Abstract
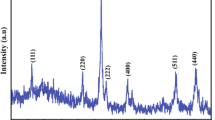
In this paper, a series of iron (Fe) containing nanoparticles were prepared by employing PAMAM (Poly(amidoamine), dendrimers with different generations (G0–G3) as templates and sodium borohydride as a reducing agent. The products have been characterized by TEM, FT-IR, XRD, VSM, TGA, and XPS. XRD analysis reveal low crystallinity of formed particles within the dendrimers, however, crystallinity of the nanoparticles was observed to increase with increasing generation of dendrimers. Dominant phases were determined as magnetite (Fe3O4 or maghemite, γ-Fe2O3). XPS analysis revealed the chemical composition of nanoparticles as iron oxide which indicated the oxidation of Fe species subsequent to the reduction process, in agreement with XRD analysis. The magnetization curves have superparamagnetic nonhysteretic characteristic at lower fields and with nonsaturation characteristic at high fields. Magnetic evaluation of samples with the 20:1 molar ratio of Fe:PAMAM showed decreasing superparamagnetic character and decreasing saturation magnetisation with increasing generation of dendrimers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, A.-H., Salabas, E.L., Schüth, F.: Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 46(8), 1222–1244 (2007). doi:10.1002/anie.200602866
Lu, A.-H., Schmidt, W., Matoussevitch, N., Bönnemann, H., Spliethoff, B., Tesche, B., Bill, E., Kiefer, W., Schüth, F.: Nanoengineering of a magnetically separable hydrogenation catalyst. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 43(33), 4303–4306 (2004). doi:10.1002/anie.200454222
Hyeon, T.: Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 8, 927–934 (2003)
Ross, C.: Patterned magnetic recording media. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 31(1), 203–235 (2001). doi:10.1146/annurev.matsci.31.1.203
Song, J., Kong, H., Jang, J.: Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by polyrhodanine-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 359(2), 505–511 (2011)
Chikazumi, S., Taketomi, S., Ukita, M., Mizukami, M., Miyajima, H., Setogawa, M., Kurihara, Y.: Physics of magnetic fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 65(2–3), 245–251 (1987)
Sun, C., Lee, J.S.H., Zhang, M.: Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60(11), 1252–1265 (2008)
McBain, S.C., Yiu, H.H., Dobson, J.: Magnetic nanoparticles for gene and drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 3(2), 12 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJNS1608
Pankhurst, Q.A., et al.: Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 36(13), R167 (2003)
Zhang, C., Liu, T., Gao, J., Su, Y., Shi, C.: Recent development and application of magnetic nanoparticles for cell labeling and imaging. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 10(3), 194–203 (2010)
Hariharan, S.G.: James: superparamagnetism and magnetocaloric effect in functional magnetic nanostructures. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 10(5), 5 (2005)
Liu, X., Geng, D., Jiang, J., Li, B., Ma, S., Li, D., Liu, W., Zhang, Z.: Magnetic properties and large cryogenic low-field magnetocaloric effect of HoCo2 nanoparticles without core/shell structure. J. Nanopart. Res. 12(4), 1167–1172 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11051-009-9717-8
Kanel, S.R., Manning, B., Charlet, L., Choi, H.: Removal of arsenic(III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(5), 1291–1298 (2005). doi:10.1021/es048991u
Huang, C.-C., Lo, S.-L., Tsai, S.-M., Lien, H.-L.: Catalytic hydrodechlorination of 1,2-dichloroethane using copper nanoparticles under reduction conditions of sodium borohydride. J. Environ. Monit. 13(9), 2406–2412 (2011)
Cook, S.M.: Assessing the use and application of zero-valent iron nanoparticle technology for remediation at contaminated sites in. Jackson State University (2009)
Myers, V.S., Weir, M.G., Carino, E.V., Yancey, D.F., Pande, S., Crooks, R.M.: Dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles: new synthetic and characterization methods and catalytic applications. Chem. Sci. 2(9), 1632–1646 (2011)
Scott, R.W.J., Wilson, O.M., Crooks, R.M.: Synthesis, characterization, and applications of dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 109(2), 692–704 (2004). doi:10.1021/jp0469665
Jin, L., Yang, S.-P., Wu, H.-X., Huang, W.-W., Tian, Q.-W.: Preparation and characterization of silver nanoparticles with dendrimers as templates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 108(6), 4023–4028 (2008). doi:10.1002/app.28056
