Abstract
Context
The role of agricultural landscapes in biodiversity conservation is an emerging topic in a world experiencing a worrying decrease of species richness. Farm systems may either decrease or increase biological diversity, depending on land-use intensities and management.
Objectives
We present an intermediate disturbance-complexity model (IDC) of cultural landscapes aimed at assessing how different levels of anthropogenic disturbance on ecosystems affect the capacity to host biodiversity depending on the land matrix heterogeneity. It is applied to the Mallorca Island, amidst the Mediterranean biodiversity hotspot.
Methods
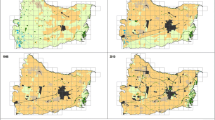
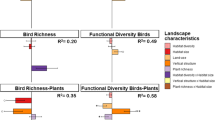
The model uses the disturbance exerted when farmers alter the Net Primary Production through land-use change as well as when they remove a share of it (HANPP), together with Shannon–Wiener index (H′) of land-cover diversity. The model is tested with a twofold-scalar experimental design (1:50,000 and 1:5000) of a set of landscape units along three time points (1956, 1989, 2011). Species richness of breeding and wintering birds, taken as a biodiversity proxy, is used in an exploratory factor analysis.
Results
The results clearly show that when intermediate levels of HANPP are performed within intermediate levels of complexity (H′) in landscape patterns, like agro-forest mosaics, great bird species richness and high socio-ecological resilience can be maintained. Yet, these complex-heterogeneous landscapes are currently vanishing due to industrial farm intensification, rural abandonment and urban sprawl.
Conclusions
The results make apparent the usefulness of transferring the concept of intermediate disturbance-complexity interplay to cultural landscapes. Our spatial-explicit IDC model can be used as a tool for strategic environmental assessment of land-use planning.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnoletti M (ed) (2006) The conservation of cultural landscapes. CABI Pub, Wallingford
Agnoletti M (2014) Rural landscapes, nature conservation and culture. Some notes on research trends and management approaches from a (southern) European perspective. Landsc Urb Plan 126:66–73
Altieri M (1999) The ecological role of biodiversity in agroecosystems. Agr Ecosyst Environ 74:19–31
Antrop M (2006) Sustainable landscapes: contradiction, fiction or utopia? Landsc Urb Plan 75:187–197
Barnes B, Sidhu HS, Roxburgh SH (2006) A model integrating patch dynamics, competing species and the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Ecol Model 194:414–420
Bengtsson J, Angelstam P, Elmqvist T, Emanuelsson U, Folke C, Ihse M, Moberg F, Nystrom M (2003) Reserves, resilience and dynamic landscapes. Ambio 32(6):389–396
Benton TG, Vickery JA, Wilson JD (2003) Farmland biodiversity: is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends Ecol Evol 18:182–188
Berkes F (2007) Community-based conservation in a globalized world. P Natl Acad Sci USA 104(39):15188–15193
Bianchi FJJA, Booij CJH, Tscharntke T (2006) Sustainable pest regulation in agricultural landscapes: a review on landscape composition, biodiversity and natural pest control. Proc R Soc Lond B 273:1715–1727
Blitzer EJ, Dormann CF, Holzschuh A, Klein A, Rand TA, Tscharntke T (2012) Spillover of functionally important organisms between managed and natural habitats. Agric Ecosyst Environ 146:34–43
Blondel J, Aronson J, Bodiou J-Y, Boeuf G (2010) The Mediterranean region. Biological diversity though time and space. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Buckling A, Kassen R, Bell G, Rainey PB (2000) Disturbance and diversity in experimental microcosms. Nature 408:961–964
Cardinale BJ, Duffy JE, Gonzalez A, Hooper DU, Perrings C, Venail P, Narwani A, Mace GM, Tilman D, Wardle DA, Kinzig AP, Daily GC, Loreau M, Grace JB, Larigauderie A, Srivastava D, Naeem S (2012) Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 486:59–67
Cattell RB (1966) The scree test for the number of factors. Multivar Behav Res 1:245–276
