Abstract
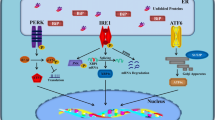
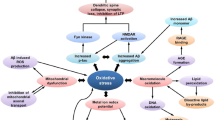
Alzheimer’s disease involves normal cellular aging and chronic cellular stress events, leading to interrelated changes in gene expression and subsequent neurodegeneration. Premature death of cholinergic neurons and the formation of amyloid fibrils separately initiated the cholinergic and amyloid hypotheses of Alzheimer’s disease. Here, we present evidence to the fact that these two distinct phenomena both associate with specific changes in acetylcholinesterase (AChE) gene expression within cholinergic neurons. For example, calcium misregulation promotes aberrant transcription and pro-apoptotic events, as well as AChE-induced modifications in cellular signal cascades. These reciprocally intercept with AChE regulation at the Endoplasmic Reticulum, modifying AChE gene expression, folding and signaling. Altered AChE properties may reflect changes in the enzymatic and/or non-enzymatic features of the multiple AChE splice variants. Under chronic cellular stress, aberrant AChE regulation may thus facilitate apoptotic pathways, promoting plaque formation, cognitive impairments and degeneration of cholinergic nerve cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. P. Mattson (2000) ArticleTitleApoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1 120–129 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35040009 Occurrence Handle11253364
X. Zhang (2004) ArticleTitleCholinergic activity and amyloid precursor protein processing in aging and Alzheimer’s disease Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 3 137–152 Occurrence Handle10.2174/1568007043482499 Occurrence Handle15078189
D. M. Walsh D. J. Selkoe (2004) ArticleTitleDeciphering the molecular basis of memory failure in Alzheimer’s disease Neuron 44 181–93 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.neuron.2004.09.010 Occurrence Handle15450169
A. V. Terry J. J. Buccafusco (2003) ArticleTitleThe cholinergic hypothesis of age and Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits: Recent challenges and their implications for novel drug development J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 306 821–827 Occurrence Handle10.1124/jpet.102.041616 Occurrence Handle12805474
I. Gordon E. Grauer I. Genis E. Sehayek D. M. Michaelson (1995) ArticleTitleMemory deficits and cholinergic impairments in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice Neurosci. Lett. 199 1–4 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3940(95)12006-P Occurrence Handle8584214
Y. Ikarashi et al. (2004) ArticleTitleDecreased level of brain acetylcholine and memory disturbance in APPsw mice Neurobiol. Aging 25 483–490 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0197-4580(03)00122-2 Occurrence Handle15013569
K. Herholz et al. (2000) ArticleTitleIn-vivo measurements of regional acetylcholine esterase activity in degenerative dementia: Comparison with blood flow and glucose metabolism J. Neural Transm. 107 1457–1468 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s007020070009 Occurrence Handle11458998
K. Herholz et al. (2004) ArticleTitleIn vivo study of acetylcholine esterase in basal forebrain, amygdala, and cortex in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease Neuroimage 21 136–143 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.09.042 Occurrence Handle14741650
T. M. Rees S. Brimijoin (2003) ArticleTitleThe role of acetylcholinesterase in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease Drugs Today (Barc.) 39 75–83 Occurrence Handle10.1358/dot.2003.39.1.740206
T. Rees P. I. Hammond H. Soreq S. Younkin S. Brimijoin (2003) ArticleTitleAcetylcholinesterase promotes beta-amyloid plaques in cerebral cortex Neurobiol. Aging 24 777–787 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0197-4580(02)00230-0 Occurrence Handle12927760
M. S. Parihar T. Hemnani (2003) ArticleTitlePhenolic antioxidants attenuate hippocampal neuronal cell damage against kainic acid induced excitotoxicity J. Biosci. 28 121–128 Occurrence Handle12682435
D. W. Dickson (2004) ArticleTitleApoptotic mechanisms in Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration: Cause or effect? J. Clin. Invest. 114 23–7 Occurrence Handle10.1172/JCI200422317 Occurrence Handle15232608
A. Kamal A. Almenar-Queralt J. F. LeBlanc E. A. Roberts L. S. Goldstein (2001) ArticleTitleKinesin-mediated axonal transport of a membrane compartment containing beta-secretase and presenilin-1 requires APP Nature 414 643–648 Occurrence Handle10.1038/414643a Occurrence Handle11740561
H. Sasamura et al. (2000) ArticleTitleAnalysis of Galpha protein recognition profiles of angiotensin II receptors using chimeric Galpha proteins Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 170 113–121 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0303-7207(00)00333-6 Occurrence Handle11162895
D. M. Walsh et al. (2003) ArticleTitlegamma-Secretase cleavage and binding to FE65 regulate the nuclear translocation of the intracellular C-terminal domain (ICD) of the APP family of proteins Biochemistry 42 6664–6673 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi027375c Occurrence Handle12779321
