Abstract
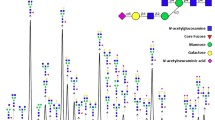
The IgG Fc glycans strongly influence the Fcγ receptor interactions and Fc-mediated effector mechanisms. Changes in the structure of IgG glycans are associated with various diseases, such as infections and autoimmunity. However, the possible role of Fc glycans in tumor immunity is not yet fully understood. The aim of this study was to profile the Fc N-glycans of IgG samples from patients with gastric cancer (n = 80) and controls (n = 51) using LC-ESI-MS method to correlate the findings with stage of cancer and patients survival. Analysis of 32 different IgG N-glycans revealed significant increase of agalactosylated (GnGnF, GnGn(bi)F), and decrease of galactosylated (AGn(bi), AGn(bi)F, AA(bi), AAF) and monosialylated IgG glycoforms (NaAF, NaA(bi)) in cancer patients. A statistically significant increase of Fc fucosylation was observed in tumor stage II and III whereas reverse changes were found for the presence of bisecting GlcNAc. Higher level of fully sialylated glycans and elevated expression of glycans with bisecting GlcNAc were associated with better survival rate. Our findings provide the first evidence that the changes in Fc glycan profile may predict the survival of patients with gastric cancer. Cancer stage-dependent changes in Fc fucosylation and the bisecting N-acteylglucosamine expression as well as an association of several IgG glycoforms with the survival suggest that IgG glycosylation is related to pathogenesis of cancer and progression of the disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, J.N., Wormald, M.R., Sim, R.B., Rudd, P.M., Dwek, R.A.: The impact of glycosylation on the biological function and structure of human immunoglobulins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. (2007). doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141702
Nose, M., Wigzell, H.: Biological significance of carbohydrate chains on monoclonal antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 6632–6636 (1983)
Jefferis, R., Lund, J., Pound, J.D.: IgG-Fc mediated effector functions: molecular definition of interaction sites for effector ligands and the role of glycosylation. Immunol. Rev. 163, 59–76 (1998)
Margni, R., Malan Borel, I.: Paradoxical behaviour of asymmetric IgG antibodies. Immunol. Rev 163, 77–87 (1998)
Shields, R.L., Lai, J., Keck, R., O’Connell, L.Y., Hong, K., Meng, Y.G., Weikert, S.H., Presta, L.G.: Lack of fucose on human IgG1 N-linked oligosaccharide improves binding to human Fcgamma RIII and antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. (2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M202069200
Shinkawa, T., Nakamura, K., Yamane, N., Shoji-Hosaka, E., Kanda, Y., Sakurada, M., Uchida, K., Anazawa, H., Satoh, M., Yamasaki, M., Hanai, N., Shitara, K.: The absence of fucose but not the presence of galactose or bisecting N-acetylglucosamine of human IgG1 complextype oligosaccharides shows the critical role of enhancing antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. (2003). doi:10.1074/jbc.M210665200
Barbin, K., Stieglmaier, J., Saul, D., Stieglmaier, K., Stockmeyer, B., Pfeiffer, M., Lang, P., Fey, G.H.: Influence of variable N-glycosylation on the cytolytic potential of chimeric CD19 antibodies. J. Immunother. (2006). doi:10.1097/01.cji.0000175684.28615.7b
Raju, T.S.: Terminal sugars of Fc glycans influence antibody effector functions of IgGs. Curr. Opin. Immunol. (2008). doi:10.1016/j.coi.2008.06.007
Schroeder, H.W. Jr., Cavacini, L.: Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.09.046
Wuhrer, M., Stam, J.C., van de Geijn, F.E., Koeleman, C.A., Verrips, C.T., Dolhain, R.J., Hokke, C.H., Deelder, A.M.: Glycosylation profiling of immunoglobulin G (IgG) subclasses from human serum. Proteomics (2007). doi:10.1002/pmic.200700289
