Abstract
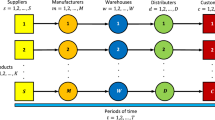
This paper develops mathematical models to coordinate facility location and inventory control for a four-echelon supply chain network consisting of multiple suppliers, warehouses, hubs and retailers. The hubs help in reducing transportation costs by consolidating products from multiple warehouses and directing the larger shipments to the retailer. The integrated models studied in this paper simultaneously determines three types of decisions: (i) facility location—the number and location of warehouses and hubs, (ii) allocation—assignment of suppliers to located warehouses and retailers to located warehouses via the location hubs, and (iii) inventory control decisions at each located warehouse. The goal is to minimize the facility location, transportation and the inventory costs. A mixed integer nonlinear programming formulation is first presented. The nonlinear integer programming formulation is then transformed into a conic mixed integer program and a novel and compact conic mixed integer programming formulation. Computational runs are conducted using commercial solvers to compare the performance of the different formulations. The compact conic mixed integer programming formulation was found to significantly outperform the other formulations by achieving significant computational savings. The results demonstrate that large scale instances of certain multi-echelon supply chain network design problems can be solved using commercial solvers through intelligent reformulation of the model.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadeh F, Goldfarb D (2003) Second-order cone programming. Math Program 95(1):3–51
Alumur S, Kara BY (2008) Network Hub location problems: the state of the Art. Eur J Oper Res 190(1):1–21
Ambrosino D, Scutellà MG (2005) Distribution network design: new problems and related models. Eur J Oper Res 165:610–624
Atamtürk A, Berenguer G, Shen ZJM (2012) A conic integer programming approach to stochastic joint location-inventory problems. Oper Res 60(2):366–381
Ben-Tal A, Nemirovski AS (2001) Lectures on Modern Convex Optimization: Analysis, Algorithms, and Engineering Applications. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia
Cambell JF, O’Kelly ME (2012) Twenty-five years of Hub location research. Transp Sci 46(2):153–169
Cheong MLF, Bhatnagar R, Graves SC (2007) Logistic network design with supplier consolidation hubs and multiple shipment options. J Ind Manag Optim 3(1):51–69
Daskin MS, Coullard CR, Shen ZJM (2002) An inventory-location model: formulation, solution algorithm and computational results. Ann Oper Res 110(1–4):83–106
Hamad R, Fares Gualda ND (2008) Model for facilities or vendors location in a global scale considering several echelons in the chain. Network Spatial Econ 8(2–3):297–307
Lin L, Gen M, Wang X (2009) Integrated multistage logistics network design by using hybrid evolutionary algorithm. Comput Ind Eng 56:854–873
Lobo MS, Vandenberghe L, Boyd S, Lebret H (1998) Applications of second-order cone programming. Lin Algebra Appl 248:193–228
Luo ZQ, Sturm JF, Zhang S (2000) Conic convex programming and self-dual embedding. Optim Meth Software 14(3):169–218
Mentzer JT, DeWitt W, Keebler JS, Min S, Nix NW, Smith CD, Zacharia ZG (2001) Defining supply chain management. J Bus Logist 22(2):1–25
Miranda PA, Garrido RA (2004) Incorporating Inventory Control Decisions into a Strategic Distribution Network Design Model with Stochastic Demand. Transportation Research Part E, pp 183–207
Miranda PA, Garrido RA (2006) A simultaneous inventory control and facility location model with stochastic capacity constraints. Network Spatial Econ 6(1):39–53
Nozick L, Turnquist M (2001) Inventory, transportation, service quality and the location of distribution centers. Eur J Oper Res 129(2):362–371
Park S, Lee TE, Sung CS (2010) A three-level supply chain network design model with risk-pooling and lead times. Transport Res E Logist Transport Rev 46(5):563–581
Romeijin HE, Shu J, Teo CP (2007) Designing two-echelon supply networks. Eur J Oper Res 178(2):449–462
Shen ZJM, Coullard CR, Daskin MS (2003) A joint location-inventory model. Transp Sci 37(1):40–55
Shu J, Sun J (2006) Designing the distribution network for an integrated supply chain. J Ind Manag Optim 2(3):339–349
Shu J, Teo CP, Shen ZJM (2005) Stochastic transportation-inventory network design problem. Oper Res 53(1):48–60
Silva F, Gao L (2013) A joint replenishment inventory-location model. Network Spatial Econ 13(1):107–122
Snyder LV, Daskin MS, Teo CP (2007) The stochastic location model with risk pooling. Eur J Oper Res 179(3):1221–1238
Sourirajan K, Ozsen L, Uzsoy R (2007) A single-product network design model with lead time and safety stock considerations. IIE Trans 39(5):411–424
Sourirajan K, Ozsen L, Uzsoy R (2009) A genetic algorithm for a single product network design model with lead time and safety stock considerations. Eur J Oper Res 197(2):599–608
Spekman RE, Kamauff JW Jr, Myhr N (1998) An empirical investigation into supply chain management: a perspective on partnerships. Supply Chain Manag 3(2):53–67
Sturm JF (1999) Using SeDuMi 1.02A MATLAB toolbox for optimization over symmetric cones. Optim Meth Software 11(1–4):625–653
Tan KC (2001) A framework of supply chain management literature. Eur J Purch Supply Manag 7:39–48
Tancrez JS, Lange JC, Semal P (2012) A location-inventory model for large three-level supply chains. Transport Res E Logist Transport Rev 48(2):485–502
Teo CP, Shu J (2004) Warehouse-retailer network design problems. Oper Res 52(3):396–408
Tütüncü RH, Toh CK, Todd MJ (2001) SDPT3—A MATLAB Software Package for Semidefinite-Quadratic-Linear Programming. MathWorks, Natick
Vidyarthi N, Çelebi E, Elhedhli S, Jewkes E (2007) Integrated production-inventory-distribution system design with risk pooling: model formulation and heuristic solution. Transport Sci 41(3):392–408
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Science Foundation for funding this work through Award Number 1069141 “Collaborative Research: Stochastic and Dynamic Hyperpath Equilibrium Models”. Any error, mistake, or omission related to this research paper is the sole responsibility of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahabi, M., Akbarinasaji, S., Unnikrishnan, A. et al. Integrated Inventory Control and Facility Location Decisions in a Multi-Echelon Supply Chain Network with Hubs. Netw Spat Econ 13, 497–514 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-013-9196-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-013-9196-4