F. M. LaFerla (2002) ArticleTitleCalcium dyshomeostasis and intracellular signalling in Alzheimer’s disease Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3 862–872 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nrn960 Occurrence Handle12415294
K. Shirotani et al. (2003) ArticleTitleGamma-secretase activity is associated with a conformational change of nicastrin J. Biol. Chem. 278 16474–16477 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.C300095200 Occurrence Handle12644462
W. P. Esler et al. (2002) ArticleTitleActivity-dependent isolation of the presenilin- gamma -secretase complex reveals nicastrin and a gamma substrate Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 2720–2725 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.052436599 Occurrence Handle11867728
W. T. Kimberly et al. (2003) ArticleTitleNotch and the amyloid precursor protein are cleaved by similar gamma-secretase(s) Biochemistry 42 137–144 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi026888g Occurrence Handle12515548
M. P. Mattson S. L. Chan (2003) ArticleTitleCalcium orchestrates apoptosis Nat. Cell Biol. 5 1041–1043 Occurrence Handle10.1038/ncb1203-1041 Occurrence Handle14647298
Z. Qiu K. A. Crutcher B. T. Hyman G. W. Rebeck (2003) ArticleTitleApoE isoforms affect neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate calcium responses and toxicity via receptor-mediated processes Neuroscience 122 291–303 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.08.017 Occurrence Handle14614897
W. J. Lukiw (2004) ArticleTitleGene expression profiling in fetal, aged, and Alzheimer hippocampus: A continuum of stress-related signaling Neurochem. Res. 29 1287–1297 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:NERE.0000023615.89699.63 Occurrence Handle15176485
A. Verkhratsky E. C. Toescu (2003) ArticleTitleEndoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) homeostasis and neuronal death J. Cell Mol. Med. 7 351–361 Occurrence Handle14754504
T. Lu et al. (2004) ArticleTitleGene regulation and DNA damage in the ageing human brain Nature 429 883–891
E. R. Kandel (2001) ArticleTitleThe molecular biology of memory storage: A dialog between genes and synapses Biosci. Rep. 21 565–611 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1014775008533 Occurrence Handle12168768
E. Meshorer et al. (2004) ArticleTitleCombinatorial complexity of 5’ alternative acetylcholinesterase transcripts and protein products J. Biol. Chem. 279 29740–29751 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M402752200 Occurrence Handle15123727
E. H. Sklan et al. (2004) ArticleTitleAcetylcholinesterase/paraoxonase genotype and expression predict anxiety scores in Health, Risk Factors, Exercise Training, and Genetics study Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101 5512–5517 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.0307659101 Occurrence Handle15060281
E. Meshorer H. Soreq (2002) ArticleTitlePre-mRNA splicing modulations in senescence Aging Cell 1 10–16 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1474-9728.2002.00005.x Occurrence Handle12882348
G. Sberna J. Saez-Valero K. Beyreuther C. L. Masters D. H. Small (1997) ArticleTitleThe amyloid beta-protein of Alzheimer’s disease increases acetylcholinesterase expression by increasing intracellular calcium in embryonal carcinoma P19 cells J. Neurochem. 69 1177–1184 Occurrence Handle9282941
R. Bernhardi Particlevon G. Ramirez G. V. Ferrari ParticleDe N. C. Inestrosa (2003) ArticleTitleAcetylcholinesterase induces the expression of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in glia and activates glial cells in culture Neurobiol. Dis. 14 447–457 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.nbd.2003.08.014 Occurrence Handle14678761
C. Erb et al. (2001) ArticleTitleCompensatory mechanisms enhance hippocampal acetylcholine release in transgenic mice expressing human acetylcholinesterase J. Neurochem. 77 638–646 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00287.x Occurrence Handle11299326
M. M. Svedberg et al. (2002) ArticleTitleUpregulation of neuronal nicotinic receptor subunits alpha4, beta2, and alpha7 in transgenic mice overexpressing human acetylcholinesterase J. Mol. Neurosci. 18 211–22 Occurrence Handle10.1385/JMN:18:3:211 Occurrence Handle12059039
D. Kaufer A. Friedman S. Seidman H. Soreq (1999) ArticleTitleAnticholinesterases induce multigenic transcriptional feedback response suppressing cholinergic neurotransmission Chem. Biol. Interact. 119-120 349–360 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0009-2797(99)00046-0 Occurrence Handle10421471
E. Meshorer et al. (2002) ArticleTitleAlternative splicing and neuritic mRNA translocation under long-term neuronal hypersensitivity Science 295 508–512 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1066752 Occurrence Handle11799248
M. Dugu J. Neugroschl M. Sewell D. Marin (2003) ArticleTitleReview of dementia Mt. Sinai J. Med. 70 45–53 Occurrence Handle12516009
Rees, T. M., et al. Memory deficits correlating with acetylcholinesterase splice shift and amyloid burden in doubly transgenic mice. Current Alzheimer Research, in press (2005).
