Abstract
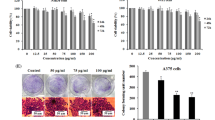
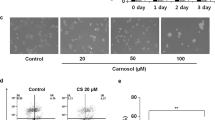
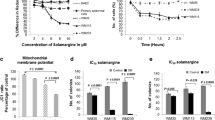
Melanoma is the most malignant skin cancer and is highly resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Curcumin is a component of turmeric, the yellow spice derived from the rhizome of Curcuma longa. It has been demonstrated to modulate multiple cell signaling pathways, including apoptosis, proliferation, angiogenesis and inflammation. In this study, we studied the signaling pathways involved in melanoma cell death after treatment with curcumin using western blotting. Colorimetric assays (MTT) assessed cell viability. Flow cytometry and DNA laddering evaluated cell apoptosis. Fluorescent microscopy was used to evaluate of Hoechst 33342 staining of nuclei. The result demonstrated that curcumin could induce apoptosis and inhibit proliferation in melanoma cells. Curcumin stimulated the expression of pro-apoptotic Bax, and inhibited the activation of anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 and Bcl-2. During curcumin treatment, caspase-8 and Caspase-3 were cleaved in time and dose-dependent manners. Curcumin treatment also altered the expressions of apoptosis associated proteins NF-κB, p38 and p53. Curcumin induced DNA double strand breaks, which were indicated by phosphorylated H2AX. Our data suggested that curcumin could be used as a novel and effective approach for the treatment of melanoma.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibrahim N, Haluska FG (2009) Molecular pathogenesis of cutaneous melanocytic neoplasms. Annu Rev Pathol 4:551–579
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E, Thun MJ (2003) Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin 53:5–26
Middleton MR, Grob JJ, Aaronson N, Fierlbeck G, Tilgen W, Seiter S, Gore M, Aamdal S, Cebon J, Coates A, Dreno B, Henz M, Schadendorf D, Kapp A, Weiss J, Fraass U, Statkevich P, Muller M, Thatcher N (2000) Randomized phase III study of temozolomide versusdacarbazine in the treatment of patients with advancedmetastatic malignant melanoma. J Clin Oncol 18:2351
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P, Aggarwal BB (2008) Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett 269:199–225
Dorai T, Cao YC, Dorai B, Buttyan R, Katz AE (2001) Therapeutic potential of curcumin in human prostate cancer. III. Curcumin inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and inhibits angiogenesis of LNCaP prostate cancer cells in vivo. Prostate 47:293–303
Dorai T, Gehani N, Katz A (2000) Therapeutic potential of curcumin in human prostate cancer-I. Curcumin induces apoptosis in both androgen-dependent and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Prostate Cancer Prostatic 3:84–93
Dorai T, Gehani N, Katz A (2000) Therapeutic potential of curcumin in human prostate cancer. II. Curcumin inhibits tyrosine kinase activity of epidermal growth factor receptor and depletes the protein. Mol Urol 4:1–6
Urbina-Cano P, Bobadilla-Morales L, Ramírez-Herrera MA, Corona-Rivera JR, Mendoza-Magaña ML, Troyo-Sanromán R, Corona-Rivera A (2006) DNA damage in mouse lymphocytes exposed to curcumin and copper. J Appl Genet 47:377–382
Cao J, Jia L, Zhou HM, Liu Y, Zhong LF (2006) Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA damage induced by curcumin in human hepatoma G2 cells. Toxicol Sci 91:476–483
Nair J, Strand S, Frank N, Knauft J, Wesch H, Galle PR, Bartsch H (2005) Apoptosis and age-dependent induction of nuclear and mitochondrial etheno-DNA adducts in Long-Evans Cinnamon (LEC) rats: enhanced DNA damage by dietary curcumin upon copper accumulation. Carcinogenesis 26:1307–1315
Ahsan H, Hadi SM (1998) Strand scission in DNA induced by curcumin in the presence of Cu(II). Cancer Lett 124:23–30
Singh S, Aggarwal BB (1995) Activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB is suppressed by curcumin (diferuloylmethane). J Biol Chem 270:24995–25000
Han SS, Chung ST, Robertson DA, Ranjan D, Bondada S (1999) Curcumin causes the growth arrest and apoptosis of B cell lymphoma by downregulation of egr-1, c-myc, bcl-XL, NF-kappaB, and p53. Clin Immunol 93:152–161
