipper domain. J Biol Chem, 277(18): 15629–15637
Du J, Chen Q, Takemori H, Xu H (2008). SIK2 can be activated by deprivation of nutrition and it inhibits expression of lipogenic genes in adipocytes. Obesity (Silver Spring), 16(3): 531–538
Erion D M, Ignatova I D, Yonemitsu S, Nagai Y, Chatterjee P, Weismann D, Hsiao J J, Zhang D, Iwasaki T, Stark R, Flannery C, Kahn M, Carmean C M, Yu X X, Murray S F, Bhanot S, Monia B P, Cline G W, Samuel V T, Shulman G I (2009). Prevention of hepatic steatosis and hepatic insulin resistance by knockdown of cAMP response element-binding protein. Cell Metab, 10(6): 499–506
Feldman J D, Vician L, Crispino M, Hoe W, Baudry M, Herschman H R (2000). The salt-inducible kinase, SIK, is induced by depolarization in brain. J Neurochem, 74(6): 2227–2238
Fisch T M, Prywes R, Roeder R G (1987). c-fos sequence necessary for basal expression and induction by epidermal growth factor, 12-Otetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and the calcium ionophore. Mol Cell Biol, 7(10): 3490–3502
Hardie D G (2004). The AMP-activated protein kinase pathway—new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci, 117(Pt 23): 5479–5487
Hawley S A, Pan D A, Mustard K J, Ross L, Bain J, Edelman A M, Frenguelli B G, Hardie D G (2005). Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-beta is an alternative upstream kinase for AMPactivated protein kinase. Cell Metab, 2(1): 9–19
Hawley S A, Selbert M A, Goldstein E G, Edelman A M, Carling D, Hardie D G (1995). 5′-AMP activates the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade, and Ca2+/calmodulin activates the calmodulindependent protein kinase I cascade, via three independent echanisms. J Biol Chem, 270(45): 27186–27191
He L, Sabet A, Djedjos S, Miller R, Sun X, Hussain M A, Radovick S, Wondisford F E (2009). Metformin and insulin suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis through phosphorylation of CREB binding protein. Cell, 137(4): 635–646
Herzig S, Long F, Jhala U S, Hedrick S, Quinn R, Bauer A, Rudolph D, Schutz G, Yoon C, Puigserver P, Spiegelman B, Montminy M (2001). CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis through the coactivator PGC-1. Nature, 413(6852): 179–183
Horike N, Kumagai A, Shimono Y, Onishi T, Itoh Y, Sasaki T, Kitagawa K, Hatano O, Takagi H, Susumu T, Teraoka H, Kusano K, Nagaoka Y, Kawahara H, Takemori H (2010). Downregulation of SIK2 expression promotes the melanogenic program in mice. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res, 23(6): 809–819
Horike N, Takemori H, Katoh Y, Doi J, Min L, Asano T, Sun X J, Yamamoto H, Kasayama S, Muraoka M, Nonaka Y, Okamoto M (2003). Adipose-specific expression, phosphorylation of Ser794 in insulin receptor substrate-1, and activation in diabetic animals of saltinducible kinase-2. J Biol Chem, 278(20): 18440–18447
Iourgenko V, Zhang W, Mickanin C, Daly I, Jiang C, Hexham J M, Orth A P, Miraglia L, Meltzer J, Garza D, Chirn G W, McWhinnie E, Cohen D, Skelton J, Terry R, Yu Y, Bodian D, Buxton F P, Zhu J, Song C, Labow M A (2003). Identification of a family of cAMP response element-binding protein coactivators by genome-scale functional analysis in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 100(21): 12147–12152
Jakobsen S N, Hardie D G, Morrice N, Tornqvist H E (2001). 5′-AMPactivated protein kinase phosphorylates IRS-1 on Ser-789 in mouse C2C12 myotubes in response to 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside. J Biol Chem, 276(50): 46912–46916
Jaleel M, Villa F, Deak M, Toth R, Prescott A R, Van Aalten DM, Alessi D R (2006). The ubiquitin-associated domain of AMPK-related kinases regulates conformation and LKB1-mediated phosphorylation and activation. Biochem J, 394(Pt 3): 545–555
Kajimura S, Seale P, Spiegelman B M (2010). Transcriptional control of brown fat development. Cell Metab, 11(4): 257–262
Katoh Y, Takemori H, Doi J, Okamoto M (2002). Identification of the nuclear localization domain of salt-inducible kinase. Endocr Res, 28(4): 315–318
Katoh Y, Takemori H, Horike N, Doi J, Muraoka M, Min L, Okamoto M (2004a). Salt-inducible kinase (SIK) isoforms: their involvement in steroidogenesis and adipogenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 217(1–2): 109–112
Katoh Y, Takemori H, Lin X Z, Tamura M, Muraoka M, Satoh T, Tsuchiya Y, Min L, Doi J, Miyauchi A, Witters L A, Nakamura H, Okamoto M (2006). Silencing the constitutive active transcription factor CREB by the LKB1-SIK signaling cascade. FEBS J, 273(12): 2730–2748
Katoh Y, Takemori H, Min L, Muraoka M, Doi J, Horike N, Okamoto M (2004b). Salt-inducible kinase-1 represses cAMP response elementbinding protein activity both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm. Eur J Biochem, 271(21): 4307–4319
