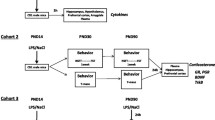
Impairments to cognitive functions in in children and adults often result from various pathologies occurring during the prenatal period and early postnatal period of development (birth traumas, hypoxia, infectious diseases). The present study identified impaired learning in a Morris water maze in adult rats given interleukin-1β during the third week of life. Differences between experimental and control animals were seen in learning to find the platform and modifying the acquired skill (on positioning the platform in a new location). There was no change in extinction of the acquired skill. The nature of impairment to learning in experimental animals suggested impairment to the mechanisms long-term but not short-term memory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. M. Klimenko and O. E. Zubareva, “The neurobiology of cytokines, behavior, and adaptive reactions,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 85, No. 9, 1244–1254 (1999).
O. E. Zubareva, A. P. Eliseeva, A. S. Simbirtsev, and V. M. Klimenko, “Effects of proinflammatory cytokines on the establishment of behavior in early postnatal ontogenesis,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 91, No. 4, 374–384 (2005).
O. E. Zubareva, K. P. Shcherbakova, S. V. Kalemenev, et al., “Impairments to conditioned reflex activity in adult rats after administration of interleukin-1β during early postnatal ontogenesis,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 61, No. 6, 1–6 (2011).
V. G. Shalyapina, N. E. Ordyan, S. G. Pivina, and V. V. Rakitskaya, “Neuroendocrine mechanisms of formation of adaptive behavior,” Ros. Fiziol. Zh., 81, No. 8, 94–100 (1995).
H. Aly, M. T. Khashaba, M. El-Ayouty, et al., “IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α and outcomes of neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy,” Brain Dev., 28, No. 3, 178–182 (2006).
S. D. Bilbo, J. W. Rudy, L. R. Watkins, and S. F. Maier, “A behavioural characterization of neonatal infection-facilitated memory impairment in adult rats,” Behav. Brain Res., 169, No. 1, 39–47 (2006).
P. Boksa, “Effects of prenatal infection on brain development and behavior: a review of findings from animal models,” Brain Behav. Immun., 24, No. 6, 881–897 (2010).
C. Csolle and B. Sperlagh, “Peripheral origin of IL-1β production in the rodent hippocampus under in vivo systemic bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge and its regulation by P2X7 receptors,” J. Neuroimmunol., 219, No. 1–2, 38–46 (2010).
K. Cui, H. Ashdown, G. N. Luheshi, and P. Boksa, “Effects of prenatal immune activation on hippocampal neurogenesis in the rat,” Schizophrenia Res., 113, No. 2–3, 288–297 (2009).
O. Dammann and A. Leviton, “Maternal intrauterine infection, cytokines, and brain damage in the preterm newborn,” Pediatr. Res., 42, No. 1, 1–8 (1997).
R. Dantzer, “Cytokine-induced sickness behavior: a neuroimmune response to activation of innate immunity,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 500, 399–411 (2004).
J. H. Gilmore, L. F. Jarskog, S. Vadlamudi, and J. M. Lauder, “Prenatal infection and risk for schizophrenia: IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα inhibit cortical neuron dendrite development,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 29, No. 7, 1221–1229 (2004).
S. Girard, H. Kadhim, A. Larouche, et al., “Pro-inflammatory disequilibrium of the IL-1β/IL-1ra ratio in an experimental model of perinatal brain damages induced by lipopolysaccharide and hypoxia-ischemia,” Cytokine, 43, No. 1, 54–62 (2008).
I. Goshen, T. Kreisel, H. Ounallah-Saad, et al., “A dual role for interleukin-1 in hippocampal-dependent memory processes,” Psychoneuroendocrinology, 32, No. 8–10, 1106–1115 (2007).
H. F. Green, E. Treacy, A. K. Keohane, et al., “A role for interleukin-1β in determining the lineage fate of embryonic rat hippocampal neural precursor cells,” Mol. Cell. Neurosci., 49, No. 3, 311–321 (2012).
E.-M. Harre, M. A. Galic, A. Mouihate, et al., “Neonatal inflammation produces selective behavioural deficits and alters N-methyl-Daspartate receptor subunit mRNA in the adult rat brain,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 27, No. 3, 644–653 (2008).
T. Ikeda, K. Mishima, N. Aoo, et al., “Dexamethasone prevents longlasting learning impairment following a combination of lipopolysaccharide and hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats,” Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol., 192, No. 3, 719–726 (2005).