Crooks, R., Lemon, B., Sun, L., Yeung, L., Zhao, M.: Dendrimer-encapsulated metals and semiconductors: synthesis, characterization, and applications dendrimers III. In: Vögtle, F. (ed.) Topics in Current Chemistry, vol. 212, pp. 81–135. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Liu, D., López-De Jesús, Y.M., Monnier, J.R., Williams, C.T.: Preparation, characterization, and kinetic evaluation of dendrimer-derived bimetallic Pt–Ru/SiO2 catalysts. J. Catal. 269(2), 376–387 (2010)
Zhao, M., Crooks, R.M.: Homogeneous hydrogenation catalysis with monodisperse, dendrimer-encapsulated Pd and Pt nanoparticles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 38(3), 364–366 (1999). doi:10.1002/(sici)1521-3773(19990201)38:3<364::aid-anie364>3.0.co;2-l
Crooks, R.M., Zhao, M., Sun, L., Chechik, V., Yeung, L.K.: Dendrimer-encapsulated metal nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and applications to catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 34(3), 181–190 (2000). doi:10.1021/ar000110a
Gröhn, F., Bauer, B.J., Akpalu, Y.A., Jackson, C.L., Amis, E.J.: Dendrimer templates for the formation of gold nanoclusters. Macromolecules 33(16), 6042–6050 (2000). doi:10.1021/ma000149v
Li, C., Liu, H., Sun, Y., Wang, H., Guo, F., Rao, S., Deng, J., Zhang, Y., Miao, Y., Guo, C., Meng, J., Chen, X., Li, L., Li, D., Xu, H., Wang, H., Li, B., Jiang, C.: PAMAM nanoparticles promote acute lung injury by inducing autophagic cell death through the Akt-TSC2-mTOR signaling pathway. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 1(1), 37–45 (2009). doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjp002
Seo, Y.-S., Kim, K.-S., Shin, K., White, H., Rafailovich, M., Sokolov, J., Lin, B., Kim, H.J., Zhang, C., Balogh, L.: Morphology of amphiphilic gold/dendrimer nanocomposite monolayers. Langmuir 18(15), 5927–5932 (2002). doi:10.1021/la025504k
Kavas, H., Durmus, Z., Tanrıverdi, E., Şenel, M., Sozeri, H., Baykal, A.: Fabrication and characterization of dendrimer-encapsulated monometallic Co nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 509(17), 5341–5348 (2011)
Chechik, V., Zhao, M., Crooks, R.M.: Self-assembled inverted micelles prepared from a dendrimer template: phase transfer of encapsulated guests. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121(20), 4910–4911 (1999). doi:10.1021/ja990445r
Oh, S.-K., Kim, Y.-G., Ye, H., Crooks, R.M.: Synthesis, characterization, and surface immobilization of metal nanoparticles encapsulated within bifunctionalized dendrimers. Langmuir 19(24), 10420–10425 (2003). doi:10.1021/la0353778
Chechik, V., Crooks, R.M.: Dendrimer-encapsulated pd nanoparticles as fluorous phase-soluble catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122(6), 1243–1244 (2000). doi:10.1021/ja9936870
Li, Y., El-Sayed, M.A.: The effect of stabilizers on the catalytic activity and stability of Pd colloidal nanoparticles in the Suzuki reactions in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 105(37), 8938–8943 (2001). doi:10.1021/jp010904m
Rahim, E.H., Kamounah, F.S., Frederiksen, J., Christensen, J.B.: Heck reactions catalyzed by PAMAM-dendrimer encapsulated Pd(0) nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 1(9), 499–501 (2001). doi:10.1021/nl015574w
Kim, Y.-G., Oh, S.-K., Crooks, R.M.: Preparation and characterization of 1–2 nm dendrimer-encapsulated gold nanoparticles having very narrow size distributions. Chem. Mater. 16(1), 167–172 (2003). doi:10.1021/cm034932o
Esumi, K., Suzuki, A., Aihara, N., Usui, K., Torigoe, K.: Preparation of gold colloids with UV irradiation using dendrimers as stabilizer. Langmuir 14(12), 3157–3159 (1998). doi:10.1021/la980162x
Michels, J.J., Huskens, J., Reinhoudt, D.N.: Dendrimer-cyclodextrin assemblies as stabilizers for gold and platinum nanoparticles. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2 2002(1), 102–105 (2002)
Niu, Y., Yeung, L.K., Crooks, R.M.: Size-selective hydrogenation of olefins by dendrimer-encapsulated palladium nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123(28), 6840–6846 (2001). doi:10.1021/ja0105257
Scott, R.W.J., Ye, H., Henriquez, R.R., Crooks, R.M.: Synthesis, characterization, and stability of dendrimer-encapsulated palladium nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 15(20), 3873–3878 (2003). doi:10.1021/cm034485c
Scott, R.W.J., Wilson, O.M., Oh, S.-K., Kenik, E.A., Crooks, R.M.: Bimetallic palladium-gold dendrimer-encapsulated catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(47), 15583–15591 (2004). doi:10.1021/ja0475860
Niu, Y., Crooks, R.M.: Dendrimer-encapsulated metal nanoparticles and their applications to catalysis. C. R., Chim. 6(8–10), 1049–1059 (2003)