Jobin C, Bradham CA, Russo MP, Juma B, Narula AS, Brenner DA, Sartor RB (1999) Curcumin blocks cytokine-mediated NF-kappaB activation and proinflammatory gene expression by inhibiting inhibitory factor I-kappaB kinase activity. J Immunol 163:3474–3483
Koh HK (1991) Cutaneous melanoma. N Engl J Med 325:171–182
Manson MM, Gescher A, Hudson EA, Plummer SM, Squires MS, Prigent SA (2000) Blocking and suppressing mechanisms of chemoprevention by dietary constituents. Toxicol Lett 112–113:499–505
Mehta K, Pantazis P, McQueen T, Aggarwal BB (1997) Antiproliferative effect of curcumin (diferuloylmethane)against human breast tumor cell lines. Anticancer Drugs 8:470–481
Chanvorachote P, Pongrakhananon V, Wannachaiyasit S, Luanpitpong S, Rojanasakul Y, Nimmannit U (2009) Curcumin sensitizes lung cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis through superoxide anion-mediated Bcl-2 degradation. Cancer Invest 27:624–635
Ko LJ, Prives C (1996) p53: puzzle and paradigm. Genes Dev 10:1054–1072
Levine AJ (1997) p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88:323–331
Liu E, Wu J, Cao W, Zhang J, Liu W, Jiang X, Zhang X (2007) Curcumin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest in a p53-dependent manner and upregulates ING4 expression in human glioma. J Neurooncol 85:263–270
He ZY, Shi CB, Wen H, Li FL, Wang BL, Wang J (2011) Upregulation of p53 expression in patients with colorectal cancer by administration of curcumin. Cancer Invest 29:208–213
Chen HW, Huang HC (1998) Effect of curcumin on cell cycle progression and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 124:1029–1040
Masuelli L, Benvenuto M, Fantini M, Marzocchella L, Sacchetti P, Di Stefano E, Tresoldi I, Izzi V, Bernardini R, Palumbo C, Mattei M, Lista F, Galvano F, Modesti A, Bei R (2013) Curcumin induces apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines and delays the growth of mammary tumors in neu transgenic mice. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 27:105–119
Khaw AK, Hande MP, Kalthur G, Hande MP (2013) Curcumin inhibits telomerase and induces telomere shortening and apoptosis in brain tumour cells. J Cell Biochem 114:1257–1270
Bill MA, Nicholas C, Mace TA, Etter JP, Li C, Schwartz EB, Fuchs JR, Young GS, Lin L, Lin J, He L, Phelps M, Li PK, Lesinski GB (2012) Structurally modified curcumin analogs inhibit STAT3 phosphorylation and promote apoptosis of human renal cell carcinoma and melanoma cell lines. PLoS ONE 7:e40724
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappa B at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3:221–227
Raisova M, Hossini AM, Eberle J, Riebeling C, Wieder T, Sturm I, Daniel PT, Orfanos CE, Geilen CC (2001) The Bax/Bcl-2 ratio determines the susceptibility of human melanoma cells to CD95/Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Invest Dermatol 117:333–340
Sebolt-Leopold JS (2000) Development of anticancer drugs targeting the MAP kinase pathway. Oncogene 19:6594–6599
Rudolf E, Kralova V, Rudolf K, John S (2013) The role of p38 in irinotecan-induced DNA damage and apoptosis of colon cancer cells. Mutat Res 741–742:27–34
Cho HW, Park SK, Heo KW, Hur DY (2013) Methotrexate induces apoptosis in nasal polyps via caspase cascades and both mitochondria-mediated and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases/Jun N-terminal kinase pathways. Am J Rhinol Allergy 27:26–31
Yang CL, Ma YG, Xue YX, Liu YY, Xie H, Qiu GR (2012) Curcumin induces small cell lung cancer NCI-H446 cell apoptosis via the reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway and not the cell death receptor pathway. DNA Cell Biol 31:139–150
Acknowledgments
This project is supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81372916), the science and technology Department of Jiangsu province (No. BK20141142), the Science and Technology Department of Xuzhou city (No. XM13B084), the “Six Talent Peaks” Project of Jiangsu Province (No. 2013-WSN-014), and Xuzhou Medical Young Talents Project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, AJ., Jiang, G., Li, LT. et al. Curcumin induces apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway and caspases activation in human melanoma cells. Mol Biol Rep 42, 267–275 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3769-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3769-2