Y. Imamura, H. Wang, N. Matsumoto, et al., “Interleukin-1β causes long-term potentiation deficiency in a mouse model of septic encephalopathy,” Neuroscience, 187, 63–69 (2011).
T. A. Jenkins, M. K. Harte, G. Stenson, and G. P. Reynolds, “Neonatal lipopolysaccharide induces pathological changes in parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of the rat,” Behav. Brain Res., 205, No. 2, 355–359 (2009).
A. Kabiersch, H. Furukawa, A. del Rey, and H. O. Besedovsky, “Administration of interleukin-1 at birth affects dopaminergic neurons in adult mice,” Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 840, 123–127 (1998).
S. Laye, P. Parnet, E. Goujon, and R. Dantzer, “Peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide induces the expression of cytokine transcripts in the brain and pituitary of mice,” Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res., 27, 157–162 (1994).
Z. D. Ling, E. D. Potter, J. W. Lipton, and P. M. Carvey, “Differentiation of mesencephalic progenitor cells into dopaminergic neurons by cytokines,” Exp. Neurol., 149, No. 2,411–423 (1998).
T. Y. Mariano, D. M. Bannerman, S. B. McHugh, et al., “Impulsive choice in hippocampal but not orbitofrontal cortex-lesioned rats on a nonspatial decision-making task,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 30, No. 3, 472–484 (2009).
S. J. Martin and R. E. Clark, “The rodent hippocampal and spatial memory: from synapses to symptoms,” Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 64, No. 4, 401–431 (2007).
Y. Matsumoto, M. Yoshida, S. Watanabe, and T. Yamamoto, “Involvement of cholinergic and glutamatergic functions in working memory impairment induced by interleukin-1beta in rats,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 430, No. 2–3, 283–288 (2001).
Y. Matsumoto, T. Yamaguchi, S. Watanabe, and T. Yamamoto, “Involvement of arachidonic acid cascade in working memory impairment induced by interleukin-1β,” Neuropharmacology, 46, No. 8, 1195–1200 (2004).
O. B. Menachem-Zidon, A. Avital, Y. Ben-Menahem, et al., “Astrocytes support hippocampal-dependent memory and long-term potentiation via interleukin-1 signaling,” Brain Behav. Immunol., 25, No. 5, 1008–1016 (2011).
R. Morris, “Development of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat,” J. Neurosci. Meth., 11, No. 1, 47–60 (1984).
D. Rice and S. J. Barone, “Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: evidence from humans and animal models,” Environ. Health Perspect., 108, No. 3, 511–533 (2000).
F. M. Ross, S. M. Allan, N. J. Rothwell, and A. Verkhratsky, “A dual role for interleukin-1 in LTP in mouse hippocampal slices,” J. Neuroimmunol., 144, 61–67 (2003).
A. V. Terry, Jr, C. M. Hernandez, and J. J. Buccafusco, “Dahl salt-sensitive and salt-resistant rats: examination of learning and memory performance, blood pressure, and the expression of central nicotinic acetylcholine receptors,” Neuroscience, 103, No. 2, 351–363 (2001).
M. Tohmi, N. Tsuda, Y. Watanabe, et al., “Perinatal inflammatory cytokine challenge results in distinct neurobehavioral alterations in rats: implication in psychiatric disorders of developmental origin,” Neurosci. Res., 50, No. 1, 67–75 (2004).
L. L. Williamson, P. W. Sholar, R. S. Mistry, et al., “Microglia and memory: modulation by early-life infection,” J. Neurosci., 31, No. 43, 15511–15521 (2011).
R. Yirmiya and I. Goshen, “Immune modulation of learning, memory, neural plasticity and neurogenesis,” Brain Behav. Immun., 25, No. 2, 181–1213 (2011).
R. Yirmiya, G. Winocur, and I. Goshen, “Brain interleukin-1 is involved in spatial memory and passive avoidance conditioning,” Neurobiol. Learning Mem., 78, No. 2, 379–389 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Rossiiskii Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal imeni I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 98, No. 6, pp. 782–792, June, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trofimov, A.N., Zubareva, O.E., Simbirtsev, A.S. et al. Effects of Neonatal Increases in Interleukin-1β Levels on the Formation of Spatial Memory in Adult Rats. Neurosci Behav Physi 44, 359–364 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-014-9918-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-014-9918-1