Abstract
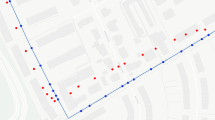
Location based services (LBSs) are gaining importance due to the advancement in mobile networks and positioning technologies. The proliferation of location-based services in recent years has highlighted the need to consider location privacy. This has led to the development of methods enhancing location privacy, and to the investigation of reasons for sharing location information. While computational attacks on location privacy and their prevention have attracted a lot of research, attacks based on humans strategies and tactics have mostly been considered implicitly. Nevertheless, in querying LBSs, a user send its exact locations to their location service providers but in the process, location information of the users are misused either purposefully or otherwise by service providers creating privacy issues for users. It has therefore become important that mechanisms necessary to protect the privacy of users are adopted when querying location based services. It’s on this premise that we introduced a novel query privacy algorithm called the authentication speed dynamic transportation mode cloaking algorithm for continuous query LBSs that considers users’ similarity in speed, direction and travelling with the same transport mode for cloaking for anonymization. Experimental evaluation of the algorithm on a real world map shows that our model ensures total privacy for users, enhanced privacy guarantee, improves quality of service significantly and achieved an excellent performance measure also we compare our method with existing privacy protection methods such as V-DCA, DSDCA, AVD-DCA,D-TC and GCA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mun, M. Y., Kim, D. H., Shilton, K., Estrin, D., Hansen, M. H., & Govindan, R. (2014). PDVLoc: A personal data vault for controlled location data sharing. Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 10(4), 58. doi:10.1145/2523820.
Memon, I., Chen, L., Majid, A., Lv, M., Hussain, I., & Chen, G. (2014). Travel recommendation using geo-tagged photos in social media for tourist. Journal Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-014-2082-7.
Memon, I., Mohammed, M. R., Akhtar, R., Memon, H., Memon, M. H., & Shaikh, R. A. (2014). Design and implementation to authentication over a GSM system using certificate-less public key cryptography (CL-PKC). Wireless Personal Communications, 79(1), 661–686.
Wernke, M., Skvortsov, P., Dürr, F., & Rothermel, K. (2014). A classification of location privacy attacks and approaches. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 18(1), 163–175.
Sun, M., & Tan, G. (2014). NativeGuard: Protecting android applications from third-party native libraries. In WiSec ’14: Proceedings of the 2014 ACM conference on security and privacy in wireless & mobile networks.
Akhtar, R., Leng, S., Memon, I., Ali, M., & Zhang, L. Architecture of hybrid mobile social networks for efficient content delivery. Journal Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-014-1996-4
Kamenyi, D. M., Wang, Y., Zhang, F., & Memon, I. (2013). Authenticated privacy preserving for continuous query in location based services. Journal of Computational Information Systems, 9(24), 9857–9864.
Chow, C.-Y., Mokbel, M. F., Bao, J., & Liu, X. (2011). Query-aware location anonymization for road networks. GeoInformatica, 15(3), 571–607.
Soria-Comas, J., Domingo-Ferrer, J., Sánchez, D., & Martínez, S. (2014). Enhancing data utility in differential privacy via microaggregation-based \(k\)k-anonymity. The International Journal on Very Large Data Bases, 23(5), 771–794.
Serwadda, A., & Phoha, V. V. (2013). Examining a large keystroke biometrics dataset for statistical-attack openings. Transactions on Information and System Security, 16(2), 1–30.
Pan, X., Meng, X., & Xu, J. (2009). Distortion-based anonymity for continuous queries in location-based mobile services, ACM GIS.
Akhtar, R., Amin, N. U., Memon, I., & Shah, M. (2013). Source: Proceedings of SPIE—The international society for optical engineering (vol. 8768).
Nilizadeh, S., Kapadia, A., & Ahn, Y.-Y. (2014). Community-enhanced de-anonymization of online social networks. In CCS ’14: Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGSAC conference on computer and communications security.
Stenneth, L., Wolfson, O., Xu, B., & Yu, P. S. (2012). PhonePark: Street parking using mobile phones. In Proceedings—2012 IEEE 13th international conference on mobile data management (MDM 2012) (pp. 278–279).
Xiong, J., Xiong, J., & Claramunt, C. (2014). A spatial entropy-based approach to improve mobile risk-based authentication. In GeoPrivacy ’14: Proceedings of the 1st ACM SIGSPATIAL international workshop on privacy in geographic information collection and analysis.
Ahmadinejad, S. H., & Fong, P. W. L. (2013). On the feasibility of inference attacks by third-party extensions to social network systems. In ASIA CCS ’13: Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGSAC symposium on information, computer and communications security.
Pan, X., Meng, X., & Xu, J. (2011). Protecting location privacy against location-dependent attack in mobile services. Knowledge and Data Engineering, 24(8), 1506–1519. doi:10.1109/TKDE.2011.105.
Wang, Y., He, l.-p., Peng, J., Zhang, T., & Li, H. (2012). Privacy preserving for continuous query in location based services. In Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), IEEE.
Gustav, Y. H., Wang, Y., Kamenyi, D. M., Zhang, F., & Memon, I. (2013). Velocity similarity anonymization for continuous query location based services. In 2013 International conference on computational problem-solving (ICCP) (pp. 433–436). doi:10.1109/ICCPS.2013.6893578
Stenneth, L., & Yu, P. S. (2010). Global privacy and transportation mode homogeneity anonymization in location based mobile systems with continuous queries. In CollaborateCom.
Gruteser, M., & Grunwald, D. (2003). Anonymous usage of location-based services through spatial and temporal cloaking. In MobiSys’03. New York, NY, USA: ACM.
Gedik, B., & Liu, L. (2008). Protecting location privacy with personalized k-anonymity: Architecture and algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing – TMC, 7(1), 1–18. doi:10.1109/TMC.2007.1062.
Xu, T., & Cai, Y. (2008). Exploring historical location data for anonymity preservation in location-based services. In INFOCOM.
Wang, Y., Zhou, L., & Wang, R. (2011). A novel frequency sense solution for cognitive radio based on tracing localization. In 2011 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC). doi:10.1109/icc.2011.5962510
Sun, Y., Yin, L., Liu, L., & Xin, S. (2014). Toward inference attacks for k-anonymity. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 18(8).
Cheng, R., Zhang, Y., Bertino, E., & Prabhakar, S. (2006). Preserving user location privacy in mobile data management infrastructures. In Proceedings of the privacy enhancing technology workshop (PET ’06).
Du, J., Xu, J., Tang, X., & Hu, H. (2007). iPDA: Enabling privacy-preserving location-based services. In Proceedings of the conference on mobile data management (MDM).
Xu, J., Tang, X., Hu, H., & Du, J. (2010). Privacy-conscious location-based queries in mobile environments. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 21(3), 313–326.
Domenic, M. K., Wang, Y., Zhang, F., Memon, I., & Gustav, Y. H. (2013). Preserving users’ privacy for continuous query services in road networks. In Proceedings of 2013 6th international conference on information management, innovation management and industrial engineering, ICIII 2013 (vol. 1, pp. 352–355).
Brinkhoff, T. (2008). Network-based generator of moving objects. http://www.fhoow.de/institute/iapg/personen/brinkhoff/generator/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Memon, I. Authentication User’s Privacy: An Integrating Location Privacy Protection Algorithm for Secure Moving Objects in Location Based Services. Wireless Pers Commun 82, 1585–1600 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2300-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2300-y