Abstract
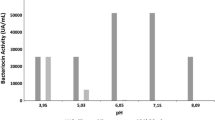
Lactococcus lactis CRL 1584 isolated from a Lithobates catesbeianus hatchery inhibits the growth of Citrobacter freundii (a bullfrog pathogen) and Listeria monocytogenes by a synergistic effect between lactic acid, hydrogen peroxide and a bacteriocin-like molecule. The chemical characterization of the bacteriocin in cell-free supernatants indicates that it has a proteinaceous nature. Hexadecane and ethyl acetate did not modify the bacteriocin activity, while 10 and 20 % (v/v) chloroform decreased the activity by 29 and 43 %, respectively. The antimicrobial peptide was heat stable since 85 % of residual activity was detected when neutralized supernatants were heated at 80 °C for 30 min. Moreover, no bacteriocin inactivation was observed when supernatants were kept at −20 °C for 3 months. The synthesis of the bacteriocin was associated with bacterial growth, highest production (2,100 AU/ml) being detected at the end of the exponential growth phase. At pH ranges of 5–6.5 and 5.0–5.5 the inhibitory molecule was stable when stored for 2 days at 4 and 25 °C, respectively. Moreover, it had a bactericidal effect on L. monocytogenes and the ultrastructural studies of pathogenic cells revealed clumping of the cytoplasmic material, increased periplasmic space and cell wall modifications. The deduced amino acid sequence of the bacteriocin was identical to nisin Z and the genetic determinants for its production are harbored in the chromosome. These results, described for the first time in L. lactis from a bullfrog hatchery, will increase knowledge of the bacteriocin under study with a view to its potential inclusion in probiotics for raniculture or biopreservatives.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammor MS, Flórez AB, Mayo B (2007) Antibiotic resistance in non-enterococcal lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Food Microbiol 24:559–570
Aymerich T, Holo H, Havarstein LS, Hugas M, Garriga M, Nes IF (1996) Biochemical and genetic characterization of enterocin A from Enterococcus faecium, a new antilisterial bacteriocin in the pediocin family of bacteriocins. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1676–1682
Balcázar JL, de Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Cunnigham D, Vendrell D, Múzquiz JL (2006) The role of probiotics in aquaculture. Vet Microbiol 114:173–186
Balcázar JL, de Blas I, Ruiz Zarzuela I, Vendrell D, Girones O (2007) Enhancement of the immune response and protection induced by probiotic lactic acid bacteria against furunculosis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 51:185–193
Bravo D, Rodríguez E, Medina M (2009) Nisin and lacticin 481 coproduction by Lactococcus lactis strains isolated from raw ewes milk. J Dairy Sci 92(10):4805–4811
Carey C, Cohen N, Rollins-Smith L (1999) Amphibian declines: an immunological perspective. Dev Comp Immunol 23:459–472
Casaus P, Nilsen T, Cintas LM, Nes IF, Hernandez PE, Holo H (1997) Enterocin B, a new bacteriocin from Enterococcus faecium T136 which can act synergistically with enterocin A. Microbiology 143:2287–2294
Cintas LM, Casaus P, Havarstein LS, Hernandez PE, Nes IF (1997) Biochemical and genetic characterization of enterocin P, a novel sec-dependent bacteriocin from Enterococcus faecium P13 with a broad antimicrobial spectrum. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4321–4330
Delves-Broughton J (2005) Nisin as food preservative. Food Aust 57(12):525–527
Densmore CL, Earl Green D (2007) Diseases of amphibians. ILAR J 48(3):235–254
Desriac F, Defer D, Bourgougnon N, Brillet B, Le Chevalier P, Fleury Y (2010) Bacteriocin as weapons in the marine animal-associated bacteria warfare: inventory and potential applications as an aquaculture probiotic. Mar Drugs 8:1153–1177
Espeche MC, Otero MC, Sesma F, Nader-Macias ME (2009) Screening of surface properties and antagonistic substances production by lactic acid bacteria isolated from the mammary gland of healthy and mastitic cows. Vet Microbiol 135:346–357