Holland, M., Takada, K., Okumoto, T., Takahashi, N., Kato, K., Adu, D., Bensmith, A., Harper, L., Savage, C.O.P., Jefferis, R.: Hypogalactosylation of serum IgG in patients with ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Immunopl. 129(1), 183–190 (2002)
Parekh, R.B., Dwek, R.A., Sutton, B.J., Fernandes, D.L., Leung, A., Stanworth, D., Rademacher, T.W., Mizuochi, T., Taniguchi, T., Matsuta, K., Takeuchi, F., Nagano, Y., Miyamoto, T., Kobata, A.: Association of rheumatoid arthritis and primary osteoarthritis with changes in the glycosylation pattern of total serum IgG. Nature 316, 452–457 (1985)
Parekh, R.B., Roitt, I.M., Isenberg, D.A., Dwek, R.A., Ansell, B.M., Rademacher, T.W.: Galactosylation of IgG associated oligosaccharides: Reduction in patients with adult and juvenile onset rheumatoid arthritis and relation to disease activity. Lancet 331, 966–969 (1988)
Bond, A., Alavi, A., Axford, J.S., Bourke, B.E., Bruckner, F.E., Kerr, M.A., Maxwell, J.D., Tweed, K.J., Weldon, M.J., Youinou, P., Hay, F.C.: A detailed lectin analysis of IgG glycosylation, demonstrating disease specific changes in terminal galactose and N-acetylglucosamine. J. Autoimmun. (1997). doi:10.1006/jaut.1996.0104
Dubé, R., Rook, G.A., Steele, J., Brealey, R., Dwek, R., Rademacher, T., Lennard-Jones, J.: Agalactosyl IgG in inflammatory bowel disease: correlation with creactive protein. Gut 31, 431–434 (1990)
Mehta, A.S., Long, R.E., Comunale, M.A., Wang, M., Rodemich, L., Krakover, J., Philip, R., Marrero, J.A., Dwek, R.A., Block, T.M.: Increased levels of galactose-deficient anti-Gal immunoglobulin G in the sera of hepatitis C virus-infected individuals with fibrosis and cirrhosis. J. Virol. (2008). doi:10.1128/JVI.01600-07
Moore, J.S., Wu, X., Kulhavy, R., Tomana, M., Novak, J., Moldoveanu, Z., Brown, R., Goepfert, P.A., Mestecky, J.: Increased levels of galactose-deficient IgG in sera of HIV-1-infected individuals. AIDS (2005). doi:10.1097/01.aids.0000161767.21405.68
Stefanović, G., Marković, D., Ilić, V., Brajović, G., Petrović, S., Milosević-Jovcić, N.: Hypogalactosylation of salivary and gingival fluid immunoglobulin G in patients with advanced periodontitis. J. Periodontol (2006). doi:10.1902/jop.2006.060049
Klaamas, K., Kodar, K., Kurtenkov, O.: An increased level of the Concanavalin A-positive IgG in the serum of patients with gastric cancer as evaluated by a lectin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (LELISA). Neoplasma 55(2), 143–50 (2008)
Kodar, K., Kurtenkov, O., Klaamas, K.: The Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen and alphaGal-specific human IgG glycoforms: concanavalin A reactivity and relation to survival of cancer patients. Immunol. Invest. (2009). doi:10.3109/08820130903147193
Wilm, M., Shevchenko, A., Houthaeve, T., Breit, S., Schweigerer, L., Fotsis, T., Mann, M.: Femtomole sequencing of proteins from polyacrylamide gels by nano-electrospray mass spectrometry. Nature (1996). doi:10.1038/379466a0
Bardor, M., Cabrera, G., Stadlmann, J., Lerouge, P., Cremata, J.A., Gomord, V., Fitchette, A.C.: N-glycosylation of plant recombinant pharmaceuticals. Methods Mol. Biol. (2009). doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-407-0_14
Stadlmann, J., Pabst, M., Kolarich, D., Kunert, R., Altmann, F.: Analysis of immunoglobulin glycosylation by LC-ESI-MS of glycopeptides and oligosaccharides. Proteomics (2008). doi:10.1002/pmic.200700968
Stadlmann, J., Weber, A., Pabst, M., Anderle, H., Kunert, R., Ehrlich, H.J., Peter, Schwarz. H,, Altmann, F.: A close look at human IgG sialylation and subclass distribution after lectin fractionation. Proteomics (2009). doi:10.1002/pmic.200800931
Zhang, X., Asara, J.M., Adamec, J., Ouzzani, M., Elmagarmid, A.K.: Data preprocessing in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Bioinformatics (2005). doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti660
Altmann, F.: What’s your name, sugar? A simple abbreviation system for complex N-glycan structures. http://www.proglycan.com (2010). Accessed 28 June 2010.