W. Paschen (2003) ArticleTitleEndoplasmic reticulum: A primary target in various acute disorders and degenerative diseases of the brain Cell Calcium 34 365–383 Occurrence Handle12909082
S. Althausen et al. (2001) ArticleTitleChanges in the phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2alpha, elongation factor eEF-2 and p70 S6 kinase after transient focal cerebral ischaemia in mice J. Neurochem. 78 779–787 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00462.x Occurrence Handle11520898
H. L. Pahl P. A. Baeuerle (1997) ArticleTitleThe ER-overload response: Activation of NF-kappa B Trends Biochem. Sci. 22 63–67 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0968-0004(96)10073-6 Occurrence Handle9048485
H. P. Harding Y. Zhang A. Bertolotti H. Zeng D. Ron (2000) ArticleTitlePerk is essential for translational regulation and cell survival during the unfolded protein response Mol. Cell 5 897–904 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80330-5 Occurrence Handle10882126
W. Tirasophon A. A. Welihinda R. J. A. Kaufman (1998) ArticleTitlestress response pathway from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus requires a novel bifunctional protein kinase/endoribonuclease (Ire1p) in mammalian cells Genes Dev. 12 1812–1824 Occurrence Handle9637683
K. Lee et al. (2002) ArticleTitleIRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response Genes Dev. 16 452–466 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gad.964702 Occurrence Handle11850408
H. Yoshida T. Matsui A. Yamamoto T. Okada K. Mori (2001) ArticleTitleXBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor Cell 107 881–891 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00611-0 Occurrence Handle11779464
C. Y. Liu R. J. Kaufman (2003) ArticleTitleThe unfolded protein response J. Cell Sci. 116 1861–1862 Occurrence Handle10.1242/jcs.00408 Occurrence Handle12692187
T. Katayama et al. (1999) ArticleTitlePresenilin-1 mutations downregulate the signalling pathway of the unfolded-protein response Nat. Cell Biol. 1 479–485 Occurrence Handle10.1038/70265 Occurrence Handle10587643
W. Paschen (2000) ArticleTitleRole of calcium in neuronal cell injury: which subcellular compartment is involved? Brain Res. Bull. 53 409–413 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0361-9230(00)00369-5 Occurrence Handle11136996
H. Y. Zhang S. Brimijoin X. C. Tang (2003) ArticleTitleApoptosis induced by beta-amyloid25-35 in acetylcholinesterase-overexpressing neuroblastoma cells Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 24 853–858 Occurrence Handle12956931
Q. H. Jin H. Y. He Y. F. Shi H. Lu X. J. Zhang (2004) ArticleTitleOverexpression of acetylcholinesterase inhibited cell proliferation and promoted apoptosis in NRK cells Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 25 1013–1021 Occurrence Handle15301733
S. E. Park N. D. Kim Y. H. Yoo (2004) ArticleTitleAcetylcholinesterase plays a pivotal role in apoptosome formation Cancer Res. 64 2652–2655 Occurrence Handle10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0649 Occurrence Handle15087373
X. J. Zhang et al. (2002) ArticleTitleInduction of acetylcholinesterase expression during apoptosis in various cell types Cell Death Differ. 9 790–800 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.cdd.4401034 Occurrence Handle12107822
L. Yang H. Y. He X. J. Zhang (2002) ArticleTitleIncreased expression of intranuclear AChE involved in apoptosis of SK-N-SH cells Neurosci. Res. 42 261–268 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-0102(02)00005-6 Occurrence Handle11985878
T. Day S. A. Greenfield (2003) ArticleTitleA peptide derived from acetylcholinesterase induces neuronal cell death: characterisation of possible mechanisms Exp. Brain Res. 153 334–342 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00221-003-1567-5 Occurrence Handle13680041
S. Belbeoc’h et al. (2004) ArticleTitleElements of the C-terminal t peptide of acetylcholinesterase that determine amphiphilicity, homomeric and heteromeric associations, secretion and degradation Eur. J. Biochem. 271 1476–1487 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04052.x Occurrence Handle15066173
S. Stamm et al. (2005) ArticleTitleFunction of alternative splicing Gene 344C 1–20 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.gene.2004.10.022
M. Aridor W. E. Balch (1999) ArticleTitleIntegration of endoplasmic reticulum signaling in health and disease Nat. Med. 5 745–751 Occurrence Handle10.1038/10466 Occurrence Handle10395318
