Abstract
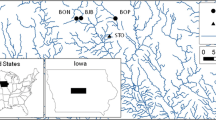
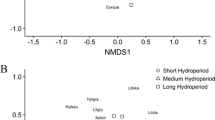
Isolated wetlands in the Southeastern United States are dynamic habitats subject to fluctuating environmental conditions. Wetlands located near marine environments are subject to alterations in water chemistry due to storm surge during hurricanes. The objective of our study was to evaluate the effect of storm surge overwash on wetland amphibian communities. Thirty-two wetlands in northwestern Florida were sampled over a 45-month period to assess amphibian species richness and water chemistry. During this study, seven wetlands were overwashed by storm surge from Hurricane Dennis which made landfall 10 July 2005 in the Florida panhandle. This event allowed us to evaluate the effect of storm surge overwash on water chemistry and amphibian communities of the wetlands. Specific conductance across all wetlands was low pre-storm (<100 μS/cm), but increased post-storm at the overwashed wetlands (\( \bar{x} \) = 7,613 μS/cm). Increased specific conductance was strongly correlated with increases in chloride concentrations. Amphibian species richness showed no correlation with specific conductance. One month post-storm we observed slightly fewer species in overwashed compared with non-overwashed wetlands, but this trend did not continue in 2006. More species were detected across all wetlands pre-storm, but there was no difference between overwashed and non-overwashed wetlands when considering all amphibian species or adult anurans and larval anurans separately. Amphibian species richness did not appear to be correlated with pH or presence of fish although the amphibian community composition differed between wetlands with and without fish. Our results suggest that amphibian communities in wetlands in the southeastern United States adjacent to marine habitats are resistant to the effects of storm surge overwash.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barichivich WJ (2003) Appendix IV: guidelines for building and operating remote field recorders. In: Dodd CK Jr (ed) Monitoring amphibians in Great Smoky Mountains National Park. USGS Circular No. 1258, pp 87–94
Christman SP (1974) Geographic variation for salt water tolerance in the frog Rana sphenocephala. Copeia 1974:773–778
Christy MT, Dickman CR (2002) Effects of salinity on tadpoles of the green and golden bell frog (Litoria aurea). Amphibia-Reptilia 23:1–11
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER v6: user manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Cortwright SA, Nelson CE (1990) An examination of multiple factors affecting community structure in an aquatic amphibian community. Oecologia 83:123–131
Daszak P, Scott DE, Kilpatrick AM, Faggioni C, Gibbons JW, Porter D (2005) Amphibian population declines at the Savannah River Site are linked to hydroperiod, not chytridiomycosis. Ecology 86:3232–3237
Dodd CK Jr, Barichivich WJ, Johnson SA, Staiger JS (2007) Changes in a Florida panhandle Gulf Coast herpetofaunal community over a 28-year period. Am Midl Nat 158:29–48
Dunson WA (1977) Tolerance to high temperature and salinity by tadpoles of the crab-eating frog, Rana cancrivora. Copeia 1977:375–378
Eason GW, Fauth JE (2001) Ecological correlates of anuran species richness in temporary pools: a field study in South Carolina, USA. Israel J Zool 47:346–365
Fishman MJ, Friedman LC (1989) Methods for determination of inorganic substances in water and fluvial sediments, Book 5, Chap. A1. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques of Water-Resources Investigations, 545 p
Florida Division of Emergency Managmement (2002) LiDAR database. Tallahassee, FL. Available onine: http://www.floridadisaster.org/gis/LiDAR/
Gomez-Mestre I, Tejedo M (2003) Local adaptation of an anuran amphibian to osmotically stressful environments. Evolution 57:1889–1899
Goodsell JA, Kats LB (1999) Effect of introduced mosquitofish on pacific treefrogs and the role of alternative prey. Conserv Biol 13:921–924
Gordon MS, Schmidt-Nielsen K, Kelly HM (1961) Osmotic regulation in the crab-eating frog (Rana cancrivora). J Exp Biol 38:659–678
Gregoire DR, Gunzburger MS (2008) Effects of predatory fish on survival and behavior of larval Gopher Frogs (Rana capito) and Southern Leopard Frogs (Rana sphenocephala). J Herpetol 42:97–103
Gunzburger MS (2007) Evaluation of seven aquatic sampling methods for amphibians and other aquatic fauna. Appl Herpetol 4:47–63
Gunzburger MS, Travis J (2004) Evaluating predation pressure on green treefrog larvae across a habitat gradient. Oecologia 140:422–429
Gunzburger MS, Dodd CK Jr, Barichivich WJ, Staiger JS (2005) Southeast amphibian research and monitoring initiative 2005 annual report. United States Geological Survey, Florida Integrated Science Center, Gainesville FL, USA
Hawley TJ (2006) Alterations in frog assemblages after Hurricane Iris in Belize. Herpetol Rev 37:407–411
Johnson SA, Barichivich WJ (2004) A simple technique for trapping Siren lacertina, Amphiuma means, and other aquatic vertebrates. J Freshwater Ecol 19:263–269
Jones MV, West RJ (2005) Spatial and temporal variability of seagrass fishes in intermittently closed and open coastal lakes in southeastern Australia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64:277–288