FAO/WHO (2001) Health and nutritional properties of probiotics in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria. Report of a joint FAO/WHO expert consultation. www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/fs_management/en/probiotics.pdf.www.fao.org
Flynn S, van Sinderen D, Thornton GM, Holo H, Nes IF, Collins JK (2002) Characterization of the genetic locus responsible for the production of ABP-118, a novel bacteriocin produced by the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus salivarius subsp. salivarius UCC118. Microbiology 148:973–984
Gatesoupe FJ (2008) Updating the importance of lactic acid bacteria in fish farming: natural occurrence and probiotic treatments. J Mol Microbiol 14(1–3):107–114
Hagi T, Hoshino T (2009) Screening and characterization of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria from cultured common carp intestine. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73(7):1479–1483
Heng NCK, Wescombe PA, Burton JP, Jack RW, Tagg JR (2007) The diversity of bacteriocins in gram-positive bacteria. In: Riley MA, Chavan MA (eds) Bacteriocins: ecology and evolution. Heidelberg, Berlin, pp 45–92
Heo WS, Kim EY, Kim YR, Hossain MT, Kong IS (2012) Salt effect of nisin Z isolated from marine fish on the growth inhibition of Streptococcus iniae, a pathogen of streptococcosis. Biotechnol Lett 34(2):315–320
Irianto A, Austin B (2002) Probiotics for aquaculture. J Fish Dis 25:633–642
Jiang Y, Xie P, Liang G (2009) Distribution and depuration of the potentially carcinogenic malachite green in tissues of three freshwater farmed Chinese fish with different food habits. Aquaculture 288:1–6
Johansen C, Gill T, Gram L (1996) Changes in cell morphology of Listeria monocytogenes and Shewanella putrefaciens resulting from the action of protamine. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(3):1058–1064
Karnovsky MJ (1965) A formaldehyde glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 27:137–138
Klaenhammer TR (1993) Genetics of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 12:39–85
Kumari A, Akkoç N, Akçelik M (2012) Purification and partial characterization of bacteriocin produced by Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis LL171. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:1647–1655
Martínez Cruz P, Ibáñez AL, Monroy Hermosillo OA, Ramirez Saad HC (2012) Use of probiotics in aquaculture. ISRN Microbiol, Article ID 916845. doi:10.5402/2012/916845
Mills S, McAuliffe OE, Coffey A, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP (2006) Plasmids of lactococci—genetic accessories or genetic necessities? FEMS Microbiol Rev 30(2):243–273
Minahk CJ, Farías ME, Sesma F, Morero RD (2000) Effect of enterocin CRL35 on Listeria monocytogenes cell membrane. FEMS Microbiol Lett 192:79–83
Muñoz-Atienza E, Gómez-Sala B, Araújo C, Campanero C, Del Campo R, Hernández PE, Herranz C, Cintas LM (2013) Antimicrobial activity, antibiotic susceptibility and virulence factors of lactic acid bacteria of aquatic origin intended for use as probiotics in aquaculture. BMC Microbiol 13:15 (open access article)
Muriana P, Klaenhammer T (1991) Cloning, phenotypic expression, and DNA sequence of the gene for lactacin F, an antimicrobial peptide produced by Lactobacillus ssp. J Bacteriol 173:1779–1788
Naghmouchi K, Drider D, Fliss I (2007) Action of divergicin M35, a class IIa bacteriocin, on liposomes and Listeria. J App Microbiol 102:1508–1517
Parada JL, Ricoy Caron C, Bianchi P, Medeiros A, Soccol CR (2007) Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: purification, properties and use as bio preservatives. Braz Arch Biol Biotechnol 50(3):521–542
Pasteris SE, Bühler MI, Nader-Macías ME (2006) Microbiological and histological studies in farmed-bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) displaying red-leg syndrome. Aquaculture 251:11–18
Pasteris SE, González A, Van Schoor A, Bühler MI, Nader-Macías ME, Vandamme P, De Vuyst L (2008) Genotypic identification of lactic acid bacteria from a Rana catesbeiana hatchery. V Argentinean Congress of General Microbiology (SAMIGE). Santa Fe, Argentina, Abstr TEC13, pp 88