M. S. Brown J. L. Goldstein (1999) ArticleTitleA proteolytic pathway that controls the cholesterol content of membranes, cells, and blood Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96 11041–11048 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.96.20.11041 Occurrence Handle10500120
T. F. Osborne (2001) ArticleTitleCREating a SCAP-less liver keeps SREBPs pinned in the ER membrane and prevents increased lipid synthesis in response to low cholesterol and high insulin Genes Dev. 15 1873–1888 Occurrence Handle10.1101/gad.916601 Occurrence Handle11485982
M. P. Mattson W. A. Pedersen (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of amyloid precursor protein derivatives and oxidative stress on basal forebrain cholinergic systems in Alzheimer’s disease Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 16 737–753 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0736-5748(98)00082-3 Occurrence Handle10198821
A. Weidemann et al. (1999) ArticleTitleProteolytic processing of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein within its cytoplasmic domain by caspase-like proteases J. Biol. Chem. 274 5823–5829 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.274.9.5823 Occurrence Handle10026204
R. L. Neve D. L. McPhie Y. Chen (2000) ArticleTitleAlzheimer’s disease: a dysfunction of the amyloid precursor protein(1) Brain Res. 886 54–66 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02869-9 Occurrence Handle11119687
C. I. Wright C. Geula M. M. Mesulam (1993) ArticleTitleProtease inhibitors and indolamines selectively inhibit cholinesterases in the histopathologic structures of Alzheimer’s disease Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 695 65–68 Occurrence Handle8239315
C. Y. Ni H. Yuan G. Carpenter (2003) ArticleTitleRole of the ErbB-4 carboxyl terminus in gamma-secretase cleavage J. Biol. Chem. 278 4561–4565 Occurrence Handle10.1074/jbc.M210504200 Occurrence Handle12454007
X. Ge et al. (2004) ArticleTitleNotch signaling in Drosophila long-term memory formation Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 101 10172–10176 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.0403497101 Occurrence Handle15220476
C. A. Saura et al. (2004) ArticleTitleLoss of presenilin function causes impairments of memory and synaptic plasticity followed by age-dependent neurodegeneration Neuron 42 23–36 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0896-6273(04)00182-5 Occurrence Handle15066262
P. Marambaud et al. (2003) ArticleTitleA CBP binding transcriptional repressor produced by the PS1/epsilon-cleavage of N-cadherin is inhibited by PS1 FAD mutations Cell 114 635–645 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.cell.2003.08.008 Occurrence Handle13678586
W. B. Grant A. Campbell R. F. Itzhaki J. Savory (2002) ArticleTitleThe significance of environmental factors in the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease J. Alzheimers Dis. 4 179–189 Occurrence Handle12226537
X. Zhu et al. (2004) ArticleTitleNeuroprotective properties of Bcl-w in Alzheimer disease J. Neurochem. 89 1233–1240 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02416.x Occurrence Handle15147516
R. Li et al. (2004) ArticleTitleTumor necrosis factor death receptor signaling cascade is required for amyloid-beta-protein-induced neuron death J. Neurosci. 24 1760–1771 Occurrence Handle10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4580-03.2004 Occurrence Handle14973251
T. Darreh-Shori et al. (2004) ArticleTitleLong-lasting acetylcholinesterase splice variations in anticholinesterase-treated Alzheimer’s disease patients J. Neurochem. 88 1102–1113 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02230.x Occurrence Handle15009666
Dori (2004) ArticleTitleFunctional Manipulations of Acetylcholinesterase Splice Variants Highlight Alternative Splicing Contributions to Murine Neocortical Development Cerebral Cortex 15 419–430 Occurrence Handle10.1093/cercor/bhh145
H Soreq S. Seidman (2001) ArticleTitleAcetylcholinesterase -- new roles for an old actor Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2 294–302 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35067589 Occurrence Handle11283752
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toiber, D., Soreq, H. Cellular Stress Reactions as Putative Cholinergic Links in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res 30, 909–919 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-6963-8
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-6963-8