Kaneko, Y., Nimmerjahn, F., Ravetch, J.V.: Anti-inflammatory activity of immunoglobulin G resulting from Fc sialylation. Science (2006). doi:10.1126/science.1129594
Nimmerjahn, F., Anthony, R.M., Ravetch, J.V.: Agalactosylated IgG antibodies depend on cellular Fc receptors for in vivo activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. (2007). doi:10.1073/pnas.0702936104
Nimmerjahn, F., Ravetch, J.V.: Analyzing antobody-Fc-receptor interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. (2008). doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-570-1_9
Iida, S., Kuni-Kamochi, R., Mori, K., Misaka, H., Inoue, M., Okazaki, A., Shitara, K., Satoh, M.: Two mechanisms of the enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) efficacy of non-fucosylated therapeutic antibodies in human blood. B.M.C. Cancer (2009). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-58
Patel, D., Guo, X., Ng, S., Melchior, M., Balderes, P., Burtrum, D., Persaud, K., Luna, X., Ludwig, D.L., Kang, X.: IgG isotype, glycosylation, and EGFR expression determine the induction of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in vitro by cetuximab. Hum. Antibodies (2010). doi:10.3233/HAB-2010-0232
Turner, G.A.: N-glycosylation of serum proteins in disease and its investigation using lectins. Clin. Chim. Acta. 266, 149–171 (1992)
Hakomori, S.: Glycosylation defining cancer malignancy: new wine in an old bottle. P.N.A.S. (2002). doi:10.1073/pnas.172380699
Brooks, S.A., Carter, T.M., Royle, L., Harvey, D.J., Fry, S.A., Kinch, C., Dwek, R.A., Rudd, P.M.: Altered glycosylation of proteins in cancer: what is the potential for new anti-tumour strategies. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 8(1), 2–21 (2008)
Arnold, J.N., Saldova, R., Galligan, M.C., Murphy, T.B., Mimura-Kimura, Y., Telford, J.E., Godwin, A.K., Rudd, P.M.: Novel glycan biomarkers for the detection of lung cancer. J. Proteome Res. (2011). doi:10.1021/pr101034t
Gerçel-Taylor, C., Bazzett, L.B., Taylor, D.D.: Presence of aberrant tumor-reactive immunoglobulins in the circulation of patients with ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. (2001). doi:10.1006/gyno.2000.6102
Bones, J., Byrne, J.C., O'Donoghue, N., McManus, C., Scaife, C., Boissin, H., Nastase, A., Rudd, P.M.: Glycomic and glycoproteomic analysis of serum from patients with stomach cancer reveals potential markers arising from host defense response mechanisms. J. Proteome Res. (2011). doi:10.1021/pr101036b
Kanoh, Y., Mashiko, T., Danbara, M., Takayama, Y., Ohtani, S., Egawa, S., Baba, S., Akahoshi, T.: Changes in serum IgG oligosaccharide chains with prostate cancer progression. Anticancer Res 24(5B), 3135–9 (2004)
Aurer, I., Lauc, G., Dumić, J., Rendić, D., Matisić, D., Milos, M., Heffer-Lauc, M., Flogel, M., Labar, B.: Aberrant glycosylation of Igg heavy chain in multiple myeloma. Coll. Antropol. 31(1), 247–51 (2007)
Rademacher, T.W., Williams, P., Dwek, R.A.: Agalactosyl glycoforms of IgG autoantibodies are pathogenic. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 91, 6123–7 (1994)
Selman, M.H., Niks, E.H., Titulaer, M.J., Verschuuren, J.J., Wuhrer, M., Deelder, A.M.: IgG Fc N glycosylation changes in Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic syndrome and Myasthenia Gravis. J. Proteome Res. (2011). doi:10.1021/pr1004373
Huhn, C., Selman, M.H., Ruhaak, L.R., Deelder, A.M., Wuhrer, M.: IgG glycosylation analysis. Proteomics (2009). doi:10.1002/pmic.200800715