Pasteris SE, Roig Babot G, Otero MC, Bühler MI, Nader-Macías ME (2009a) Beneficial properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from a Rana castesbeiana hatchery. Aquac Res 40:1605–1615
Pasteris SE, Vera Pingitore E, Roig Babot G, Otero MC, Bühler MI, Nader-Macías ME (2009b) Characterization of the beneficial properties of lactobacilli isolated from bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) hatchery. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 95:375–385
Pasteris SE, Guidoli MG, Otero MC, Bühler MI, Nader-Macías ME (2011) In vitro inhibition of Citrobacter freundii, a red-leg syndrome associated pathogen in raniculture, by indigenous Lactococcus lactis CRL 1584. Vet Microbiol 151:336–344
Pérez-Sánchez T, Balcázar JL, Merrifield DL, Carnevali O, Gioacchini G, de Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I (2011) Expression of immune-related genes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) induced by probiotic bacteria during Lactococcus garvieae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31(2):196–201
Pospiech A, Neumann B (1995) A versatile quick-prep of genomic DNA from gram-positive bacteria. Trends Genet 11:217–218
Quadri LE, Sailer M, Roy KL, Vederas JC, Stiles ME (1994) Chemical and genetic characterization of bacteriocins produced by Carnobacterium piscicola LV17B. J Biol Chem 269:12204–12211
Raibaud P, Gapin JV, Ducluzeau R, Mocquot G, Oliver G (1963) Le genre Lactobacillus dans le tube digestif du Rat. II Caractères de souches hétérofermentaires isolées de rats “Holo” et “Gnotoxeniques”. Annales de Microbiologie (Annales de L’Institut Pasteur) 124:2223–2235
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Sequeiros C, Vallejo M, Marguet ER, Olivera NL (2010) Inhibitory activity against the fish pathogen Lactococcus garvieae produced by Lactococcus lactis TW34, a lactic acid bacterium isolated from the intestinal tract of a Patagonian fish. Arch Microbiol 192:237–245
Shiri Harzevili AR, Van Duffel H, Dhert Ph, Swings J, Sorgeloos P (1998) Use of a potential probiotic Lactococcus lactis AR21 for the enhancement of growth in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis (Müller). Aquac Res 29:411–417
Sugimura Y, Hagi T, Hoshino T (2011) Correlation between in vitro mucus adhesion and the in vivo colonization ability of lactic acid bacteria: screening of new candidate carp probiotics. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75(3):511–515
Sugita H, Ohta K, Kuruma A, Sagesaka T (2007) An antibacterial effect of Lactococcus lactis isolated from the intestinal tract of Amur catfish, Silurus asotus Linnaeus. Aquac Res 38:1002–1004
Tichaczek PS, Vogel RF, Hammes WP (1993) Cloning and sequencing of curA encoding curvacin A, the bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus curvatus LTH1174. Arch Microbiol 160:279–283
Venable JR, Coggeshall R (1965) A simplified lead-citrate stain for use in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 25:407–408
Verschuere L, Rombaut G, Zorruelos P, Verstraete W (2000) Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64(4):655–671
Yoneyama F, Fukao M, Zendo T, Nakayama J, Sonomoto K (2008) Biosynthetic characterization and biochemical features of the third natural nisin variant, nisin Q, produced by Lactococcus lactis 61-14. J Appl Microbiol 105(6):1982–1990
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grants from Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (PIP 632), Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (PICT 543) and Consejo de Investigaciones de la Universidad Nacional de Tucumán (26 D/414).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasteris, S.E., Vera Pingitore, E., Ale, C.E. et al. Characterization of a bacteriocin produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis CRL 1584 isolated from a Lithobates catesbeianus hatchery. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30, 1053–1062 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1524-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1524-9