Abstract
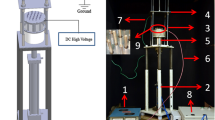
Random and highly aligned bead-free chitosan nanofibers (NFs) were successfully prepared via electrospinning by keeping the applied voltage (22 kV), flow rate (0.4 mL h−1), needle diameter (0.8 mm), and needle to collector distance (100 mm) constant while varying the solution concentration and collector rotation speed. No electrospinning was observed for lower solution concentrations, i.e., 1–3 wt% (w/v), whereas a decrease in the number and size of beads and microspheres, and bead-free NFs were obtained when the concentration of solution was increased from 4 to 6 wt%. Increase in the polymer concentration increased the solution viscosity (from 3.53 to 243 mPa s) and conductivity (from 29.80 to 192.00 μs cm−1) to critical values, which led to beadless NFs. The optimized conditions (i.e., concentration of solution 6 wt%, applied electrical potential 22 kV, flow rate 0.4 mL h−1, needle diameter 0.8 mm, and needle to collector distance 100 mm) were further used for the alignment of chitosan NFs. The alignment of the NFs increased from 35.6 to 94.4 % and the diameter decreased from 163.9 to 137.4 nm as the rotation speed of the cylindrical collector drum was increased from 2.09 to 21.98 m s−1. The aligned and small diameter chitosan NFs might find potential applications in biomedical, environmental, solar fuel cell applications, etc. Several target devices and polymer systems in the literature have been used to obtain aligned NFs; however, almost no work has been reported on individual chitosan alignment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greiner A, Wendorff JH (2007) Electrospinning: a fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:5670–5703
Cooley JF (1902) Apparatus for electrically dispersing fluids. US Patent 692,631
Formhals A (1934) Process and apparatus for preparing artificial threads. US Patent 1,975,504
Doshi J, Reneker DH (1995) Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J Electrost 35:151–160
Reneker DH, Chun I (1996) Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 7:216–223
Jian F, Xungai W, Tong L (2011) Functional applications of electrospun nanofibers. In: Lin T (ed) Nanofibers: production, properties and functional applications. InTech, Rijeka, pp 287–326
Li D, Xia Y (2004) Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel? Adv Mater 16:1151–1170
Usman A, Yaqiong Z, Xungai W, Tong L (2011) Electrospinning of continuous nanofiber bundles and twisted nanofiber yarns. In: Lin T (ed) Nanofibers: production, properties and functional applications. InTech, Rijeka, pp 420–427
Ohkawa K, Cha D, Kim H, Nishida A, Yamamoto H (2004) Electrospinning of chitosan. Macromol Rapid Commun 25:1600–1605
Buchko CJ, Chen LC, Shen Y, Martin DC (1999) Processing and microstructural characterization of porous biocompatible protein polymer thin films. Polymer 40:7397–7407
Qin XH, Wang SY (2006) Filtration properties of electrospinning nanofibers. J Appl Polymer Sci 102:1285–1290
Zahedia P, Rezaeiana I, Ranaei-Siadatb SO, Jafaria SH, Supaphol PA (2010) Review on wound dressings with an emphasis on electrospun nanofibrous polymeric bandages. Polym Adv Technol 21:77–95
Yu DG, Zhu LM, White K, White CB (2009) Electrospun nanofiber-based drug delivery systems. Health 1:67–75
Pham QP, Sharma U, Mikos AG (2006) Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: a review. Tissue Eng 12:1197–1211
Shim HS, Kim JW, Kim WB (2009) Fabrication and optical properties of conjugated polymer composited multi-arrays of TiO2 nanowires via sequential electrospinning. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:4721–4726
Liao IC, Chew SY, Leong KW (2006) Aligned core-shell Nanofibers delivering bioactive proteins. Nanomedicine (Lond) 1:465–471
Tamura T, Kawakami H (2010) Aligned electrospun nanofiber composite membranes for fuel cell electrolytes. Nano Lett 10:1324–1328
Meng ZX, Wang YS, Ma C, Zheng W, Li L, Zheng YF (2010) Electrospinning of PLGA/gelatin randomly-oriented and aligned nanofibers as potential scaffold in tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 30:1204–1210
