Abstract
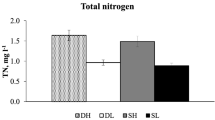
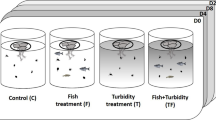
Information on the effects of water level changes on microbial planktonic communities in lakes is limited but vital for understanding ecosystem dynamics in Mediterranean lakes subjected to major intra- and inter-annual variations in water level. We performed an in situ mesocosm experiment in an eutrophic Turkish lake at two different depths crossed with presence/absence of fish in order to explore the effects of water level variations and the role of top-down regulation at contrasting depths. Strong effects of fish were found on zooplankton, weakening through the food chain to ciliates, HNF and bacterioplankton, whereas the effect of water level variations was overall modest. Presence of fish resulted in lower biomass of zooplankton and higher biomasses of phytoplankton, ciliates and total plankton. The cascading effects of fish were strongest in the shallow mesocosms as evidenced by a lower zooplankton contribution to total plankton biomass and lower zooplankton:ciliate and HNF:bacteria biomass ratios. Our results suggest that a lowering of the water level in warm shallow lakes will enhance the contribution of bacteria, HNF and ciliates to the plankton biomass, likely due to increased density of submerged macrophytes (less phytoplankton); this effect will, however, be less pronounced in the presence of fish.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, T. & D. O. Hessen, 1991. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus content of freshwater zooplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 36: 807–814.
Auer, B., U. Elzer & H. Arndt, 2004. Comparison of pelagic food webs in lakes along a trophic gradient and with seasonal aspects: influence of resource and predation. Journal of Plankton Research 26: 697–709.
Beklioğlu, M. & C. O. Tan, 2008. Restoration of a shallow Mediterranean lake by biomanipulation complicated by drought. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 171: 105–118.
Beklioğlu, M., Ö. İnce & İ. Tüzün, 2003. Restoration of eutrophic Lake Eymir, Turkey, by biomanipulation undertaken following a major external nutrient control I. Hydrobiologia 489: 93–105.
Beklioğlu, M., G. Altinayar & C. O. Tan, 2006. Water level control over submerged macrophyte development in five shallow lakes of Mediterranean Turkey. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 166: 535–556.
Beklioğlu, M., S. Romo, I. Kagalou, X. Quintana & E. Becares, 2007. State of the art in the functioning of shallow Mediterranean lakes: workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 584: 317–326.
Biddanda, B., M. Ogdahl & J. Cotner, 2001. Dominance of bacterial metabolism in oligotrophic relative to eutrophic waters. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 730–739.
Borsheim, K. Y. & G. Bratback, 1987. Cell volume to carbon conversion factors for bacterivorous Monas sp. enriched from seawater. Marine Ecology Progress Series 36: 171–175.
Bratbak, G. & I. Dundas, 1984. Bacterial dry matter content and biomass estimations. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 48: 755–757.
Bucak, T., E. Saraoğlu, E. E. Levi, Ü. N. Tavşanoğlu, Aİ. Çakiroğlu, E. Jeppesen & M. Beklioğlu, 2012. The influence of water level on macrophyte growth and trophic interactions in eutrophic Mediterranean shallow lakes: a mesocosm experiment with and without fish. Freshwater Biology 57: 1631–1642.
Carrick, H. J., G. L. Fahnenstiel, E. F. Stoermer & R. G. Wetzel, 1991. The importance of zooplankton–protozoan trophic couplings in Lake Michigan. Limnology and Oceanography 36: 1335–1345.
Christoffersen, K., B. Riemann, A. Klysner & M. Søndergaard, 1993. Potential role of natural populations of zooplankton on plankton community structure in eutrophic lake water. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 561–573.
Coops, H., M. Beklioğlu & T. L. Crisman, 2003. The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems: workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 506: 23–27.
Cotner, J. B. & B. A. Biddanda, 2002. Small players, large role: microbial influence on biogeochemical processes in pelagic aquatic ecosystem. Ecosystems 5: 105–121.
