Abstract
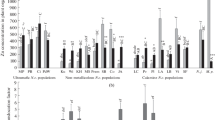
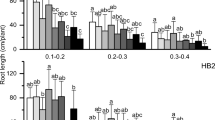
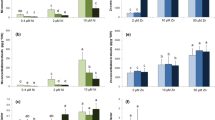
Sedum alfredii Hance has been identified as a Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species native to China. The characteristics of Zn uptake and accumulation in the hyperaccumulating ecotype (HE) and non-hyperaccumulating ecotype (NHE) of S. alfredii were investigated under nutrient solution and soil culture conditions. The growth of HE was normal up to 1000 μM Zn in nutrient solution, and 1600 mg Zn kg−1 soil in a Zn-amended soil. Growth of the NHE was inhibited at Zn levels ≥250 μM in nutrient solution. Zinc concentrations in the leaves and stems increased with increasing Zn supply levels, peaking at 500 and 250 μM Zn in nutrient solution for the HE and the NHE, respectively, and then gradually decreased or leveled off with further increase in solution Zn. Minimal increases in root Zn were noted at Zn levels up to 50 μM; root Zn sharply increased at higher Zn supply. The maximum Zn concentration in the shoots of the HE reached 20,000 and 29,000 mg kg−1 in the nutrient solution and soil experiments, respectively, approximately 20 times greater than those of the NHE. Root Zn concentrations were higher in the NHE than in the HE when plants were grown at Zn levels ≥50 μM. The time-course of Zn uptake and accumulation exhibited a hyperbolic saturation curve: a rapid linear increase during the first 6 days in the long-term and 60 min in the short-term studies; followed by a slower increase or leveling off with time. More than 80% of Zn accumulated in the shoots of the HE at half time (day 16) of the long-term uptake in 500 μM Zn, and also at half time (120 min) of the short-term uptake in 10 μM 65Zn2+. These results indicate that Zn uptake and accumulation in the shoots of S. alfredii exhibited a down-regulation by internal Zn accumulated in roots or leaves under both nutrient solution and soil conditions. An altered Zn transport system and increased metal sequestration capacity in the shoot tissues, especially in the stems, may be the factors that allow increased Zn accumulation in the hyperaccumulating ecotype of S. alfredii.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A G L Assuncão P D A Costa Martins S D E Foleter R Vooijs H Schat M G M Aarta (2001) ArticleTitleElevated expression of metal transporter genes in three accessions of the metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens Plant Cell Environ. 24 217–226
A G L Assuncão W M Bookum H J M Nelissen R Vooijs H Schat W H O Ernst (2003) ArticleTitleDifferential metal-specific tolerance and accumulation patterns among Thlaspi caerulescens populations originating from different soil types New Phytol. 159 411–419 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00819.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmsl2rsLo%3D
A J M Baker S P McGrath R D Reeves J A C Smith (2000) Metal hyperaccumulator plants: a review of the ecology and physiology resource for phytoremediation of metal-polluted soils N Terry G Banuelos J Vangronsveld (Eds) Phytoremediation of Contaminated Soil and Water Lewis publishers Boca Raton, FL 85–107
M Becher I N Talk L Krall U Kramer (2004) ArticleTitleCross-species microarray transcript profiling reveals high constitutive expression of metal homeostasis genes in shoots of the zinc hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri Plant J. 37 251–268 Occurrence Handle14690509 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhsVGlur8%3D
V Bert M R Macnair P Delaguerie P Saumitou-Laprade D Petit (2000) ArticleTitleZinc tolerance and accumulation in mrttalicolous and non-metallicolous populations of Arabidopsis halleri (Brassicaceae) New Phytol. 146 225–233 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXktlGlsL0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00634.x
V Bert M R Macnair P Laguerie Particlede P Saumitou-laprade D Petit (2002) ArticleTitleDo Arabidopsis halleri from non-metallicolous populations accumulate zinc and cadmium more effectively than those from non-mettalicolous populations? New Phytol. 155 47–57 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlsF2mt7w%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00432.x
S L Brown R L Chaney J S Angle AJM Baker (1995a) ArticleTitleZinc and cadmium uptake by hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens and metal tolerant Silene vulgaris grown on sludge-amended soils Environ. Sci. Technol. 29 1581–1585 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXlsFeltLw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1021/es00006a022
S L Brown R L Chaney J S Angle AJM Baker (1995b) ArticleTitleZinc and cadmium uptake by hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens grown in nutrient solution Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 59 125–133 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXjtleltr0%3D Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1995.03615995005900010020x
J Escarri C Lefebvre W Gruber M Leblanc J Lepart Y Riviere B Delay (2000) ArticleTitleZinc and cadmium hyperaccumulation by Thlaspi caerulescens from metalliferous and non-metalliferous sites in the Mediterranean area: implications for phytoremediation New Phytol. 145 429–437 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00599.x
L V Kochian (1991) Mechanisms of micronutrient uptake and translocation in plants J J Mortvedt (Eds) Micronutrients in Agriculture Soil Science Society of America Madison, WI 229–296
L V Kochian (1993 ) Zinc absorption from hydroponic solutions by plant roots A D Robson (Eds) Zinc in Soil and Plants Kluwer Academic Publishers Dordrecht, The Netherlands 45–57
