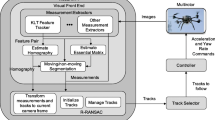
Abstract
In this paper, we apply a hierarchical tracking strategy of planar objects (or that can be assumed to be planar) that is based on direct methods for vision-based applications on-board UAVs. The use of this tracking strategy allows to achieve the tasks at real-time frame rates and to overcome problems posed by the challenging conditions of the tasks: e.g. constant vibrations, fast 3D changes, or limited capacity on-board. The vast majority of approaches make use of feature-based methods to track objects. Nonetheless, in this paper we show that although some of these feature-based solutions are faster, direct methods can be more robust under fast 3D motions (fast changes in position), some changes in appearance, constant vibrations (without requiring any specific hardware or software for video stabilization), and situations in which part of the object to track is outside of the field of view of the camera. The performance of the proposed tracking strategy on-board UAVs is evaluated with images from real-flight tests using manually-generated ground truth information, accurate position estimation using a Vicon system, and also with simulated data from a simulation environment. Results show that the hierarchical tracking strategy performs better than well-known feature-based algorithms and well-known configurations of direct methods, and that its performance is robust enough for vision-in-the-loop tasks, e.g. for vision-based landing tasks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campoy, P., Correa, J.F., Mondragón, I., Martínez, C., Olivares, M., Mejías, L., Artieda, J.: Computer vision onboard uavs for civilian tasks. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 54(1–3), 105–135 (2009)
Mondragón, I.F., Campoy, P., Martinez, C., Olivares-Mendez, M.: 3D pose estimation based on planar object tracking for UAVs control. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation 2010 ICRA2010, Anchorage, AK, USA (2010)
Mondragon, I., Campoy, P., Correa, J., Mejias, L.: Visual model feature tracking for uav control. In: IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing, 2007. WISP 2007, pp. 1–6, 3–5 (2007)
Torr, P.H.S., Zisserman, A.: Feature based methods for structure and motion estimation. In: ICCV ’99: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Vision Algorithms, pp. 278–294. Springer, London (2000)
Bouguet, J.Y.: Pyramidal implementation of the Lucas Kanade feature tracker: description of the algorithm. Technical report, OpenCV Document, Intel Microprocessor Research Labs (2002)
Irani, M., Anandan, P.: About direct methods. In: Triggs, B., Zisserman, A., Szeliski, R. (eds.) Vision Algorithms: Theory and Practice, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 1883, pp. 267–277. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Zhang, H., Yuan, F.: Vehicle tracking based on image alignment in aerial videos. In: EMMCVPR’07: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Energy Minimization Methods in Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 295–302. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Ali, S., Shah, M.: Cocoa—tracking in aerial imagery. In: Proc. Int. Conf. on Computer Vision (2005)
Mejias, L., Saripalli, S., Campoy, P., Sukhatme, G.: Visual servoing approach for tracking features in urban areas using an autonomous helicopter. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, Florida, pp. 2503–2508 (2006)
Choi, J.H., Lee, D., Bang, H.: Tracking an unknown moving target from uav: Extracting and localizing an moving target with vision sensor based on optical flow. In: 2011 5th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA), pp. 384–389 (2011)
Dame, A., Marchand, E.: Accurate real-time tracking using mutual information. In: IEEE Int. Symp. on Mixed and Augmented Reality, ISMAR’10, Seoul, Korea, pp. 47–56 (2010)
Baker, S., Matthews, I.: Equivalence and efficiency of image alignment algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, vol. 1, pp. 1090–1097 (2001)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60(2), 91–110 (2004)
ViconMotion Systems: VICONMXdigital optical motion capture system. http://www.vicon.com (2011). Accessed 1 Oct 2011
Hartley, R., Zisserman, A.: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. Cambridge University Press, New York (2003)
Martinez, C., Mejias, L., Campoy, P.: A multi-resolution image alignment technique based on direct methods for pose estimation of aerial vehicles. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications (DICTA), 2011, pp. 542–548 (2011)
Anderson, C.H., Bergen, J.R., Burt, P.J., Ogden, J.M.: Pyramid methods in image processing. RCA Eng. 29(6), 33–41 (1984)
Burt, P., Adelson, E.: The laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. IEEE Trans. Commun. 31(4), 532–540 (1983)
Bergen, J.R., Anandan, P., Hanna, T.J., Hingorani, R.: Hierarchical model-based motion estimation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 237–252 (1992)
Szeliski, R.: Image alignment and stitching: a tutorial. Found. Trends. Comput. Graph. Vis. 2(1), 1–104 (2006)
Buenaposada, J.M., Baumela, L.: Real-time tracking and estimation of plane pose. In: ICPR, pp. 697–700 (2002)
Benhimane, S., Malis, E.: Real-time image-based tracking of planes using efficient second-order minimization. In: 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2004. (IROS 2004). Proceedings (2004)
Irani, M., Peleg, S.: Motion analysis for image enhancement: resolution, occlusion, and transparency. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 4, 324–335 (1993)
Shum, H.-Y., Szeliski, R.: Construction of panoramic image mosaics with global and local alignment. In: Panoramic Vision, pp. 227–268. Springer, New York (2001)
Baker, S., Matthews, I.: Lucas-kanade 20 years on: a unifying framework. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 56(1), 221–255 (2004)
Lucas, B.D., Kanade, T.: An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 674–679 (1981)
Hager, G.D., Belhumeur, P.N.: Efficient region tracking with parametric models of geometry and illumination. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20(10), 1025–1039 (1998)
Bradski, G., Kaehler, A.: Learning OpenCV: Computer Vision with the OpenCV Library. O’Reilly (2008)
Simon, G., Berger, M.-O.: Pose estimation for planar structures. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 22(6), 46–53 (2002)
Buenaposada, J.M., Baumela, L.: Real-time tracking and estimation of plane pose. In: Proceedings 16th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2002, vol. 2, pp. 697–700 (2002)
Zhang, Z.: Flexible camera calibration by viewing a plane from unknown orientations. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, vol. 1, p. 666 (1999)
Bouguet, J.Y.: Camera calibration toolbox for Matlab (2008)
Zhang, Z.: A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(11), 1330–1334 (2000)
Videos. http://www.vision4uav.com/?q=HMPMRtracker. Accessed 1 Oct 2012
Computer Vision Group. Universidad Politécnica de Madrid. CVG 2010. http://www.vision4uav.com/. Accessed 1 Oct 2012
Quigley, M., Conley, K., Gerkey, B.P., Faust, J., Foote, T., Leibs, J., Wheeler, R., Ng, A.Y.: ROS: an open-source Robot Operating System. In: ICRA Workshop on Open Source Software (2009)
ROS-Gazebo. http://www.ros.org/wiki/simulator_gazebo (2012). Accessed 1 Sept 2012
Starmac-ros package. http://www.ros.org/wiki/starmac-ros-pkg. Accessed 1 Sept 2012
Hess, R.: SIFT feature detector implementation in C. http://www.web.engr.oregonstate.edu/hess/index.html (2007). Accessed 7 Mar 2013
Hess, R.: An open-source SIFT library. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1493–1496 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez, C., Mondragón, I.F., Campoy, P. et al. A Hierarchical Tracking Strategy for Vision-Based Applications On-Board UAVs. J Intell Robot Syst 72, 517–539 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-013-9814-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-013-9814-x