Farjalla, V. F., D. A. Azevedo, F. A. Esteves, R. L. Bozelli, F. Roland & A. Enrich-Prast, 2006. Influence of hydrological pulse on bacterial growth and DOC uptake in a clear-water Amazonian lake. Microbial Ecology 52: 334–344.
Foissner, W. & H. Berger, 1996. A user-friendly guide to the ciliates (Protozoa, Ciliophora) commonly used by hydrobiologists as bioindicators in rivers, lakes, and waste waters, with notes on their ecology. Freshwater Biology 35: 375–482.
Foissner, W., H. Berger & J. Schaumburg, 1999. Identification and Ecology of Limnetic Plankton Ciliates. Informations berichte des Bayer. Landesamtes für Wasserwirtschaft. 3, 793 pp.
Fonte, E. S., L. S. Carneiro, A. Caliman, R. L. Bozelli, F. D. A. Esteves & V. F. Farjalla, 2011. Effects of resources and food web structure on bacterioplankton production in a tropical humic lagoon. Journal of Plankton Research 33: 1596–1605.
Gaedke, U. & D. Straile, 1994. Seasonal changes of the quantitative importance of protozoans in a large lake: an ecosystem approach using mass-balanced carbon flow diagrams. Marine Microbial Food Webs 8: 163–188.
Gafny, S., A. Gasith & M. Goren, 1992. Effect of water level fluctuation on shore spawning of Mirogrex terraesanctae (Steinitz), Cyprinidae in Lake Kinneret, Israel. Journal of Fish Biology 41: 863–871.
Gasol, J. M. & C. M. Duarte, 2000. Comparative analyses in aquatic microbial ecology: how far do they go? FEMS Microbiology Ecology 31: 99–106.
Havens, K. E., B. Sharfstein, M. A. Brady, T. L. East, M. C. Harwell, R. P. Maki & A. J. Rodusky, 2004. Recovery of submerged plants from high water stress in a large subtropical Lake in Florida, USA. Aquatic Botany 78: 67–82.
Jeppesen, E., Ma Søndergaard, Mo Søndergaard, K. Christoffersen, K. Jürgens, J. Theil-Nielsen & L. Schlüter, 2002. Cascading trophic interactions in the littoral zone: an enclosure experiment in shallow Lake Stigsholm, Denmark. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 153: 533–555.
Jeppesen, E., B. Kronvang, M. Meerhoff, M. Søndergaard, K. M. Hansen, H. E. Andersen, T. L. Lauridsen, L. Liboriussen, M. Beklioğlu, A. Özen & J. E. Olesen, 2009. Climate change effects on runoff, catchment phosphorus loading and lake ecological state, and potential adaptations. Journal of Environmental Quality 38: 1930–1941.
Jeppesen, E., B. Kronvang, J. E. Olesen, M. Søndergaard, C. C. Hoffmann, H. E. Andersen, T. L. Lauridsen, L. Liboriussen, S. Larsen, M. Beklioğlu, M. Meerhoff, A. Özen & K. Özkan, 2011. Climate change effect on nitrogen loading from catchment in Europe: implications for nitrogen retention and ecological state of lakes and adaptations. Hydrobiologia 663: 1–21.
Jürgens, K. & E. Jeppesen, 2000. The impact of metazooplankton on the structure of the microbial food web in a shallow, hypertrophic lake. Journal of Plankton Research 22: 1047–1070.
Jürgens, K., H. Arndt & K. O. Rothhaupt, 1994. Zooplankton-mediated changes of bacterial community structure. Microbial Ecology 27: 27–42.
Leira, M. & M. Cantonati, 2008. Effects of water-level fluctuations on lakes: an annotated bibliography. Hydrobiologia 613: 171–184.
Markosova, R. & J. Jezek, 1993. Bacterioplankton interactions with daphnia and algae in experimental enclosures. Hydrobiologia 264: 85–99.
Müller-Solger, A., M. T. Brett, C. Luecke, J. J. Elser & C. R. Goldman, 1997. The effects of planktivorous fish (golden shiners) on the ciliate community of a mesotrophic lake. Journal of Plankton Research 12: 1815–1828.
