Abstract
Background and aims
Ecological stoichiometry plays important roles in ecosystem dynamics and functioning, but relationships between above- and belowground stoichiometry and stoichiometric effects on the growth of different plant functional groups in forests remain poorly understood.
Methods
In an age sequence of 2-, 4- and 6-year-old Eucalyptus plantations in subtropical China, we examined C, N and P concentrations and their ratios in the soil and leaves. Each plantation was divided into overstory and understory plant functional groups. The relationships between stoichiometric characteristics and forest growth were analyzed.
Results
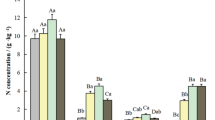
Soil C and P decreased in the Eucalyptus age sequence, which led to changes in soil stoichiometric characteristics. Leaf C:P and N:P ratios were higher for Eucalyptus trees than for understory plants because of the low P concentrations in Eucalyptus leaves. Soil and plant N:P ratios were strongly related. Understory biomass was positively related to N:P ratios, while overstory growth was negatively related to N:P ratios.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that nutrient concentrations in soil and plants are tightly linked in Eucalyptus plantations and that P limitation increases with stand age. Stoichiometric characteristics appear to mediate forest properties and functions under nutrient limitation in subtropical regions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ågren GI (2004) The C : N : P stoichiometry of autotrophs–theory and observations. Ecol Lett 7:185–191
Attiwill P, May B (2001) Does nitrogen limit the growth of native eucalypt forests: some observations for mountain ash (Eucalyptus regnans). Mar Freshw Res 52:111–117
Bao SD (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis, 3rd edn. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Bardgett RD, Wardle DA (2003) Herbivore-mediated linkages between aboveground and belowground communities. Ecology 84:2258–2268
Bardgett RD, Wardle DA (2010) Aboveground-belowground linkages: biotic interactions, ecosystem processes, and global change. Oxford series in ecology and evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Bardgett RD, Bowman WD, Kaufmann R, Schmidt SK (2005) A temporal approach to linking aboveground and belowground ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 20:634–641
Batjes N (2014) Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur J Soil Sci 65:10–21
Binkley D, Giardina C, Bashkin MA (2000) Soil phosphorus pools and supply under the influence of Eucalyptus saligna and nitrogen-fixing Albizia facaltaria. For Ecol Manag 128:241–247
Binkley D, Stape J, Ryan M, Barnard H, Fownes J (2002) Age-related decline in forest ecosystem growth: an individual-tree, stand-structure hypothesis. Ecosystems 5:58–67
Boyden S, Binkley D, Senock R (2005) Competition and facilitation between Eucalyptus and nitrogen-fixing Falcataria in relation to soil fertility. Ecology 86:992–1001
Bui EN, Henderson BL (2013) C : N : P stoichiometry in Australian soils with respect to vegetation and environmental factors. Plant Soil 373:553–568
Chen D, Zhang C, Wu J, Zhou L, Lin Y, Fu S (2011) Subtropical plantations are large carbon sinks: evidence from two monoculture plantations in South China. Agric For Meteorol 151:1214–1225
Dixon R, Brown S, Houghton R, Solomon A, Trexler M, Wisniewski J (1994) Carbon pools and flux of global forest ecosystems. Science 263:185–189
Elser J, Sterner R, Gorokhova E, Fagan W, Markow T, Cotner J, Harrison J, Hobbie S, Odell G, Weider L (2000) Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecol Lett 3:540–550
Elser JJ, Bracken ME, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10:1135–1142
Elser J, Fagan W, Kerkhoff A, Swenson N, Enquist B (2010) Biological stoichiometry of plant production: metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol 186:593–608
Falkowski P, Scholes R, Boyle E, Canadell J, Canfield D, Elser J, Gruber N, Hibbard K, Högberg P, Linder S (2000) The global carbon cycle: a test of our knowledge of earth as a system. Science 290:291–296