Koo S H, Flechner L, Qi L, Zhang X, Screaton R A, Jeffries S, Hedrick S, Xu W, Boussouar F, Brindle P, Takemori H, Montminy M (2005). The CREB coactivator TORC2 is a key regulator of fasting glucose metabolism. Nature, 437(7062): 1109–1111
Kozhemyakina E, Cohen T, Yao T P, Lassar A B (2009). Parathyroid hormone-related peptide represses chondrocyte hypertrophy through a protein phosphatase 2A/histone deacetylase 4/MEF2 pathway. Mol Cell Biol, 29(21): 5751–5762
Lanjuin A, Sengupta P (2002). Regulation of chemosensory receptor expression and sensory signaling by the KIN-29 Ser/Thr kinase. Neuron, 33(3): 369–381
Le Lay J, Tuteja G, White P, Dhir R, Ahima R, Kaestner K H (2009). CRTC2 (TORC2) contributes to the transcriptional response to fasting in the liver but is not required for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis. Cell Metab, 10(1): 55–62
Lerner R G, Depatie C, Rutter G A, Screaton R A, Balthasar N (2009). A role for the CREB co-activator CRTC2 in the hypothalamic mechanisms linking glucose sensing with gene regulation. EMBO Rep, 10(10): 1175–1181
Lin X, Takemori H, Katoh Y, Doi J, Horike N, Makino A, Nonaka Y, Okamoto M (2001). Salt-inducible kinase is involved in the ACTH/cAMP-dependent protein kinase signaling in Y1 mouse adrenocortical tumor cells. Mol Endocrinol, 15(8): 1264–1276
Liu J S, Park E A, Gurney A L, Roesler WJ, Hanson RW (1991). Cyclic AMP induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene transcription is mediated by multiple promoter elements. J Biol Chem, 266(28): 19095–19102
Lizcano J M, Göransson O, Toth R, Deak M, Morrice N A, Boudeau J, Hawley S A, Udd L, Mäkelä T P, Hardie D G, Alessi D R (2004). LKB1 is a master kinase that activates 13 kinases of the AMPK subfamily, including MARK/PAR-1. EMBO J, 23(4): 833–843
Magnusson I, Rothman D L, Katz L D, Shulman R G, Shulman G I (1992). Increased rate of gluconeogenesis in type II diabetes mellitus. A 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study. J Clin Invest, 90(4): 1323–1327
Mayr B, Montminy M (2001). Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2(8): 599–609
Mayr B M, Canettieri G, Montminy M R (2001). Distinct effects of cAMP and mitogenic signals on CREB-binding protein recruitment impart specificity to target gene activation via CREB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 98(19): 10936–10941
Moller D E (2001). New drug targets for type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Nature, 414(6865): 821–827
Momcilovic M, Hong S P, Carlson M (2006). Mammalian TAK1 activates Snf1 protein kinase in yeast and phosphorylates AMP-activated protein kinase in vitro. J Biol Chem, 281(35): 25336–25343
Muraoka M, Fukushima A, Viengchareun S, Lombès M, Kishi F, Miyauchi A, Kanematsu M, Doi J, Kajimura J, Nakai R, Uebi T, Okamoto M, Takemori H (2009). Involvement of SIK2/TORC2 signaling cascade in the regulation of insulin-induced PGC-1alpha and UCP-1 gene expression in brown adipocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 296(6): E1430–E1439
Okamoto M, Takemori H, Katoh Y (2004). Salt-inducible kinase in steroidogenesis and adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 15(1): 21–26
Raghow R, Yellaturu C, Deng X, Park E A, Elam M B (2008). SREBPs: the crossroads of physiological and pathological lipid homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 19(2): 65–73
Ravnskjaer K, Kester H, Liu Y, Zhang X, Lee D, Yates J R 3rd, Montminy M (2007). Cooperative interactions between CBP and TORC2 confer selectivity to CREB target gene expression. EMBO J, 26(12): 2880–2889
Romito A, Lonardo E, Roma G, Minchiotti G, Ballabio A, Cobellis G (2010). Lack of sik1 in mouse embryonic stem cells impairs cardiomyogenesis by down-regulating the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57kip2. PLoS One, 5(2): e9029
Ruiz J C, Conlon F L, Robertson E J (1994). Identification of novel protein kinases expressed in the myocardium of the developing mouse heart. Mech Dev, 48(3): 153–164
Saberi M, Bjelica D, Schenk S, Imamura T, Bandyopadhyay G, Li P, Vargeese C, Wang W, Bowman K, Zhang Y, Polisky B, Olefsky J M (2009). Novel liver-specific TORC2 siRNA corrects hyperglycemia in rodent models of type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 297(5): e1137–e1146
Sakamoto K, McCarthy A, Smith D, Green K A, Grahame Hardie D, Ashworth A, Alessi D R (2005). Deficiency of LKB1 in skeletal muscle prevents AMPK activation and glucose uptake during contraction. EMBO J, 24(10): 1810–1820
Salway J G (2004). Metabolism at a Glance. 3rd Edition, MA: Blackwell Publishing, Ltd.
