Abstract
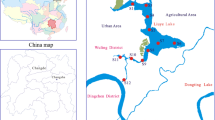
Concentrations and risk assessment of chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As), lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd) and mercury (Hg) were investigated in 106 samples of surface sediments from the East Lake, China in this study. The mean concentration of Zn was highest among the eight heavy metals (225 mg kg−1), followed by As (191 mg kg−1), Cr (145 mg kg−1), Cu (55 mg kg−1), Ni (27.1 mg kg−1), Pb (7.93 mg kg−1), Cd (0.94 mg kg−1) and Hg (0.21 mg kg−1). Niuchao Hu was less polluted by heavy metals compare to the other four lakelets of the East Lake. The correlations among these heavy metals and the results of principal component analysis indicated that the distribution of Cd, Pb and Hg was related to anthropogenic activities, whereas Cu, As and Cr were affected by the parent rocks. Zinc and Ni were influenced both by anthropogenic activities and parent rocks. Based on the Sediment Quality Guidelines, the results of toxicity assessment indicated that adverse effects caused by Cr and As would be expected frequently. Nickel, Zn, Cd and Hg may cause adverse effects occasionally and Cu and Pb may cause toxicity infrequently. Arsenic was found to have the highest acute toxicity by toxic units (TUs), followed by Cr, Ni, Zn, Hg, Cu, Cd and Pb. The potential ecological risk index analysis indicated that As, Cd and Hg had considerable or high ecological risk, whereas Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn and Pb had low ecological risk. The potential ecological risk index (RI) of the heavy metals in the surface sediments of East Lake was 483, indicating considerable ecological risk. Close attention should be paid to pollution of the heavy metals in East Lake, China.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy A, Demirezen D, Duman F (2005) Bioaccumulation, detection and analyses of heavy metal pollution in Sultan Marsh and its environment. Water Air Soil Pollut 164(1–4):241–255
Alloway BJ (2013) Heavy metals in soils-trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability. Springer, Dordrecht
Audry S, Schafer J, Blanc G, Jouanneau JM (2004) Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France). Environ Pollut 132(3):413–426
Bai J, Cui B, Chen B, Zhang K, Deng W, Gao H, Xiao R (2011a) Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland, China. Ecol Model 222(2):301–306
Bai J, Xiao R, Cui B, Zhang K, Wang Q, Liu X, Gao H, Huang L (2011b) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from the young and old reclaimed regions in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ Pollut 159(3):817–824
Bastami KD, Bagheri H, Haghparast S, Soltani F, Hamzehpoor A, Bastami MD (2012) Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of selected heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Gorgan Bay, Iran. Mar Pollut Bull 64(12):2877–2884
Bragato C, Brix H, Malagoli M (2006) Accumulation of nutrients and heavy metals in Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steudel and Bolboschoenus maritimus(L.) Palla in a constructed wetland of the Venice lagoon watershed. Environ Pollut 144(3):967–975
Chen X, Xia X, Zhao Y, Zhang P (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):640–646
Cheng S, Grosse W, Karrenbrock F, Thoennessen M (2002) Efficiency of constructed wetlands in decontamination of water polluted by heavy metals. Ecol Eng 18(3):317–325
Choi MS, Yi HI, Yang SY, Lee CB, Cha HJ (2007) Identification of Pb sources in Yellow Sea sediments using stable Pb isotope ratios. Mar Chem 107(2):255–274
Cooke J, Andrews S, Johnson M (1990) Lead, zinc, cadmium and fluoride in small mammals from contaminated grassland established on fluorspar tailings. Water Air Soil Pollut 51(1–2):43–54
Dauvalter V, Rognerud S (2001) Heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pasvik River drainage. Chemosphere 42(1):9–18
Dou Y, Li J, Zhao J, Hu B, Yang S (2013) Distribution, enrichment and source of heavy metals in surface sediments of the eastern Beibu Bay, South China sea. Mar Pollut Bull 67(1–2):137–145
Fan C, Zhu Y, Ji Z, Zhang L, Yang L (2002) Characteristics of the pollution of heavy metals in the sediments of Yilihe River, Taihu Basin. J Lake Sci 14(3):235–241
Feng H, Han X, Zhang W, Yu L (2004) A preliminary study of heavy metal contamination in Yangtze River intertidal zone due to urbanization. Mar Pollut Bull 49(11):910–915
Gaur VK, Gupta SK, Pandey S, Gopal K, Misra V (2005) Distribution of heavy metals in sediment and water of river Gomti. Environ Monit Assess 102(1–3):419–433
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Hu X, Wang C, Zou L (2011) Characteristics of heavy metals and Pb isotopic signatures in sediment cores collected from typical urban shallow lakes in Nanjing, China. J Environ Manag 92(3):742–748
Huang S, Liao Q, Hua M, Wu X, Bi K, Yan C, Chen B, Zhang X (2007) Survey of heavy metal pollution and assessment of agricultural soil in Yangzhong district, Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 67(11):2148–2155
Kamala-Kannan S, Prabhu Dass Batvari B, Lee KJ, Kannan N, Krishnamoorthy R, Shanthi K, Jayaprakash M (2008) Assessment of heavy metals (Cd, Cr and Pb) in water, sediment and seaweed (Ulva lactuca) in the Pulicat lake, southeast India. Chemosphere 71(7):1233–1240
