Abstract
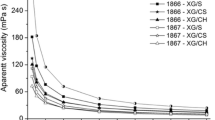
Xanthan gum is a polysaccharide that is widely used as stabilizer and thickener with many industrial applications in food industry. Our aim was to estimate the ability of Xanthomonas campestris ATCC 13951 for the production of xanthan gum by using whey as a growth medium, a by-product of dairy industry. X. campestris ATCC 13951 has been studied in batch cultures using a complex medium for the determination of the optimal concentration of glucose, galactose and lactose. In addition, whey was used under various treatment procedures (de-proteinated, partially hydrolyzed by β-lactamase and partially hydrolyzed and de-proteinated) as culture medium, to study the production of xanthan in a 2 l bioreactor with constant stirring and aeration. A production of 28 g/l was obtained when partially hydrolysed β-lactamase was used, which proved to be one of the highest xanthan gum production reported so far. At the same time, an effort has been made for the control and selection of the most appropriate procedure for the preservation of the strain and its use as inoculant in batch cultures, without loss of its viability and its capability of xanthan gum production. The pre-treatment of whey (whey permeate medium hydrolyzed, WPH) was very important for the production of xanthan by the strain X. campestris ATCC 13951 during batch culture conditions in a 2 l bioreactor. Preservation methods such as lyophilization, cryopreservation at various glycerol solution and temperatures have been examined. The results indicated that the best preservation method for the producing strain X. campestris ATCC 13951 was the lyophilization. Taking into account that whey permeate is a low cost by-product of the dairy industry, the production of xanthan achieved under the studied conditions was considered very promising for industrial application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amanullah A, Tuttiett B, Nienow AW (1998) Agitator speed and dissolved oxygen effects in xanthan fermentations. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:198–210
Chaitali M, Kapadi M, Suraishkumar GK, Gudi RD (2003) Productivity improvement in xanthan gum fermentation using multiple substrate optimization. Biotechnol Prog 19:1190–1198
De Vuyst L, Vermeire A (1994) Use of industrial medium components for xanthan gum production by Xanthomonas campestris NRRL B-1459. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:187–191
Demirel B, Yenigun O, Onay TT (2005) Anaerobic treatment of dairy wastewaters: a review. Process Biochem 40:2583–2595
Ekateriniadou LV, Papoutsopoulou SV, Kyriakidis DA (1994) High production of xanthan gum by a strain of Xanthomonas campestris conjugated with Lactococcus lactis. Biotechnol Lett 16:517–522
Faria S, Vieira PA, Resende MM, França FP, Cardoso VL (2009) A comparison between shaker and bioreactor performance based on the kinetic parameters of xanthan gum production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 156:475–488
Garcia-Ochoa F, Santos VE, Casas JA, Gomez E (2000) Xanthan gum: production, recovery, and properties. Biotechnol Adv 18:549–579
Hatzinikolaou DG, Katsifas E, Mamma D, Karagouni AD, Christakopoulos P, Kekos D (2005) Modelling of the simultaneous hydrolysis–ultrafiltration of whey permeate by a thermostable β-galactosidase from Aspergillus niger. Biochem Eng J 24:161–172
Huang Y, Yang ST (1998) Acetate production from whey lactose using co-immobilized cells of homolactic and homoacetic bacteria in a fibrous-bed bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 20:498–507
Koutinas AA, Papapostolou H, Dimitrellou D, Kopsahelis N, Katechaki E, Bekatorou A, Bosnea LA (2009) Whey valorisation: a complete and novel technology development for dairy industry starter culture production. Bioresour Technol 100:3734–3739
Martinez-Salazar JM, Palacios AN, Sanchez R, Caro AD, Soberdn-Chavez G (1993) Genetic stability and xanthan gum production in Xanthomonas campestris pv, campestris NRRL B1459. Mol Microbiol 8:1053–1061
Outinen M, Rantamäki P, Heino A (2010) Effect of milk pretreatment on the whey composition and whey powder functionality. J Food Sci 75:E1–E10
Plank J (2004) Applications of biopolymers and other biotechnological products in building materials. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:1–9
Rodríguez H, Aguilar L, LaO M (1997) Variations in xanthan production by antibiotic-resistant mutants of Xanthomonas campestris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:626–629
Shu CH, Yang ST (1990) Effects of temperature on cell growth and xanthan production in batch cultures of Xanthomonas campestris. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:454–458
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the General Secretariat of Research and Development of Greece for its financial support on this project. They would like to thank also Professor D. A. Kyriakides (Department of Chemistry, Aristotle University of Thessalonica, Greece) for providing the X. campestris strain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savvides, A.L., Katsifas, E.A., Hatzinikolaou, D.G. et al. Xanthan production by Xanthomonas campestris using whey permeate medium. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 2759–2764 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1087-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1087-1