Chesson P, Huntly N (1997) The roles of disturbance, mortality, and stress in the dynamics of ecological communities. Am Nat 150:519–553
Collins SL, Glenn SM (1997) Intermediate disturbance and its relationship to within and between-patch dynamics. N Z J Ecol 21(1):103–110
Connell JH (1978) Diversity in tropical rain forest and coral reefs. High diversity of trees and corals is maintained only in a nonequilibrium state. Science 199:1302–1309
Costello AB, Osborne JW (2005) Best practices in exploratory factor analysis: four recommendations for getting the most from your analysis. Pract Assess Res Eval 10(7):1–9
Cusens J, Wright SD, McBride PD, Gillman LN (2012) What is the form of the productivity–animal–species-richness relationship? A critical review and meta-analysis. Ecology 93(10):2241–2252
Dale VH, Efroymson RA, Kline KL (2011) The land use-climate change-energy nexus. Landscape Ecol 26:755–773
Darlington RB, Weinberg SL, Walberg HJ (1973) Canonical variate analysis and related techniques. Rev Educ Res 43(4):433–454
De Groot R (2006) Function-analysis and valuation as a tool to assess land use conflicts in planning for sustainable, multi-functional landscapes. Landsc Urb Plan 75:175–186
Dial R, Roughgarden J (1998) Theory of marine communities: the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. Ecology 79:1412–1424
Donald RF, Green RE, Heath MF (2001) Agricultural intensification and the collapse of Europe’s farmland bird populations. Proc R Soc Lond B 268:25–29
Elmqvist T, Folke C, Nyström M, Peterson G, Bengtsson J, Walker B, Norberg J (2003) Response diversity, ecosystem change, and resilience. Front Ecol Environ 1:488–494
Fahrig L, Jonsen I (1998) Effect of habitat patch characteristics on abundance and diversity of insects in an agricultural landscape. Ecosystems 1(2):197–205
Farina A (1997) Landscape structure and breeding bird distribution in a sub-Mediterranean agroecosystem. Landscape Ecol 12:365–378
Farina A (2000) The cultural landscape as a model for the integration of ecology and economics. Bioscience 50:313–320
Firbank LG, Petit S, Smart S, Blain A, Fuller RJ (2008) Assessing the impacts of agricultural intensification on biodiversity: a British perspective. Philos Trans R Soc B 363:777–787
Fischer J, Brosi B, Daily GC, Ehrlich PR, Goldman R, Goldstein J, Lindenmayer DB, Manning AD, Mooney HA, Pejchar L, Ranganathan J, Tallis H (2008) Should agricultural policies encourage land sparing or wildlife-friendly farming? Front Ecol Environ 6(7):380–385
Fischer-Kowalski M, Haberl H (eds) (2007) Socioecological transitions and global change. Trajectories of social metabolism and land use. Edward Elgar, Cheltenham
Folke C (2006) Resilience: the emergence of a perspective for social-ecological systems analyses. Glob Environ Change 16(3):253–267
Forman RTT (1995) Some general principles of landscape and regional ecology. Landscape Ecol 10:133–142
Fox WF (2013) The intermediate disturbance hypothesis should be abandoned. Trends Ecol Evol 28(2):86–92
Gabriel D, Roschewitz I, Tscharntke T, Thies C (2006) Beta diversity at different spatial scales: plant communities in organic and conventional agriculture. Ecol Appl 16:2011–2021
Gerard F, Petit S, Smith G, Thomson A, Brown N, Manchester S, Wadsworth R, Bugar G, Halada L, Bezák P, Boltiziar M, De badts E, Halabuk A, Mojses M, Petrovic F, Gregor M, Hazeu G, Mücher CA, Wachowicz M, Huitu H, Tuominen S, Pino J, Pons X, Rodà F, Roscher M, Feranec J (2010) Land cover change in Europe between 1950 and 2000 determined employing aerial photography. Prog Phys Geogr 34:183–205
Gliessman SR (ed) (1990) Agroecology: researching the ecological basis for sustainable agriculture. Springer, New York
GOB (2008) Atles dels Aucells Nidificants de Mallorca i Cabrera 2003-2007. Grup Balear d’Ornitologia i Defensa de la Naturalesa, Palma de Mallorca
Godfray HCJ, Beddington JR, Crute IR, Haddad L, Lawrence D, Muir JF, Pretty J, Robinson S, Thomas SM, Toulim C (2010) Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 327:812–818
Gomiero T, Paoletti MG, Pimentel D (2008) Energy and environmental issues in organic and conventional agriculture. Crit Rev Plant Sci 27:239–254
