Abstract
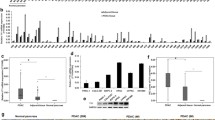
NF45, also referred to as nuclear factor of activated T cells, has been reported to promote the progression of multiple cancer types. However, the expression and physiological significance of NF45 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remain largely elusive. In this study, we investigated the clinical relevance and potential role of NF45 expression in PDAC development. Western blot analysis revealed that NF45 was remarkably upregulated in PDAC tissues, compared with the adjacent non-tumorous ones. In addition, the expression of NF45 in 122 patients with PDAC was evaluated using immunohistochemistry. In this way, we found that NF45 was abundantly expressed in PDAC tissues, and the expression of NF45 was correlated with tumor size (p = 0.007), histological differentiation (p = 0.033), and TNM stage (p = 0.001). Importantly, patients with low levels of NF45 expression exhibited better postoperative prognosis as compared with those with high NF45 expression. Furthermore, using PDAC cell cultures, we found that interference of NF45 expression using siRNA oligos suppressed PDAC cell proliferation and retarded cell cycle progression. Moreover, depletion of NF45 impaired the levels of cellular cyclin E and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Conversely, overexpression of NF45 facilitated the cell growth and accelerated cell cycle progression. Our results establish NF45 as an important indicator of PDAC prognosis with potential utility as a therapeutic target in this lethal disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N (2014) Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 371:1039–1049. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1404198
Schneider G, Siveke JT, Eckel F, Schmid RM (2005) Pancreatic cancer: basic and clinical aspects. Gastroenterology 128:1606–1625
Collisson EA, Sadanandam A, Olson P, Gibb WJ, Truitt M, Gu S, Cooc J, Weinkle J, Kim GE, Jakkula L, Feiler HS, Ko AH, Olshen AB, Danenberg KL, Tempero MA, Spellman PT, Hanahan D, Gray JW (2011) Subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and their differing responses to therapy. Nat Med 17:500–503. doi:10.1038/nm.2344
Edlund H (2002) Pancreatic organogenesis—developmental mechanisms and implications for therapy. Nat Rev Genet 3:524–532. doi:10.1038/nrg841
Kao PN, Chen L, Brock G, Ng J, Kenny J, Smith AJ, Corthesy B (1994) Cloning and expression of cyclosporin A- and FK506-sensitive nuclear factor of activated T-cells: NF45 and NF90. J Biol Chem 269:20691–20699
Reichman TW, Muniz LC, Mathews MB (2002) The RNA binding protein nuclear factor 90 functions as both a positive and negative regulator of gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol 22:343–356. doi:10.1128/mcb.22.1.343-356.2002
Zhao G, Shi L, Qiu D, Hu H, Kao PN (2005) NF45/ILF2 tissue expression, promoter analysis, and interleukin-2 transactivating function. Exp Cell Res 305:312–323. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.12.030
Sakamoto S, Aoki K, Higuchi T, Todaka H, Morisawa K, Tamaki N, Hatano E, Fukushima A, Taniguchi T, Agata Y (2009) The NF90–NF45 complex functions as a negative regulator in the microRNA processing pathway. Mol Cell Biol 29:3754–3769. doi:10.1128/MCB.01836-08
Stricker RL, Behrens SE, Mundt E (2010) Nuclear factor NF45 interacts with viral proteins of infectious bursal disease virus and inhibits viral replication. J Virol 84:10592–10605. doi:10.1128/JVI.02506-09
Isken O, Baroth M, Grassmann CW, Weinlich S, Ostareck DH, Ostareck-Lederer A, Behrens SE (2007) Nuclear factors are involved in hepatitis C virus RNA replication. RNA 13:1675–1692. doi:10.1261/rna.594207
Huang Q, He X, Qiu X, Liu X, Sun G, Guo J, Ding Z, Yang L, Ban N, Tao T, Wang D (2014) Expression of NF45 correlates with malignant grade in gliomas and plays a pivotal role in tumor growth. Tumour Biol 35:10149–10157. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2310-5
Shamanna RA, Hoque M, Pe’ery T, Mathews MB (2012) Induction of p53, p21 and apoptosis by silencing the NF90/NF45 complex in human papilloma virus-transformed cervical carcinoma cells. Oncogene 32:5176–5185. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.533
Ni S, Zhu J, Zhang J, Zhang S, Li M, Ni R, Liu J, Qiu H, Chen W, Wang H, Guo W (2014) Expression and clinical role of NF45 as a novel cell cycle protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Tumor Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2683-5
Graber TE, Baird SD, Kao PN, Mathews MB, Holcik M (2010) NF45 functions as an IRES trans-acting factor that is required for translation of cIAP1 during the unfolded protein response. Cell Death Differ 17:719–729. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.164
Faye MD, Graber TE, Liu P, Thakor N, Baird SD, Durie D, Holcik M (2013) Nucleotide composition of cellular internal ribosome entry sites defines dependence on NF45 and predicts a posttranscriptional mitotic regulon. Mol Cell Biol 33:307–318. doi:10.1128/MCB.00546-12
