Abstract
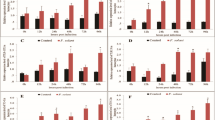
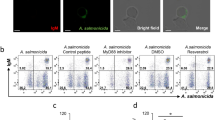
In aquaculture, antibiotics are the traditional treatment used against bacterial infections. However, their use has increasingly come into question given their effects on fish and, possibly, on human health. Consequently, there is interest in developing alternative treatments aimed at stimulating the innate immune response of fish, which is the first line of defense against pathogens. In relation to this, the Toll-like receptors (TLR) aid in the selective identification of pathogens. The present study evaluated immunostimulatory activity of prolactin (PRL) hormone on expression levels of TLR1, 9, and 22, MyD88, and IL-1β during in vitro infection with the fish pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis, in primary cultures of Oncorhynchus mykiss head kidney cells. Results indicated that PRL increased expression of TLRs and MyD88 during the first hours of bacterial infection, while a constant increase in expression was found for IL-1β. These findings suggest that PRL indirectly modulates expression of TLRs by activating expression of suppressors of cytokine signaling, thereby regulating immune response over long periods of time during bacterial infection.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- PAMPs:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- MyD88:
-
Myeloid differentiation factor 88
- HK:
-
Head kidney
- Ct:
-
Cycle threshold
References
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Andersen O, Skibeli V, Gautvik K (1989) Purification and characterization of Atlantic salmon prolactin. Gen Comp Endocrinol 73:354–360
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250
Arnemo M, Kavaliauskis A, GjØen T (2014) Effect of TLR agonists and viral infection on cytokine and TLR expression in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Dev Comp Immunol 46:139–145
Basu M, Swain B, Maiti NK, Routray P, Samanta M (2012) Inductive expression of toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) and associated downstream signaling molecules following ligand exposure and bacterial infection in the Indian major carp (C. mrigala). Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:121–131
Boltaña S, Roher N, Goetz F, McKenzie S (2011) PAMPs, PRRs and the genomics of gram negative bacterial recognition in fish. Dev Comp Immunol 35:1195–1203
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brietzke A, Goldammer T, Rebl H, Korytár T, Köllner B, Yang W, Rebl A, Seyfert H (2014) Characterization of the interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4)-encoding gene in salmonid fish: the functional copy is rearranged in Oncorhynchus mykiss and that factor can impair TLR signaling in mammalian cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol 36:206–214
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Ellis AE (2001) The immunology of teleosts. In: Roberts RJ (ed) Fish pathology, 3rd edn. W. B. Saunders, London, pp 133–150
Fryer J, Hedrick R (2003) Piscirickettsia salmonis: a gram negative intracellular bacterial pathogen of fish. J Fish Dis 26:251–262
Fux C, Shirtliff M, Stoodley P, Costerton J (2005) Can laboratory reference strains mirror real-word pathogenesis? Trends Microbiol 13:58–63
Ingerslev H, Lunder T, Nielsen M (2010) Inflammatory and regenerative responses in salmonids following mechanicals tissue damage and natural infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:440–450
Kruse H, Sørum H (1995) Transfer of multiple drug resistance plasmids between bacteria of diverse origins in natural microenvironments. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:4015–4021
Kumar H, Kawai T, Akira S (2009) Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. BBRC 388:621–625
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Medzhitov R (2001) Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 1:135–145
O’Neill L, Golenbock D, Bowie A (2013) The history of toll-like receptors-redefining innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 13:453–460
Olavarria VH, Figueroa J, Mulero V (2013) Induction of gene encoding NADPH oxidase components and activation of IFN regulatory factor-I by prolactin in fish macrophage. Innate Immun 19:644–654
Olavarría V, Sepulcre M, Figueroa J, Mulero V (2010) Prolactin-induced production of reactive oxygen species and IL-1β in leukocytes from the bony fish gilthead seabream involves Jak/Stat and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Inmunol 185:3873–3883
Oshiumi H, Matsuo A, Tsujita T, Mitani H, Kasai H, Yoshimizu M, Matsumoto M, Seya T (2008) Teleost TLR22 recognizes RNA duplex to induce IFN and protect cells for birnaviruses. J Immunol 181:3474–3485
Palti Y (2011) Toll-like receptors in bony fish: from genomics to functions. Dev Comp Immunol 35:1263–1272
Paredes M, Gonzalez K, Figueroa J, Motiel-Eulefi E (2013) Immunomodulatory effect of prolactin on Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) macrophage function. Fish Physiol Biochem 39:1215–1221
Pérez-Sánchez T, Balcázar JL, Merrifield DL, Carnevali O, Gioacchini G, de Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I (2011) Expression of immune-related genes in rainbow trout (O. mykiss) induced by probiotic bacteria during Lactococcus garvieae infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:196–201
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Rebl A, Goldammer T, Seyfert H (2010) Toll-like receptors signaling in bony fish. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 134:139–150
Ripio M, Domínguez-Bernal G, Suárez M, Brehm K, Berche P, Vázquez-Boland J (1996) Transcriptional activation of virulence genes in wild-type strains of Listeria monocytogenes in response to a change in the extracellular medium composition. Res Microbiol 147:371–384
Rojas V, Galanti N, Bols N, Marshall S (2009) Productive infection of Piscirickettsia salmonis in macrophages and monocyte-like cells from rainbow trout, a possible survival strategy. J Cell Biochem 108:631–637
Rozas M, Enríquez R (2014) Piscirickettsiosis and Piscirickettsia salmonis in fish: a review. J Fish Dis 37:163–188
Salazar C, Haussmann D, Kausel G, Figueroa J (2015) Molecular cloning of Salmo salar toll-like receptors (TLR1, TLR22, TLR5M and TLR5S) and expression analysis in SHK-1 cells during Piscirickettsia salmonis infection. J Fish Dis. doi:10.1111/jfd.12354
Seya T, Akasawa T, Tsujita T, Matsumoto M (2006) Role of toll-like receptors in adjuvant augmented immune therapies. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 3:31–38
Underhill D, Ozinsky A (2002) Toll-like receptors: key mediators of microbe detection. Curr Opin Immunol 14:103–110
Vera T, Isla A, Cuevas A, Figueroa J (2012) A new liquid medium for the pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis. Arch Med Vet 44:273–277
Werling D, Jann OC, Offord V, Glass EJ, Coffey TJ (2009) Variation matters: TLR structure and species-specific pathogen recognition. Trends Immunol 30:124–130
Wilhelm V, Miquel A, Burzio L, Rosemblatt M, Engel E, Valenzuela S, Parada G, Valenzuela P (2006) A vaccine against the salmonid pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis based on recombinant proteins. Vaccine 24:5083–5091
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FONDECYT 1130069 and FONDAP No 15110027 (the Interdisciplinary Center for Aquaculture Research, INCAR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peña, B., Isla, A., Haussmann, D. et al. Immunostimulatory effect of salmon prolactin on expression of Toll-like receptors in Oncorhynchus mykiss infected with Piscirickettsia salmonis . Fish Physiol Biochem 42, 509–516 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0155-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0155-5