Green RE, Cornell SJ, Scharlemann JPW, Balmford A (2005) Farming and the fate of wild nature. Science 307:550–551
Haberl H (2001) The energetic metabolism of societies. Part I: Accounting concepts. J Ind Ecol 5:107–136
Haberl H, Schulz NB, Plutzar C, Erb KH, Krausmann F, Loibl W, Moser D, Sauberer N, Weisz H, Zechmeister HG, Zulka P (2004) Human appropriation of net primary production and species diversity in agricultural landscapes. Agric Ecosyst Environ 102:213–218
Haberl H, Erb KH, Krausmann F, Gaibe V, Bondeau A, Plutzar C, Gingrich S, Lucht W, Fischer-Kowalski M (2007) Quantifying and mapping the human appropriation of net primary production in earth’s terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(34):12942–12947
Harper KA, Macdonald SE, Burton P, Chen J, Brosofsky KD, Saunders S, Euskirchen ES, Roberts D, Jaiteh M, Esseen P-A (2005) Edge influence on forest structure and composition in fragmented landscapes. Conserv Biol 19:768–782
Hawkins BA, Field R, Cornell HV, Currie DJ, Guégan J-F, Kaufman DM, Kerr JT, Mittelbach GG, Oberdorff T, O'Brien EM, Porter EE, Turner JRG (2003) Energy, water, and broad-scale geographic patterns of species richness. Ecology 84(12):3105–3117
Heikkinen RK, Luoto M, Virkkala R, Rainio K (2004) Effects of habitat cover, landscape structure and spatial variables on the abundance of birds in an agricultural–forest mosaic. J Appl Ecol 41:824–835
Helming K, Perez-Soba M, Tabbush P (eds) (2007) Sustainability impact assessment of land use changes. Springer, New York
Huston MA (2014) Disturbance, productivity, and species diversity: empiricism vs. logic in ecological theory. Ecology 95(9):2382–2396
Inger R, Gregory R, Duffy JP, Scott I, Voříšek P, Gaston KJ (2014) Common European birds are declining rapidly while less abundant species’ numbers are rising. Ecol Lett. doi:10.1111/ele.12387
Kaiser HF (1960) The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas 20:141–151
Lambin EF, Geist H (eds) (2006) Land-use and land-cover change: local processes and global impacts. Springer, New York
Lang DJ, Wiek A, Bergmann M, Stauffacher M, Martens P, Moll P, Swilling M, Thomas CJ (2012) Transdisciplinary research in sustainability science: practice, principles, and challenges. Sustain Sci 7(1):25–43
Li B-L (2000) Why is the holistic approach becoming so important in landscape ecology? Landsc Urb Plan 50:27–41
Lindenmayer D, Cunningham S (2013) Six principles for managing forests as ecologically sustainable ecosystems. Landscape Ecol 28:1099–1110
Loreau M (2000) Are communities saturated? On the relationship between α, β and γ diversity. Ecol Lett 3:73–76
Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P, Bengtsson J, Grime JP, Hector A, Hooper DU, Huston MA, Raffaelli D, Schmid B, Tilman D, Wardle DA (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: current knowledge and future challenges. Science 294:804–808
Loreau M, Mouquet N, Gonzalez A (2003) Biodiversity as spatial insurance in heterogeneous landscapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(22):12765–12770
Margalef R (2006) Ecological theory and prediction in the study of the interaction between man and the rest of biosphere. Medi Ambient Tecnologia i Cultura 38:114–125
Marull J, Mallarach JM (2005) A new GIS methodology for assessing and predicting landscape and ecological connectivity: applications to the Metropolitan Area of Barcelona (Catalonia, Spain). Landsc Urban Plan 71:243–262
Marull J, Pino J, Mallarach JM, Cordobilla MJ (2007) A land suitability index for strategic environmental assessment in metropolitan areas. Landsc Urban Plan 81:200–212
Marull J, Pino J, Tello E, Cordobilla MJ (2010) Social metabolism, landscape change and land-use planning in the Barcelona Metropolitan Region. Land Use Policy 27:497–510
Marull J, Tello E, Wilcox PT, Coll F, Pons M, Warde P, Valldeperas N, Ollés A (2014) Recovering the landscape history behind a Mediterranean edge environment (The Congost Valley, Catalonia, 1854–2005): the importance of agroforestry systems in biological conservation. Appl Geogr 54:1–17