Muylaert, K., K. Van der Gucht, N. Vloemans, L. De Meester, M. Gillis & W. Vyverman, 2002. Relationship between bacterial community composition and bottom-up versus top-down variables in four eutrophic shallow lakes. Applied Environmental Microbiology 68: 4740–4750.
Naselli-Flores, L., 2003. Man-made lakes in Mediterranean semi-arid climate: the strange case of Dr Deep Lake and Mr Shallow Lake. Hydrobiologia 506: 13–21.
Nishimura, Y., T. Ohtsuka, K. Yoshiyama, D. Nakai, F. Shibahara & M. Maehata, 2011. Cascading effects of larval Crucian carp introduction on phytoplankton and microbial communities in a paddy field: top-down and bottom-up controls. Ecological Research 26: 615–626.
Nixdorf, B. & H. Arndt, 1993. Seasonal dynamics of plankton component including the microbial web in Lake Müggelsee. Internationale Revue gesamten Hydrobiologie 78: 403–410.
Nõges, P., T. Nõges & A. Laas, 2010. Climate-related changes of phytoplankton seasonalityin large shallow Lake Võrtsjärv, Estonia. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management 13: 154–163.
Pace, M. L. & J. J. Cole, 1994. Comparative and experimental approaches to top down and bottom up regulation of bacteria. Microbial Ecology 28: 181–193.
Pace, M. L. & E. Funke, 1991. Regulation of planktonic microbial communities by nutrients and herbivores. Ecology 73: 904–914.
Porter, K. G. & Y. S. Feig, 1980. The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnology and Oceanography 25: 943–948.
Putt, M. & D. K. Stoecker, 1989. An experimentally determined carbon:carbon:volume ratio for marine oligotrichous ciliates from estuarine and coastal waters. Limnology and Oceanography 34: 1097–1103.
Reynolds, C. S., 1984. The Ecology of Freshwater Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 384.
Riemann, B., 1985. Potential importance of fish predation and zooplankton grazing on natural populations of freshwater bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 50: 187–193.
Roozen, F. C. J. M., M. Lürling, H. Vlek, E. A. J. V. P. Kraan, B. W. Ibelings & M. Scheffer, 2007. Resuspension of algal cells by benthivorous fish boosts phytoplankton biomass and alters community structure in shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 52: 977–987.
Özen, A., B. Karapinar, I. Küçük, E. Jeppesen & M. Beklioğlu, 2010. Drought-induced changes in nutrient concentrations and retention in two shallow Mediterranean lakes subjected to different degrees of management. Hydrobiologia 646: 61–72.
Özkan, K., E. Jeppesen, L. S. Johansson & M. Beklioğlu, 2010. The response of periphyton and submerged macrophytes to nitrogen and phosphorus loadings in shallow warm lakes: a mesocosm experiment. Freshwater Biology 55: 463–475.
Saad, J. F., M. R. Schiaffino, A. Vinocur, I. O’Farrell, G. Tell & I. Izaguirre, 2013. Microbial planktonic communities of freshwater environments from Tierra del Fuego: dominant trophic strategies in lakes with contrasting features. Journal of Plankton Research 35: 1220–1233.
Stanley, E. H., M. D. Johnson & A. K. Ward, 2003. Evaluating the influence of macrophytes on algal and bacterial production in multiple habitats of a freshwater wetland. Limnology and Oceanography 48: 1101–1111.
Tan, C. & M. Beklioğlu, 2006. Modelling complex nonlinear responses of shallow lakes to fish and hydrology using artificial neural networks. Ecological Modelling 196: 183–194.
Tzaras, A., F. R. Pick, A. Mazumder & D. R. S. Lean, 1999. Effects of nutrients, planktivorous fish and water column depth on components of the microbial food web. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 19: 67–80.
Utermöhl, H., 1958. Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton Methodik. Mitteilungen-Internationale Vereinigung Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 9: 1–38.
Vanni, M. J., 2002. Nutrient cycling by animals in freshwater ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 33: 341–370.