Samuel V T, Beddow S A, Iwasaki T, Zhang X M, Chu X, Still C D, Gerhard G S, Shulman G I (2009). Fasting hyperglycemia is not associated with increased expression of PEPCK or G6Pc in patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 106(29): 12121–12126
Sasaki T, Takemori H, Yagita Y, Terasaki Y, Uebi T, Horike N, Takagi H, Susumu T, Teraoka H, Kusano K, Hatano O, Oyama N, Sugiyama Y, Sakoda S, Kitagawa K (2011). SIK2 is a key regulator for neuronal survival after ischemia via TORC1-CREB. Neuron, 69(1): 106–119
Screaton R A, Conkright M D, Katoh Y, Best J L, Canettieri G, Jeffries S, Guzman E, Niessen S, Yates J R 3rd, Takemori H, Okamoto M, Montminy M (2004). The CREB coactivator TORC2 functions as a calcium- and cAMP-sensitive coincidence detector. Cell, 119(1): 61–74
Shaw R J, Kosmatka M, Bardeesy N, Hurley R L, Witters L A, DePinho R A, Cantley L C (2004). The tumor suppressor LKB1 kinase directly activates AMP-activated kinase and regulates apoptosis in response to energy stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 101(10): 3329–3335
Shaw R J, Lamia K A, Vasquez D, Koo S H, Bardeesy N, Depinho R A, Montminy M, Cantley L C (2005). The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin. Science, 310(5754): 1642–1646
Song Y, Altarejos J, Goodarzi MO, Inoue H, Guo X, Berdeaux R, Kim J H, Goode J, Igata M, Paz J C, Hogan MF, Singh P K, Goebel N, Vera L, Miller N, Cui J, Jones M R, Chen Y D, Taylor K D, Hsueh W A, Rotter J I, Montminy M, the CHARGE Consortium, the GIANT Consortium (2010). CRTC3 links catecholamine signalling to energy balance. Nature, 468(7326): 933–939
Takemori H, Katoh Y, Horike N, Doi J, Okamoto M (2002). ACTHinduced nucleocytoplasmic translocation of salt-inducible kinase. Implication in the protein kinase A-activated gene transcription in mouse adrenocortical tumor cells. J Biol Chem, 277(44): 42334–42343
Takemori H, Katoh Hashimoto Y, Nakae J, Olson E N, Okamoto M (2009). Inactivation of HDAC5 by SIK1 in AICAR-treated C2C12 myoblasts. Endocr J, 56(1): 121–130
van der Linden A M, Nolan K M, Sengupta P (2007). KIN-29 SIK regulates chemoreceptor gene expression via an MEF2 transcription factor and a class II HDAC. EMBO J, 26(2): 358–370
Wang B, Goode J, Best J, Meltzer J, Schilman P E, Chen J, Garza D, Thomas J B, Montminy M (2008). The insulin-regulated CREB coactivator TORC promotes stress resistance in Drosophila. Cell Metab, 7(5): 434–444
Wang Y, Inoue H, Ravnskjaer K, Viste K, Miller N, Liu Y, Hedrick S, Vera L, Montminy M (2010). Targeted disruption of the CREB coactivator Crtc2 increases insulin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 107(7): 3087–3092
Wang Z, Takemori H, Halder S K, Nonaka Y, Okamoto M (1999). Cloning of a novel kinase (SIK) of the SNF1/AMPK family from high salt diet-treated rat adrenal. FEBS Lett, 453(1–2): 135–139
Witczak C A, Fujii N, Hirshman M F, Goodyear L J (2007). Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-alpha regulates skeletal muscle glucose uptake independent of AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt activation. Diabetes, 56(5): 1403–1409
Xie M, Zhang D, Dyck J R, Li Y, Zhang H, Morishima M, Mann D L, Taffet G E, Baldini A, Khoury D S, Schneider M D (2006). A pivotal role for endogenous TGF-beta-activated kinase-1 in the LKB1/AMPactivated protein kinase energy-sensor pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 103(46): 17378–17383
Yamashita H, Takenoshita M, Sakurai M, Bruick R K, Henzel W J, Shillinglaw W, Arnot D, Uyeda K (2001). A glucose-responsive transcription factor that regulates carbohydrate metabolism in the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 98(16): 9116–9121
Yoon J C, Puigserver P, Chen G, Donovan J, Wu Z, Rhee J, Adelmant G, Stafford J, Kahn C R, Granner D K, Newgard C B, Spiegelman B M (2001). Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis through the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Nature, 413(6852): 131–138
Yoon Y S, Seo WY, Lee MW, Kim S T, Koo S H (2009). Salt-inducible kinase regulates hepatic lipogenesis by controlling SREBP-1c phosphorylation. J Biol Chem, 284(16): 10446–10452
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berdeaux, R. Metabolic regulation by salt inducible kinases. Front. Biol. 6, 231–241 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-011-1148-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-011-1148-0