H Küpper E Lombi F J Zhao S P McGrath (2000) ArticleTitleCellular compartmentation of cadmium and zinc in relation to other elements in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis haller Planta 212 75–84 Occurrence Handle11219586 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004250000366
M M Lasat A J Baker M Kochian (1996) ArticleTitlePhysoilogical characterisation of root Zn2+ absorption and translocation to shoots in hyperaccumulator and non-hyperaccumulator species of Thlaspi Plant Physiol. 112 1715–1722 Occurrence Handle12226473 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXlsVKr
M M Lasat A J M Baker L V Kochian (1998) ArticleTitleAltered Zn compartmentation in the root ymplasm and stimulated Zn absorption into the leaf as mechanisms involved in Zn hyperaccumulation in Thlaspi caerulescens Plant Physiol. 118 875–883 Occurrence Handle9808732 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnsFekt7k%3D Occurrence Handle10.1104/pp.118.3.875
T Q Li X E Yang Z L He J Y Yang (2005) ArticleTitleRoot morphology and Zn2+ uptake kinetics of the Zn hyperaccumulator of Sedum alfredii Hance J. Intergrative Plant Biol. 47 927–934 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXhtlWktLfM Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1744-7909.2005.00117.x
X X Long X E Yang Z Q Ye W Z Ni (2002) ArticleTitleStudy of the differences of uptake and accumulation of zinc in four species of Sedum Acta Bot. Sin. 44 152–157 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitlGju7w%3D
P Meerts N Isacker Particlevan (1997) ArticleTitleHeavy metal tolerance and accumulation in metallicolous and non-metallicolous populations of Thlaspi caerulescens from continental Europe Plant Ecol. 133 221–231 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1009717619579
W Z Ni X E Yang X X Long (2004) ArticleTitleComparative studies on zinc tolerance and accumulation between two ecotypes of Sedum alfrediii Hance in Southeast China J. Plant Nutr. 27 627–635 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXitFyns70%3D Occurrence Handle10.1081/PLN-120030372
S N Pence P B Larsen S D Ebbs D L D Letham M M Lasat D F Garvin D Eide L V Kochian (2000) ArticleTitleThe molecular physiology of heavy metal transport in the Zn/Cd hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 97 4956–4960 Occurrence Handle10781104 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXivFKisrk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.97.9.4956
D E Salt R D Smith I Raskin (1998) ArticleTitlePhytoremediation Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49 643–668 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXjvVSgs7g%3D Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.643
G E Santa Maria D H Cogliatti (1988) ArticleTitleBidirectional Zn-fluxes and compartmentation in wheat seedling roots J. Plant Physiol. 132 312–315 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXksFWkurw%3D
W Veltrup (1978) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of zinc uptake by barley roots Physiol. Plant. 42 190–194 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXhtlGmsb4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1399-3054.1978.tb02546.x
M Weber E Harada C Vess E Roepenack-Lahaya S Clemens (2004) ArticleTitleComparative microarray analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis halleri roots identifies nicotianamine synthase, a ZIP transporter and other genes as potential metal hyperaccumulation factors Plant J. 37 269–281 Occurrence Handle14690510 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjtFChurk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-313X.2003.02013.x
X E Yang V C Baligar D C Martens R B Clark (1996) ArticleTitleCadmium effects on influx and transport of mineral nutrients in plant species J. Plant Nutri. 19 643–656 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XisVSgu7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/01904169609365148
X E Yang X X Long W Z N i (2001) ArticleTitleZinc tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new ecotype of Sedum alfredii Hance Acta Phytoecol. Sin. 25 670–677
X E Yang X X Long W Z Ni (2002) ArticleTitleSedum alfredii Hance – a new ecotype of Zn-hyperaccumulator plant species native to China Chin. Sci. Bull. 47 1003–1006 Occurrence Handle10.1360/02tb9225
X E Yang H B Ye X X Long B He Z L He P J Stoffella D V Calvert (2004) ArticleTitleUptake and accumulation of cadmium and zinc by Sedum alfredii Hance at different Cd/Zn supply levels J. Plant Nutri. 27 1963–1977 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXnvVertro%3D Occurrence Handle10.1081/PLN-200030082
F J Zhao E Lombi T Breedon S P McGrath (2000) ArticleTitleZinc hyperaccumulation and cellular distribution in Arabidopsis halleri Plant Cell Environ. 23 507–514 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXktVClsbw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-3040.2000.00569.x
F J Zhao S J Dunham S P McGrath (2002) ArticleTitleArsenic hyperaccumulation by different fern species New Phytol. 156 27–31 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvFyhtr4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1469-8137.2002.00493.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: F. J. Zhao
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X.E., Li, T.Q., Long, X.X. et al. Dynamics of zinc uptake and accumulation in the hyperaccumulating and non-hyperaccumulating ecotypes of Sedum alfredii Hance. Plant Soil 284, 109–119 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-0033-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-0033-0