Karraker NE (2007) Are embryonic and larval green frogs (Rana clamitans) insensitive to road deicing salt? Herpetol Conserv Biol 2:35–41
Karraker NE, Gibbs JP, Vonesh JR (2008) Impacts of road deicing salt on the demography of vernal pool-breeding amphibians. Ecol Appl 18:724–734
Katz U (1973) Studies on the adaptation of the toad Bufo viridis to high salinities: oxygen consumption, plasma concentration, and water content of the tissues. J Exp Biol 58:785–796
Konno N, Hyodo S, Matsuda K, Uchiyama (2006) Effect of osmotic stress on expression of a putative facilitative urea transporter in the kidney and urinary bladder of the marine toad Bufo marinus. J Exp Biol 209:1207–1216
Loope L, Duever M, Herndon A, Snyder J, Jansen D (1994) Hurricane impacts on uplands and freshwater swamp forest. Bioscience 44:238–246
MacKenzie DI, Royle JA (2005) Designing occupancy studies: general advice and allocating survey effort. J Appl Ecol 42:1105–1114
Milto KD (2008) Amphibians breed in the Baltic Sea. Russ J Herpetol 15:8–10
Morey SL, Baig S, Bourassa MA, Dukhovskoy DS, O’Brien JJ (2006) Remote forcing contribution to storm-induced sea level rise during Hurricane Dennis. Geophys Res Lett 33:L19603
Neill WT (1958) The occurrence of amphibians and reptiles in saltwater areas, and a bibliography. Bull Mar Sci Gulf Carib 8:1–97
Odum WE (1988) Comparative ecology of tidal freshwater and salt marshes. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 19:147–176
Piscart C, Lecerf A, Usseglio-Polatera P, Moreteau J, Beisel J (2005) Biodiversity patterns along a salinity gradient: the case of net spinning caddisflies. Biodivers Conserv 14:2235–3349
Roman CT, Aumen NG, Trexler JC, Fennema RJ, Loftus WF, Soukup MA (1994) Hurricane Andrew’s impact on freshwater resources. Bioscience 44:247–255
Ruibal R (1959) The ecology of a brackish water population of Rana pipiens. Copeia 1959:315–322
Sanzo D, Hecnar SJ (2006) Effects of road de-icing salt (NaCl) on larval wood frogs. Environ Pollut 140:247–256
Schriever TA, Ramspott J, Crother BI, Fontenot CL Jr (2009) Effects of Hurricanes Ivan, Katrina, and Rita on a southern Lousisiana herpetofauna. Wetlands 29:112–122
Semlitsch RD, Bodie JR (1998) Are small, isolated wetlands expendable? Conserv Biol 12:1129–1133
Smith LL, Barichivich WJ, Staiger JS, Smith KG, Dodd CK Jr (2006) Detection probabilities and site occupancy estimates for amphibians at Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge. Am Midl Nat 155:149–161
Snodgrass JW, Komoroski MJ, Bryan AL Jr, Burger J (2000) Relationships among isolated wetland size, hydroperiod, and amphibian species richness: implications for wetland regulations. Conserv Biol 14:414–419
SYSTAT Software, Inc (2005) SYSTAT 11 manual. Point Richmond, CA
Taylor EH (1943) A new ambystomid salamander adapted to brackish water. Copeia 1943:151–156
U.S. Geological Survey (1997 to present) National field manual for the collection of water-quality data, Book 9, Chaps. A1–A9. U.S. Geological Survey Techniques of Water-Resource Investigations. http://pubs.water.usgs.gov/twri9A
Vilella FJ, Fogarty JH (2005) Diversity and abundance of forest frogs (Anura: Leptodactylidae) before and after Hurricane Georges in the Cordillera Central of Puerto Rico. Carib J Sci 41:157–162
Walker LR, Lodge DJ, Brokaw NV, Waide RB (1991) An introduction to hurricanes in the Caribbean. Biotropica 23:313–316
Wellborn GA, Skelly DK, Werner EE (1996) Mechanisms creating community structure across a freshwater habitat gradient. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 27:337–363
Whitney E, Means DB, Rudloe A (2004) Priceless Florida: natural ecosystems and native species. Pineapple Press, Sarasota, p 423
Woolbright LL (1991) The impact of hurricane Hugo on forest frogs in Puerto Rico. Biotropica 23:462–467
Woolbright LL (1996) Disturbance influences longterm population patterns in the Puerto Rican frog, Eleutherodactylus coqui (Anura: Leptodactylidae). Biotropica 28:493–501
Wright P, Anderson P, Weng L, Frick N, Wong WP, Ip YK (2004) The crab-eating frog, Rana cancrivora, up-regulates hepatic carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I activity and tissue osmolyte levels in response to increased salinity. J Exp Zool 301A:559–568
Acknowledgements
We thank James Burnett, Joe Reinman and Michael Keys of SMNWR. For assistance with amphibian field sampling we thank Steve Johnson, Linda Casey, Julia Earl, Denise Gregoire, Clint Smith, Andy Sheldon, Linda Sheldon, David Cook, Kevin Enge, Matthew Aresco, and Pierson Hill. Sue Hartley, Dan Calhoun, Mindi Dalton, Alan Cressler, and Deedee Black assisted with water sampling. C. Kenneth Dodd, Jr., Erin Muths, Steve Lawrence, and Matthew Aresco provided comments on an earlier draft of the manuscript. This research was funded by the USGS Amphibian Research and Monitoring Initiative and a USGS Bureau Venture Capital Grant to MSG and WBH. Research was conducted under SMNWR Special Use Permit 41640-02011 and USGS IACUC Protocol # 2006-04.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunzburger, M.S., Hughes, W.B., Barichivich, W.J. et al. Hurricane storm surge and amphibian communities in coastal wetlands of northwestern Florida. Wetlands Ecol Manage 18, 651–663 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-010-9185-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-010-9185-z