Stadlmann, J., Pabst, M., Altmann, F.: Analytical and Functional Aspects of Antibody Sialylation. J. Clin. Immunol. (2010). doi:10.1007/s10875-010-9409-2
Takahashi, M., Kuroki, Y., Ohtsubo, K., Taniguchi, N.: Core fucose and bisecting GlcNAc, the direct modifiers of the N-glycan core: their functions and target proteins. Carbohydr. Res. (2009). doi:10.1016/j.carres.2009.04.031
Yamada, E., Tsukamoto, Y., Sasaki, R., Yagyu, K., Takahashi, N.: Structural changes of immunoglobulin G oligosaccharides with age in healthy human serum. Glycoconj. J. 14, 401–405 (1997)
Pucic, M., Knezevic, A., Vidic, J., Adamczyk, B., Novokmet, M., Polasek, O., Gornik, O., Supraha-Goreta, S., Wormald, M.R., Redzic, I., Campbell, H., Wright, A., Hastie, N.D., Wilson, J.F., Rudan, I., Wuhrer, M., Rudd, P.M., Josic, D., Lauc, G.: High throughput isolation and glycosylation analysis of IgG-variability and heritability of the IgG glycome in three isolated human populations. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 10, (2011). doi:10.1074/mcp.M111.010090
Ruhaak, L.R., Uh, H.W., Beekman, M., Koeleman, C.A., Hokke, C.H., Westendorp, R.G., Wuhrer, M., Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J., Slagboom, P.E., Deelder, A.M.: Decreased levels of bisecting GlcNAc glycoforms of IgG are associated with human longevity. P.Lo.S. One (2010). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012566
Kurtenkov, O., Miljukhina, L., Smorodin, J., Klaamas, K., Bovin, N., Ellamaa, M., Chuzmarov, V.: Natural IgM and IgG antibodies to Thomsen-Friedenreich (T) antigen in serum of patients with gastric cancer and blood donors–relation to Lewis (a, b) histo-blood group phenotype. Acta. Oncol. 38(7), 939–43 (1999)
Kurtenkov, O., Klaamas, K., Mensdorff-Pouilly, S., Miljukhina, L., Shljapnikova, L., Chuzmarov, V.: Humoral immune response to MUC1 and to the Thomsen-Friedenreich (TF) glycotope in patients with gastric cancer: relation to survival. Acta. Oncol. (2007). doi:10.1080/02841860601055441
Raman, D., Baugher, P.J., Mon Thu, Y., Richmond, A.: Role of chemokines in tumor growth. Cancer Lett. (2007). doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2007.05.013
Goldberg, J.E., Schwertfeder, K.L.: Proinflammatory cytokines in breast cancer: mechanism of action and potential targets for therapeutics. Curr. Drug Targets 11, 1133–46 (2010)
Kazatchkine, M.D., Kaveri, S.V.: Immunomodulation of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases with intravenous immune globulin. N. Engl. J. Med. (2001). doi:10.1056/NEJMra993360
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Dr. Friedrich Altmann for providing the MS instrument and for the opportunity to work in his laboratory (Glycobiology Division, University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences). This work was supported by the Estonian Science Foundation (Grants #7317 and #8399) and by Archimedes Foundation scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Esm 1
(PDF 55 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kodar, K., Stadlmann, J., Klaamas, K. et al. Immunoglobulin G Fc N-glycan profiling in patients with gastric cancer by LC-ESI-MS: relation to tumor progression and survival. Glycoconj J 29, 57–66 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-011-9364-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-011-9364-z