Theron A, Zussman E, Yarin AL (2001) Electrostatic field-assisted alignment of electrospun nanofibers. Nanotechnology 12:384–390
Bhattarai N, Edmondson D, Veiseh O, Matsen FA, Zhang M (2005) Electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers and their cellular compatibility. Biomaterials 26:6176–6184
Cooper A, Jana S, Bhattarai N, Zhang M (2010) Aligned chitosan-based nanofibers for enhanced myogenesis. J Mater Chem 20:8904–8911
NASA Langley’s (2008) Highly aligned electrospun fibers and mats. NP-2008-04-77-LaRC:1(4). http://technologygateway.nasa.gov/docs/TOA_LARC04_AlignElectroNano_16web.pdf. Accessed 11 Aug 2012
Sundaray B, Subramanian V, Natarajan TS, Xiang RZ, Chang CC, Fann WS (2004) Electrospinning of continuous aligned polymer fibers. Appl Phys Lett 84:1222–1224
Katta P, Alessandro M, Ramsier RD, Chase GG (2004) Continuous electrospinning of aligned polymer nanofibers onto a wire drum collector. Nano Lett 4:2215–2218
Chuangchote S, Supaphol P (2006) Fabrication of aligned poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers by electrospinning. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 6:125–129
Khamforoush M, Mahjob M (2011) Modification of the rotating jet method to generate highly aligned electrospun nanofibers. Mater Lett 65:453–455
Park SH, Yang DY (2011) Fabrication of aligned electrospun nanofibers by inclined gap method. J Appl Polymer Sci 120:1800–1807
Afifi AM, Yamamoto M, Yamane H, Kimura Y, Salmawy AE, Nakano S (2011) Electrospinning and characterization of aligned nanofibers from chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol mixtures: comparison of several target devices newly designed. Sen-I Gakkaishi 67:103–108
Mincheva R, Manolova N, Rashkov I (2007) Bicomponent aligned nanofibers of N-carboxyethyl chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol). Eur Polym J 43:2809–2818
Haider S, Park SY (2009) Preparation of the electrospun chitosan nanofibers and their applications to the adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from an aqueous solution. J Membr Sci 328:90–96
Taylor G (1969) Electrically driven jets. Proc R Soc Lond A 313:453–475
Ramakrishna S, Fujihara K, Teo WE, Lim TC, Ma Z (2005) Introduction to electrospinning and nanofibers. World Scientific, Singapore
Liu Y, He JH, Yu JY, Zeng HM (2008) Controlling numbers and sizes of beads in electrospun nanofibers. Polym Int 57:632–636
Kriegel C, Kit KM, McClements DJ, Weiss J (2009) Electrospinning of chitosan–poly(ethylene oxide) blend nanofibers in the presence of micellar surfactant solutions. Polymer 50:189–200
Homayoni H, Abdolkarim S, Ravandi H, Valizadeh M (2009) Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: processing optimization. Carbohydr Polym 77:656–661
Rutledge GC, Warner SB, Ugbolue SC (2001) Electrostatic spinning and properties of ultrafine fibres. National Textile Centre Annual Report. http://www.ntcresearch.org/pdf-rpts/AnRp04/M01-MD22-A4.pdf. Accessed 22 Feb 2013
Afifi AM, Nakajima H, Yamane H, Kimura Y, Nakano S (2009) Fabrication of aligned poly(l-lactide) fibers by electrospinning and drawing. Macromol Mater Eng 294:658–665
Teo WE, Inai R, Ramakrishna S (2011) Technological advances in electrospinning of nanofibers. Sci Technol Adv Mater 12:013002
Liu L (2006) Studies on deposition and alignment of electrospun nanofiber assemblies. University of Nebraska, Lincoln. http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/dissertations/AAI3296165. Accessed 11 Aug 2012
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the National Plan for Science and Technology, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia under the grant 09-NANO869-02 is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haider, S., Al-Zeghayer, Y., Ahmed Ali, F.A. et al. Highly aligned narrow diameter chitosan electrospun nanofibers. J Polym Res 20, 105 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0105-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-013-0105-9