Abstract
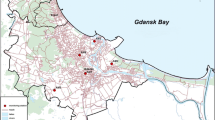
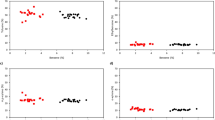
Atmospheric BTEX [benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, o-xylene and (m + p)-xylene] concentrations have been determined in the Naples metropolitan area (NMA) and in two suburban areas located on the north within about 25 km, during 2006. The pollutants were collected by passive samplers (24-h samplings), and analysed by GC-MS. In all the areas analysed the average atmospheric benzene concentrations were higher than the limit value fixed by the European Union for 2010 and in NMA the average concentration (9.8 μg m-) also exceeded the limit fixed for 2006. High linear correlation coefficients between the average daily concentrations of the different BTEX are indicative of a single major source, most likely the vehicular traffic. The temporal and spatial distribution of BTEX relative concentrations suggest that massive emissions in NMA negatively affect the quality of the air in northern suburban areas, prevalently during the hottest months of the year, probably due to transport by local seasonal winds. The ratios between BTEX daily concentrations showed a clear dependence on the intensity of solar actinic flow, indicating a major role of photochemical processes in the air cleaning from these volatile organic pollutants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brocco, D., Fratarcangeli, R., Lepore, L., Petricca, M., & Ventrone, I. (1997). Determination of aromatic hydrocarbons in urban air of Rome. Atmospheric Environment, 31, 557–566.
Bruno, P., Caputi, M., Caselli, M., De Gennaro, G., & De Rienzo, M. (2005). Reliability of a BTEX radial diffusive sampler for thermal desorbtion: field measurements. Atmospheric Environment, 39, 1347–1355.
Chan, L. Y., Lau, W. L., Wang, X. M., & Tang, J. H. (2003). Preliminary measurements of aromatic VOCs in public transportation modes in Guangzhou, China. Environment International, 29, 429–435.
Cocheo, V., Sacco, P., Boaretto, C., De Saeger, E., Ballesta, P. P., Skov, H., et al. (2000). Urban benzene and human exposure. Nature, 404, 141–142.
Ferrari, C. P., Kaluzny, P., & Roche, A. (1998). Aromatic hydrocarbons and aldehydes in the atmosphere of Grenoble, France. Chemosphere, 37, 1587–1601.
Heeb, N. V., Forss, A. M., & Bach, C. (1999). Fast and quantitative measurement of benzene, toluene and C2-benzenes in automotive exhaust during transient engine operation with and without catalytic exhaust gas treatment. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 205–215.
Heeb, N. V., Forss, A. M., Bach, C., & Mattrel, P. (2000). Velocity-dependent emission factors of benzene, toluene and C2-benzenes of a passenger car equipped with and without a regulated 3-way catalyst. Atmospheric Environment, 34, 1123–1137.
Hinwood, A. L., Rodriguez, C., Runnion, T., Farrar, D., Murray, F., Horton, A., et al. (2007). Risk factor for increased BTEX exposure in four Australian cities. Chemosphere, 66, 533–541.
Ho, K. F., Lee, S. C., Guo, H., & Tsai, W. T. (2004). Seasonal and diurnal variations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere of Hong Kong. Science of the Total Environment, 322, 155–166.
Kerbachi, R., Boughedaoui, M., Bounoua, L., & Keddam, M. (2006). Ambient air pollution by aromatic hydrocarbons in Algiers. Atmospheric Environment, 40, 3995–4003.
Kim, Y. M., Harrad, S., & Harrison, R. M. (2001). Concentrations and sources of VOCs in urban domestic and public microenvironments. Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 997–1004.
Kongtip, P., Thongsuk, W., Yoosook, W., & Chantanakul, S. (2006). Health effect of metropolitan traffic-related air pollutants on street vendors. Atmospheric Environment, 40, 7138–7145.
Iovino, P., Salvestrini, S., & Capasso, S. (2006). Background atmospheric levels of BTEX in a medium-sized city and surrounding area in Southern Italy. Air Pollution, XIV, 611–618.
Meybeck, M., Della Massa, J. P., Simon, V., Grasset, E., & Torres, L. (2000). Etude de la distribution atmosphérique de Composés Organiques Volatils (COV) monoaromatiques: Benzène, Toluène, Xylènes (BTX) et du dioxyde d’azote sur l’agglomération toulousaine. Pollution Atmospherique, 168, 569–582.
Moschonas, N., & Glavas, S. (1996). C3–C10 hydrocarbons in the atmosphere of Athens, Greece. Atmospheric Environment, 30, 2769–2772.
Pilidis, G. A., Karakitsios, S. P., & Kassomenos, P. A. (2005). BTX measurements in a medium-sized European city. Atmospheric Environment, 18, 6051–6065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iovino, P., Polverino, R., Salvestrini, S. et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of BTEX pollutants in the atmosphere of metropolitan areas and neighbouring towns. Environ Monit Assess 150, 437–444 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0242-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0242-5