FAO (2006) World reference base for soil resources 2006, 2nd edn. World Soil Resources Reports NO.103. FAO, Rome
Fife DN, Nambiar EKS, Saur E (2008) Retranslocation of foliar nutrients in evergreen tree species planted in a Mediterranean environment. Tree Physiol 28:187–196
Güsewell S (2004) N : P ratios in terrestrial plants: variation and functional significance. New Phytol 164:243–266
Han W, Fang J, Guo D, Zhang Y (2005) Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol 168:377–385
Hedin LO (2004) Global organization of terrestrial plant–nutrient interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:10849–10850
Hessen DO, Ågren GI, Anderson TR, Elser JJ, de Ruiter PC (2004) Carbon sequestration in ecosystems: the role of stoichiometry. Ecology 85:1179–1192
Houlton BZ, Wang Y-P, Vitousek PM, Field CB (2008) A unifying framework for dinitrogen fixation in the terrestrial biosphere. Nature 454:327–330
Huang W, Liu J, Wang YP, Zhou G, Han T, Li Y (2013) Increasing phosphorus limitation along three successional forests in southern China. Plant Soil 364:181–191
Janssens I, Dieleman W, Luyssaert S, Subke J A, Reichstein M, Ceulemans R, Ciais P, Dolman A, Grace J, Matteucci G (2010) Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat Geosci 3: 315–322
Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB (2001) The distribution of soil nutrients with depth: global patterns and the imprint of plants. Biogeochemistry 53:51–77
Laclau JP, Ranger J, de Moraes Gonçalves JL, Maquère V, Krusche AV, M’Bou AT, Nouvellon Y, Saint-André L, Bouillet JP, de Cassia Piccolo M, Deleporte P (2010) Biogeochemical cycles of nutrients in tropical eucalyptus plantations: main features shown by intensive monitoring in Congo and Brazil. For Ecol Manag 259:1771–1785
Lamb D, Erskine PD, Parrotta JA (2005) Restoration of degraded tropical forest landscapes. Science 310:1628–1632
Lambers H, Mougel C, Jaillard B, Hinsinger P (2009) Plant-microbe-soil interactions in the rhizosphere: an evolutionary perspective. Plant Soil 321:83–115
Liao Y, McCormack ML, Fan H, Wang H, Wu J, Tu J, Liu W, Guo D (2014) Relation of fine root distribution to soil C in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation in subtropical China. Plant Soil 381:225–234
Liu X, Zhou G, Zhang D, Liu S, Zhu G, Yan J (2010) N and P stoichiometry of plant and soil in lower subtropical forest successional series in southern China. Chin J Plant Ecol 34:64–71
Mao R, Zeng DH, Hu YL, Li LJ, Yang D (2010) Soil organic carbon and nitrogen stocks in an age-sequence of poplar stands planted on marginal agricultural land in Northeast China. Plant Soil 332:277–287
Matzek V, Vitousek PM (2009) N : P stoichiometry and protein: RNA ratios in vascular plants: an evaluation of the growth-rate hypothesis. Ecol Lett 12:765–771
McGroddy ME, Daufresne T, Hedin LO (2004) Scaling of C : N : P stoichiometry in forests worldwide: implications of terrestrial Redfield-type ratios. Ecology 85:2390–2401
Niinemets Ü, Tamm Ü (2005) Species differences in timing of leaf fall and foliage chemistry modify nutrient resorption efficiency in deciduous temperate forest stands. Tree Physiol 25:1001–1014
Niklas KJ, Owens T, Reich PB, Cobb ED (2005) Nitrogen/phosphorus leaf stoichiometry and the scaling of plant growth. Ecol Lett 8:636–642
Nilsson MC, Wardle DA (2005) Understory vegetation as a forest ecosystem driver: evidence from the northern Swedish boreal forest. Front Ecol Environ 3:421–428
Paul KI, Polglase PJ, Nyakuengama JG, Khanna PK (2002) Change in soil carbon following afforestation. For Ecol Manag 168:241–257
Paul KI, Polglase PJ, Richards GP (2003) Predicted change in soil carbon following afforestation or reforestation, and analysis of controlling factors by linking a C accounting model (CAMFor) to models of forest growth (3PG), litter decomposition (GENDEC) and soil C turnover (RothC). For Ecol Manag 177:485–501
Reich PB (2005) Global biogeography of plant chemistry: filling in the blanks. New Phytol 168:263–266
Reich PB, Oleksyn J (2004) Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:11001–11006