Marull J, Tello E, Fullana N, Murray I, Jover G, Font C, Coll F, Domene E, Leoni V, Decolli T (2015a) Long-term socio-ecological transition at different spatial scales: Exploring the intermediate disturbance hypothesis in cultural landscapes (Mallorca, 1856–2012). Biodivers Conserv. doi:10.1007/s10531-015-0955-z
Marull J, Font C, Padró R, Tello E, Panazzolo A (2015b) Energy–Landscape Integrated Analysis: A proposal for measuring complexity in internal agro-ecosystem pr ocesses (Barcelona Metropolitan Region, 1860–2000). Ecol Model (submitted)
Matson PA, Vitousek PM (2006) Agricultural Intensification: will land spared from farming be land spred for nature? Conserv Biol 20(3):709–710
Matson PA, Parton WJ, Power AG, Swift MJ (1997) Agricultural intensification and ecosystem properties. Science 277:504–509
Matthews R, Selman P (2006) Landscape as a focus for integrating human and environmental processes. J Agric Econ 57:121–199
McDonnell MJ, Pickett STA (eds) (1993) Humans as components of ecosystems. The ecology of subtle human effects and populated areas. Springer, New York
Miller A, Reilly D, Bauman S, Shea K (2012) Interactions between frequency and size of disturbance affect competitive outcomes. Ecol Res 27:783–791
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GAB, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 403:853–858
Padisak J (1993) The influence of different disturbance frequencies on the species richness, diversity and equitability of phytoplankton in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 249:135–156
Parcerisas L, Marull J, Pino J, Tello E, Coll F, Basnou C (2012) Land use changes, landscape ecology and their socioeconomic driving forces in the Spanish Mediterranean coast (El Maresme County, 1850–2005). Environ Sci Policy 23:123–132
Perfecto I, Vandermeer J (2010) The agroecological matrix as alternative to the land-sparing/agriculture intensification model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(13):5786–5791
Phalan B, Onial M, Balmford A, Green RE (2011) Reconciling food production and biodiversity conservation: land sharing and land sparing compared. Science 333:1289–1291
Pickett STA, White PS (1985) The ecology of natural disturbance and patch dynamics. Academic Press, London
Pierce S (2014) Implications for biodiversity conservation of the lack of consensus regarding the humped-back model of species richness and biomass production. Funct Ecol 28:253–257
Pino J, Marull J (2012) Ecological networks: are they enough for connectivity conservation? A case study in the Barcelona Metropolitan Region (NE Spain). Land Use Policy 29:684–690
Reynolds CS (1995) The intermediate disturbance hypothesis and its applicability to planktonic communities. Comments on the views expressed in Padisak vs. Wilson. N Z J Ecol 19:219–225
Rindfuss RR, Walsh SJ, Turner BL, Fox J, Mishra V (2008) Developing a science of land change: challenges and methodological issues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(39):13976–13981
Roxburgh SH, Shea K, Wilson JB (2004) The intermediate disturbance hypothesis, patch dynamics and mechanisms of species coexistence. Ecology 85:359–371
Sasaki T, Okubo S, Okayasu T, Jamsran U, Ohkuro T, Takeuchi K (2009) Management applicability of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis across Mongolian rangeland ecosystems. Ecol Appl 19(2):423–432
Schröter D, Cramer W, Leemans R, Prentice IC, Araújo MB, Arnell NW, Bondeau A, Bugmann H, Carter TR, Gracia CA, de la Vega-Leinert AC, Erhard M, Ewert F, Glendining M, House JI, Kankaanpää S, Klein RJ, Lavorel S, Lindner M, Metzger MJ, Meyer J, Mitchell TD, Reginster I, Rounsevell M, Sabaté S, Sitch S,Smith B, Smith J, Smith P, Sykes MT, Thonicke K, Thuiller W, Tuck G, Zaehle S, Zierl B (2005) Ecosystem service supply and vulnerability to global change in Europe. Science 310:1333–1337
Schwarzlmüller E (2009) Human appropriation of aboveground net primary production in Spain, 1955–2003: an empirical analysis of the industrialization of land use. Ecol Econ 69(2):282–291