Tomalia, D.A., Naylor, A.M., Goddard, W.A.: Starburst dendrimers: molecular-level control of size, shape, surface chemistry, topology, and flexibility from atoms to macroscopic matter. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 29(2), 138–175 (1990). doi:10.1002/anie.199001381
Endo, T., Yoshimura, T., Esumi, K.: Synthesis and catalytic activity of gold–silver binary nanoparticles stabilized by PAMAM dendrimer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 286(2), 602–609 (2005)
Tan, H., Luo, Y.J.: Dendritic Polymer. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing (2002)
Jin, L., Yang, S.-P., Tian, Q.-W., Wu, H.-X., Cai, Y.-J.: Preparation and characterization of copper metal nanoparticles using dendrimers as protectively colloids. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112(3), 977–983 (2008)
Socrates, G.: Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts. Wiley, Chichester (2000)
Liu, D., Gao, J., Murphy, C.J., Williams, C.T.: In situ attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy of dendrimer-stabilized platinum nanoparticles adsorbed on alumina. J. Phys. Chem. B 108(34), 12911–12916 (2004). doi:10.1021/jp048879i
Pielaszek, R.: Analytical expression for diffraction line profile for polydispersive powders. In: 19th Conference on Applied Crystallography, Kraków, Poland, 2003, pp. 43–50. World Scientific, Singapore (2003)
Wejrzanowski, T., Pielaszek, R., Opalińska, A., Matysiak, H., Łojkowski, W., Kurzydłowski, K.J.: Quantitative methods for nanopowders characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(1), 204–208 (2006)
Pan, B.-F., Gao, F., Gu, H.-C.: Dendrimer modified magnetite nanoparticles for protein immobilization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 284(1), 1–6 (2005)
Joyner, D.J., Johnson, O., Hercules, D.M.: A study of the iron borides. 1. Electron spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102(6), 1910–1917 (1980). doi:10.1021/ja00526a025
Tan, B.J., Klabunde, K.J., Sherwood, P.M.A.: X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy studies of solvated metal atom dispersed catalysts. Monometallic iron and bimetallic iron-cobalt particles on alumina. Chem. Mater. 2(2), 186–191 (1990). doi:10.1021/cm00008a021
Hawn, D.D., DeKoven, B.M.: Deconvolution as a correction for photoelectron inelastic energy losses in the core level XPS spectra of iron oxides. Surf. Interface Anal. 10(2–3), 63–74 (1987). doi:10.1002/sia.740100203
Brion, D.: Etude par spectroscopie de photoelectrons de la degradation superficielle de FeS2, CuFeS2, ZnS et PbS a l’air et dans l’eau. Appl. Surf. Sci. 5(2), 133–152 (1980)
Fujii, T., de Groot, F.M.F., Sawatzky, G.A., Voogt, F.C., Hibma, T., Okada, K.: In situ XPS analysis of various iron oxide films grown by NO_{2}-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. Phys. Rev. B 59(4), 3195–3202 (1999)
Durmus, Z., Kavas, H., Baykal, A., Sozeri, H., Alpsoy, L., Çelik, S.Ü., Toprak, M.S.: Synthesis and characterization of l-carnosine coated iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 509(5), 2555–2561 (2011)
Kodama, R.H., Berkowitz, A.E., McNiff, J.E.J., Foner, S.: Surface spin disorder in NiFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(2), 394–397 (1996)
Unal, B., Toprak, M., Durmus, Z., Sözeri, H., Baykal, A.: Synthesis, structural and conductivity characterization of alginic acid–Fe3O4 nanocomposite. J. Nanopart. Res. 12(8), 3039–3048 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11051-010-9898-1
Kittel, C.: Introduction to Solid State Physics. Wiley, New York (1971)
Aydın, M., Ünal B., Esat, B., Baykal, A., Karaoglu, E., Toprak, M.S., Sözeri, H.: Synthesis, magnetic and electrical characteristics of poly(2-thiophen-3-yl-malonic acid)/Fe3O4 nanocomposite. J. Alloys Compd. 514, 45–53 (2012)
Gómez-Lopera, S.A., Plaza, R.C., Delgado, A.V.: Synthesis and characterization of spherical magnetite/biodegradable polymer composite particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 240(1), 40–47 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Fatih University, Research Project Foundation (Contract nos: P50021104-B and P50021104-G), and Turkish Ministry of Industry and TUBITAK (Contract no: 110T487) for financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baykal, A., Toprak, M.S., Durmus, Z. et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Dendrimer-Encapsulated Iron and Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 25, 1541–1549 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-012-1454-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-012-1454-z