Ritter E (2007) Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in volcanic soils following afforestation with native birch (Betula pubescens) and introduced larch (Larix sibirica) in Iceland. Plant Soil 295:239–251
Ryan MG, Binkley D, Fownes JH, Giardina CP, Senock RS (2004) An experimental test of the causes of forest growth decline with stand age. Ecol Monogr 74:393–414
Saur E, Nambiar EKS, Fife DN (2000) Foliar nutrient retranslocation in eucalyptus globulus. Tree Physiol 20:1105–1112
Schlesinger WH (1997) Biogeochemistry: An Analysis of Global Change, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, CA
Specht RL, Specht A (2010) The ratio of foliar nitrogen to foliar phosphorus: a determinant of leaf attributes and height in life-forms of subtropical and tropical plant communities. Aust J Bot 58:527–538
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press
Stone R (2009) Nursing China’s ailing forests back to health. Science 325:556–558
Townsend AR, Cleveland CC, Asner GP, Bustamante MM (2007) Controls over foliar N : P ratios in tropical rain forests. Ecology 88:107–118
van der Heijden MGA, Bardgett RD, van Straalen NM (2008) The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 11:296–310
Vesterdal L, Ritter E, Gundersen P (2002) Change in soil organic carbon following afforestation of former arable land. For Ecol Manag 169:137–147
Wang S, Yu G (2008) Ecological stoichiometry characteristics of ecosystem carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements. Acta Ecol Sin 28:3937–3947
Wardle DA, Zackrisson O (2005) Effects of species and functional group loss on island ecosystem properties. Nature 435:806–810
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setälä H, Van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science 304:1629–1633
Wu J, Liu Z, Wang X, Sun Y, Zhou L, Lin Y, Fu S (2011) Effects of understory removal and tree girdling on soil microbial community composition and litter decomposition in two eucalyptus plantations in South China. Funct Ecol 25:921–931
Wu J, Liu Z, Sun Y, Zhou L, Lin Y, Fu S (2013) Introduced eucalyptus urophylla plantations change the composition of the soil microbial community in subtropical China. Land Degrad Dev 24:400–406
Wu J, Liu Z, Huang G, Chen D, Zhang W, Shao Y, Wan S, Fu S (2014) Response of soil respiration and ecosystem carbon budget to vegetation removal in eucalyptus plantations with contrasting ages. Sci Rep 4:6262. doi:10.1038/srep06262
Yang Y, Luo Y (2011) Carbon: nitrogen stoichiometry in forest ecosystems during stand development. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 20:354–361
Yang M, Xie Y, Liu J (2011) Thirty years of eucalyptus research in China (1981–2010). China Forestry Press, China
Yu Q, Chen Q, Elser JJ, He N, Wu H, Zhang G, Wu J, Bai Y, Han X (2010) Linking stoichiometric homoeostasis with ecosystem structure, functioning and stability. Ecol Lett 13:1390–1399
Yuan Z, Chen HY, Reich PB (2011) Global-scale latitudinal patterns of plant fine-root nitrogen and phosphorus. Nat Commun 2:344. doi:10.1038/ncomms1346
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the two anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript. This work was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (no. 31160153; 31200406), the Jiangxi Natural Science Foundation (20142BAB214006), Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (KJLD12097; GJJ14744), and Opening Funding of KLVRMDE, SCBG, CAS (201010).
Ethical Statement
The authors declare no ethical issues for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jeffrey Walck .
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure 1
Location of the Eucalyptus chronosequence research site in Zhangzhou, China. (DOC 165 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, H., Wu, J., Liu, W. et al. Linkages of plant and soil C:N:P stoichiometry and their relationships to forest growth in subtropical plantations. Plant Soil 392, 127–138 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2444-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2444-2