Shea K, Chesson P (2002) Community ecology theory as a framework for biological invasions. Trends Ecol Evol 17:170–176
Shea K, Roxburgh SH, Rauschert ESJ (2004) Moving from pattern to process: coexistence mechanisms under intermediate disturbance regimes. Ecol Lett 7:491–508
Sheil D, Burslem D (2003) Disturbing hypotheses in tropical forests. Trends Ecol Evol 18:18–26
Shreeve TG, Dennis RLH, Van Dick H (2004) Resources, habitats and metapopulations—whither reality? Oikos 106:404–408
Sirami C, Brotons L, Burfield I, Fonderflick J, Martin J-L (2008) Is land abandonment having an impact on biodiversity? A meta-analytical approach to bird distribution changes in the north-western Mediterranean. Biol Conserv 141(2):450–459
Svensson JR, Lindegarth M, Jonsson PR, Pavia H (2012) Disturbance-diversity models: what do they really predicst and how are tested? Proc R Soc Lond B 279:2163–2170
Swift MJ, Izac AMN, van Noordwijk M (2004) Biodiversity and ecosystem services in agricultural landscapes—are we asking the right questions? Agric Ecosyst Environ 104(1):113–134
Tilman D (1994) Competition and biodiversity in spatially structured habitats. Ecology 75(1):2–16
Tilman D, Cassman KG, Matson PA, Naylor R, Polasky S (2002) Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 418:671–677
Tischendorf L (2001) Can landscape indices predict ecological processes consistently? Landscape Ecol 16:235–254
Tress B, Tress G, Décamps H, d’Hauteserre AM (2001) Bridging human and natural sciences in landscape research. Landsc Urban Plan 57:137–141
Tscharntke T, Klein AM, Kruess A, Steffan-Dewenter I, Thies C (2005) Landscape perspectives on agricultural intensification and biodiversity-ecosystem service management. Ecol Lett 8:857–874
Tscharntke T, Clough Y, Wanger TC, Jackson L, Motzke I, Perfecto I, Vandermeer J, Whitbread A (2012) Global food security, biodiversity conservation and the future of agricultural intensification. Biol Conserv 151:53–59
Turner MG (2005) Landscape ecology: what is the state of the science? Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 36:319–344
Turner BL, Robbins P (2008) Land-change science and political ecology: similarities, differences, and implications for sustainability science. Annu Rev Environ Resour 33:295–316
Turner BL, Lambin EF, Reenberg A (2007) The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(52):20666–20671
Turner MG, Donato DC, Romme WH (2013) Consequences of spatial heterogeneity for ecosystem services in changing forest landscapes: priorities for future research. Landscape Ecol 28:1081–1097
Van der Maarel E (1993) Some remarks on disturbance and its relations to diversity and stability. J Veg Sci 4:733–736
Verburg PH, van de Steeg J, Veldkamp A, Willemen L (2009) From land cover change to land function dynamics: a major challenge to improve land characterization. J Environ Manag 90:1327–1335
Wilkinson DM (1999) The disturbing history of intermediate disturbance. Oikos 84(1):145–147
Wilson JB (1994) The ‘intermediate disturbance hypothesis’ of species coexistence is based in on patch dynamics. N Z J Ecol 18:176–181
Wrbka T, Erb KH, Schulz NB, Peterseil J, Hahn C, Haberl H (2004) Linking pattern and process in cultural landscapes. An empirical study based on spatially explicit indicators. Land Use Policy 21:289–306
Wu JG (2013) Landscape sustainability science: ecosystem services and human well-being in changing landscapes. Landscape Ecol 28:999–1023
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Spanish research project HAR2012-38920-C02-02, and the international Partnership Grant SSHRC- 895-2011-1020 on ‘Sustainable farm systems: long-term socio-ecological metabolism in western agriculture’ funded by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marull, J., Font, C., Tello, E. et al. Towards an energy–landscape integrated analysis? Exploring the links between socio-metabolic disturbance and landscape ecology performance (Mallorca, Spain, 1956–2011). Landscape Ecol 31, 317–336 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0245-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0245-x