Vanni, M. J. & C. D. Layne, 1997. Nutrient recycling and herbivory as mechanisms in the “top-down” effect of fish on algae in lakes. Ecology 78: 21–40.
Weisse, T., 1991. The annual cycle of heterotrophic freshwater nanoflagellates: role of bottom-up versus top-down control. Journal of Plankton Research 13: 167–185.
Wetzel, R. G. & M. Søndergaard, 1998. Role of submerged macrophytes for the microbial community and dynamics of dissolved organic carbon in aquatic ecosystems. In Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, M. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Springer, New York: 133–148.
Wickham, S. A., 1998. The direct and indirect impact of Daphnia and Cyclops on a freshwater microbial food web. Journal of Plankton Research 20: 739–755.
Wilcock, R. J., P. D. Champion, J. W. Nagels & G. F. Croker, 1999. The influence of aquatic macrophytes on the hydraulic and physico-chemical properties of a New Zealand lowland stream. Hydrobiologia 416: 203–214.
Yamazaki, M., T. Ohtsuka, Y. Kusuoka, M. Maehata, H. Obayashi, K. Imai, F. Shibahara & M. Kimura, 2010. The impact of nigorobuna crucian carp larvae/fry stocking and rice-straw application on the community structure of aquatic organisms in Japanese rice fields. Fisheries Science 76: 207–217.
Zhang, Y., X. Liu, M. Wang & B. Qin, 2013. Compositional differences of chromophoric dissolved organic matter derived from phytoplankton and macrophytes. Organic Geochemistry 55: 26–37.
Zingel, P. & T. Nõges, 2008. Protozoan grazing in shallow macrophyte and plankton lakes. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 171: 15–25.
Zöllner, E., B. Santer, M. Boersma, H. G. Hoppe & K. Jürgens, 2003. Cascading predation effects of Daphnia and copepods on microbial foodweb components. Freshwater Biology 48: 2174–2193.
Zöllner, E., H. G. Hoppe, U. Sommer & K. Jürgens, 2009. Effect of zooplankton mediated trophic cascades on marine microbial food web components (bacteria, nanoflagellates, ciliates). Limnology and Oceanography 54: 262–275.
Acknowledgments
This study and Arda Özen were supported by a Middle East Technical University grant from the METU-BAP programme of Turkey (BAP-07-02-2009), the METU-DPT ÖYP programme of Turkey (BAP-08-11-DP T-2002-K120510) and by TUBITAK-ÇAYDAĞ (Project nos: 105Y332, 109Y181 and 110Y125). During the writing phase, support was given by FP7-ENV-2009-1, REFRESH (Adaptive strategies to Mitigate the Impacts of Climate Change on European Freshwater Ecosystems, Contract No: 244121) and the MARS project (Managing Aquatic ecosystems and water Resources under multiple Stress) funded under the 7th EU Framework Programme, Theme 6 (Environment including Climate Change), Contract No: 603378 (http://www.mars-project.eu). TB was supported by the TÜBİTAK 2211 Scholarship programme during her graduate study; JC is supported by the TÜBİTAK 2215 Scholarship programme; EEL, ÜNT and AİC were also supported by TÜBITAK ÇAYDAĞ (Project nos: 105Y332 and 110Y125), and EJ was supported by CLEAR (a Villum Kann Rasmussen Centre of Excellence project) and by The Research Council for Nature and Universe, Denmark (272-08-0406), CIRCE and CRES. We also want to thank Gizem Bezirci, Merve Tepe, Betül Acar, Nergis İrem Ertan, Mert Elverici and Soner Oruç for their great efforts during the fieldwork. We thank Anne Mette Poulsen for valuable editorial assistance. This study was a part of the PhD dissertation of Arda Özen at the Middle East Technical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Handling editor: Mariana Meerhoff
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özen, A., Bucak, T., Tavşanoğlu, Ü.N. et al. Water level and fish-mediated cascading effects on the microbial community in eutrophic warm shallow lakes: a mesocosm experiment. Hydrobiologia 740, 25–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1934-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1934-1