Abstract
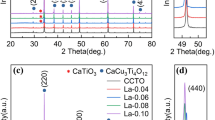
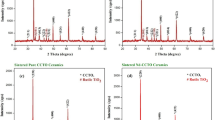
Cobalt-doped CCTO (CaCu3Ti4O12) ceramics were prepared by a conventional sol–gel synthesis method and the effects of Cobalt doping on the microstructures and dielectrical properties were investigated. The phase composition and microstructure were studied by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and high resolution scanning electron microscopy (HRSEM). Efficient crystalline phase formation accompanied by Cobalt induced lattice constant expansion was confirmed through XRD studies. HRSEM results show that doping effectively enhanced grain growth or densification. A compositional study reveals the variation of Cobalt diffusion in CCTO structure by the reduction of Ti presence according to the doping ratio. The dielectric constant reached a value as high as (εr = 25,400 at 1,000 and εr = 111,000 at 1,050 °C) at a cobalt-doping concentration of x = 0.2 at low frequency (50 Hz). The dielectrical constant and dielectric loss of the pure and cobalt-doped CCTO ceramics was measured for different concentrations and discussed in detail.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang T, Lin W, Lin C (2007) Phys Rev B 76:045115-8
Home CC, Vogt T, Shapiro SM, Wakimoto S, Ramirez AP (2001) Science 293:673–676
Kant C, Rudolf T, Mayr F, Krohns S, Lunkenheimer P, Ebbinghaus SG, Loidl A (2008) Phys Rev B 77:045131–045137
Liu P, He Y, Li J, Zhu GQ, Bian XB (2007) Acta Phys Sin 56:5489–5493
Subramanian MA, Sleight AW (2002) Solid State Sci 4:347–351
Ke SM, Huang HT, Fan HQ (2006) Appl Phys Lett 89:182904-3
Zhu Y, Zheng JC, Wu L, Frenkel AI, Hanson J, Northrup P, Ku W (2007) Phys Rev Lett 99:037602–037604
Subramanian MA, Dong L, Duan N, Reisner BA, Sleight AW (2000) J Solid State Chem 151:323–325
Carazeanu Popovici I, Prodan G (2012) J Sol-Gel Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s10971-012-2807-6
Capsoni D, Bini M, Massarotti V, Chiodelli G, Mozzati MC, Azzoni CB (2004) J Solid State Chem 177:4494–4500
Kobayashi W, Teresaki I (2003) Physica B 329:771–772
Xu D, Zhang C, Lin Y, Jiao L, Yuan H, Zhao G, Cheng X (2012) J Alloy Comp 522:157–161
Xu LF, Qi PB, Chen SS, Wang RL, Yang CP (2012) Mat Sci Eng B 177:494–498
Li M, Chen XL, Zhang DF, Wang WY, Wang WJ (2010) Sens Actuators B 147:447–452
Mu C, Zhang H, He Y, Liu P (2010) Physica B 405:386–389
Fang L, Shen M, Zheng F, Li Z, Yang J (2008) J Appl Phys 104:064110-8
Sulaiman M, Hutagalung D, Fadzil Ain M, Ahmad A (2010) J Alloy Comp 493:486–492
Jesurani S, Kanagesan S, Kalaivani T, Ashok K (2012) J Mater Sci Mater Electron 23:692–696
Chunhong MU, Huaiwu Z, Yingli L, Yuanqiang S, Peng L (2010) J Rare Earths 28:43–47
Dronskowski R (2007) Computational chemistry of solid state materials. Wiley, London, pp 13–16
Ouyang G, Yang GW, Sun CQ, Zhu WG (2008) Small 4:1359
Ouyang G, Zhu WG, Sun CQ, Zhu ZM, Liao SZ (2010) Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:1543–1549
West AR, Adams TB, Morrison FD, Sinclair DC (2004) J Eur Ceram Soc 24:1439–1448
Irvine JTS, Sinclair DC, West AR (1990) Adv Mater 2:132
Mandal KD, Rai AK, Singh L, Parkash O (2012) Bull Mater Sci 35:433–438
Mu CH, Zhang HW, He Y, Shen J, Liu P (2009) J Phys D Appl Phys 42:175410
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the University Grants Commission—New Delhi (ETFTNMK 097-FIP-XI Plan) under the Faculty improvement programme XI Plan. We thank SRM University for providing the Nanotechnology Center Facilities. We wish to acknowledge DST-FIST (India)—SR/FST/PS1-155/2010 for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jesurani, S., Kanagesan, S. & Ashok, K. Microstructure and dielectrical responses of pure and cobalt-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 ceramics by sol–gel synthesis route. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 64, 335–341 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2862-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-012-2862-z