Haselmann V, Kurz A, Bertsch U, Hubner S, Olempska-Muller M, Fritsch J, Hasler R, Pickl A, Fritsche H, Annewanter F, Engler C, Fleig B, Bernt A, Roder C, Schmidt H, Gelhaus C, Hauser C, Egberts JH, Heneweer C, Rohde AM, Boger C, Knippschild U, Rocken C, Adam D, Walczak H, Schutze S, Janssen O, Wulczyn FG, Wajant H, Kalthoff H, Trauzold A (2014) Nuclear death receptor TRAIL-R2 inhibits maturation of let-7 and promotes proliferation of pancreatic and other tumor cells. Gastroenterology 146:278–290. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.10.009
Wolfgang CL, Herman JM, Laheru DA, Klein AP, Erdek MA, Fishman EK, Hruban RH (2013) Recent progress in pancreatic cancer. CA Cancer J Clin 63:318–348. doi:10.3322/caac.21190
Costello E, Greenhalf W, Neoptolemos JP (2012) New biomarkers and targets in pancreatic cancer and their application to treatment. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:435–444. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2012.119
Kern SE, Shi C, Hruban RH (2011) The complexity of pancreatic ductal cancers and multidimensional strategies for therapeutic targeting. J Pathol 223:295–306. doi:10.1002/path.2813
Guan D, Altan-Bonnet N, Parrott AM, Arrigo CJ, Li Q, Khaleduzzaman M, Li H, Lee CG, Pe’ery T, Mathews MB (2008) Nuclear factor 45 (NF45) is a regulatory subunit of complexes with NF90/110 involved in mitotic control. Mol Cell Biol 28:4629–4641. doi:10.1128/MCB.00120-08
Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Maitra A, Olsen M, Lowe AW, van Heek NT, Rosty C, Walter K, Sato N, Parker A, Ashfaq R, Jaffee E, Ryu B, Jones J, Eshleman JR, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Kern SE, Hruban RH, Brown PO, Goggins M (2003) Exploration of global gene expression patterns in pancreatic adenocarcinoma using cDNA microarrays. Am J Pathol 162:1151–1162. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63911-9
Cartier J, Berthelet J, Marivin A, Gemble S, Edmond V, Plenchette S, Lagrange B, Hammann A, Dupoux A, Delva L, Eymin B, Solary E, Dubrez L (2011) Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein-1 (cIAP1) can regulate E2F1 transcription factor-mediated control of cyclin transcription. J Biol Chem 286:26406–26417. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.191239
Bharadwaj U, Li M, Chen C, Yao Q (2008) Mesothelin-induced pancreatic cancer cell proliferation involves alteration of cyclin E via activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription protein 3. Mol Cancer Res 6:1755–1765. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0095
Skalicky DA, Kench JG, Segara D, Coleman MJ, Sutherland RL, Henshall SM, Musgrove EA, Biankin AV (2006) Cyclin E expression and outcome in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 15:1941–1947. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0319
Reichman TW, Parrott AM, Fierro-Monti I, Caron DJ, Kao PN, Lee CG, Li H, Mathews MB (2003) Selective regulation of gene expression by nuclear factor 110, a member of the NF90 family of double-stranded RNA-binding proteins. J Mol Biol 332:85–98
Kuwano Y, Pullmann R Jr, Marasa BS, Abdelmohsen K, Lee EK, Yang X, Martindale JL, Zhan M, Gorospe M (2010) NF90 selectively represses the translation of target mRNAs bearing an AU-rich signature motif. Nucleic Acids Res 38:225–238. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp861
Kenneth NS, Duckett CS (2012) IAP proteins: regulators of cell migration and development. Curr Opin Cell Biol 24:871–875. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2012.11.004
Vogler M, Durr K, Jovanovic M, Debatin KM, Fulda S (2007) Regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by XIAP in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Oncogene 26:248–257. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209776
Vogler M, Walczak H, Stadel D, Haas TL, Genze F, Jovanovic M, Bhanot U, Hasel C, Moller P, Gschwend JE, Simmet T, Debatin KM, Fulda S (2009) Small molecule XIAP inhibitors enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis and antitumor activity in preclinical models of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 69:2425–2434. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2436
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Martin Holcik of University of Ottawa for kindly offering us the pcDNA3-Flag-NF45 construct. This work was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (No. 81072028) and Jiangsu Province’s Outstanding Medical Academic Leader program (No. LJ101135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Chunhua Wan and Chen Gong have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, C., Gong, C., Ji, L. et al. NF45 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and enhanced cell proliferation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem 410, 25–35 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2535-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2535-7