Kishe MA, Machiwa JF (2003) Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of Mwanza Gulf of Lake Victoria, Tanzania. Environ Int 28(7):619–625
Kowalkowski T, Zbytniewski R, Szpejna J, Buszewski B (2006) Application of chemometrics in river water classification. Water Res 40(4):744–752
Liang LN, He B, Jiang GB, Chen DY, Yao ZW (2004) Evaluation of mollusks as biomonitors to investigate heavy metal contaminations along the Chinese Bohai Sea. Sci Total Environ 324(1–3):105–113
Lim HS, Lee JS, Chon HT, Sager M (2008) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of the abandoned Songcheon Au–Ag mine in Korea. J Geochem Explor 96(2):223–230
Liu ZD, Liu QS, Liu Y, Liu ZY (2006) Characteristics of heavy elements in sediments of Lake Dong hu (Wuhan) and relations to urban pollution. J Lake Sci 18(1):79–85 (in chinese)
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll C, Berger T (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39(1):20–31
Mays P, Edwards G (2001) Comparison of heavy metal accumulation in a natural wetland and constructed wetlands receiving acid mine drainage. Ecol Eng 16(4):487–500
Niu L, Yang F, Xu C, Yang H, Liu W (2013) Status of metal accumulation in farmland soils across China: from distribution to risk assessment. Environ Pollut 176:55–62
Ouyang Y, Higman J, Thompson J, O’Toole T, Campbell D (2002) Characterization and spatial distribution of heavy metals in sediment from Cedar and Ortega rivers subbasin. J Contam Hydrol 54(1–2):19–35
Ozmen H, Kulahci F, Cukurovali A, Dogru M (2004) Concentrations of heavy metal and radioactivity in surface water and sediment of Hazar Lake (Elazig, Turkey). Chemosphere 55(3):401–408
Pedersen F, Bjørnestad E, Andersen HV, Kjølholt J, Poll C (1998) Characterization of sediments from Copenhagen Harbour by use of biotests. Water Sci Technol 37(6):233–240
Samecka-Cymerman A, Kempers A (2001) Concentrations of heavy metals and plant nutrients in water, sediments and aquatic macrophytes of anthropogenic lakes (former open cut brown coal mines) differing in stage of acidification. Sci Total Environ 281(1):87–98
Senthil Kumar K, Sajwan KS, Richardson JP, Kannan K (2008) Contamination profiles of heavy metals, organochlorine pesticides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and alkylphenols in sediment and oyster collected from marsh/estuarine Savannah GA, USA. Mar Pollut Bull 56(1):136–149
Sin S, Chua H, Lo W, Ng L (2001) Assessment of heavy metal cations in sediments of Shing Mun River, Hong Kong. Environ Int 26(5):297–301
Singh M, Müller G, Singh IB (2003) Geogenic distribution and baseline concentration of heavy metals in sediments of the Ganges River, India. J Geochem Explor 80(1):1–17
Suresh G, Sutharsan P, Ramasamy V, Venkatachalapathy R (2012) Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:117–124
Tang W, Shan B, Zhang H, Mao Z (2010) Heavy metal sources and associated risk in response to agricultural intensification in the estuarine sediments of Chaohu Lake Valley, East China. J Hazard Mater 176(1–3):945–951
Tao Y, Yuan Z, Xiaona H, Wei M (2012) Distribution and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in aquatic organisms of different trophic levels and potential health risk assessment from Taihu lake, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 81:55–64
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang C, Liu S, Zhao Q, Deng L, Dong S (2012a) Spatial variation and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediments in the Manwan Reservoir, Lancang River. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 82:32–39
Wang Y, Hu J, Xiong K, Huang X, Duan S (2012b) Distribution of Heavy Metals in Core Sediments from Baihua Lake, Procedia. Environ Sci 16:51–58
Weng HX, Zhu YM, Qin YC, Chen JY, Chen XH (2008) Accumulation discrepancy of heavy metal and organic pollutants in three near-shore depositional environments, southeastern China. J Asian Earth Sci 31(4):522–532
Yan JP, He Y, Huang H (2007) Characteristics of Heavy Metals and Their Evaluation in Sediments from Middle and Lower Reaches of the Huaihe River. J China Univ Min Technol 17(3):414–417
Yang Z, Wang Y, Shen Z, Niu J, Tang Z (2009) Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J Hazard Mater 166(2–3):1186–1194
Yao QZ, Zhang J, Wu Y, Xiong H (2007) Hydrochemical processes controlling arsenic and selenium in the Changjiang River (Yangtze River) system. Sci Total Environ 377(1):93–104
Yeomans J, Bremner JM (1988) A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil 1. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19(13):1467–1476
Yi Y, Yang Z, Zhang S (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159(10):2575–2585
Yuan H, Song J, Li X, Li N, Duan L (2012) Distribution and contamination of heavy metals in surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 64(10):2151–2159
Zhang M, Cui L, Sheng L, Wang Y (2009) Distribution and enrichment of heavy metals among sediments, water body and plants in Hengshuihu Wetland of Northern China. Ecol Eng 35(4):563–569
Zhang W, Liu X, Cheng H, Zeng EY, Hu Y (2012) Heavy metal pollution in sediments of a typical mariculture zone in South China. Mar Pollut Bull 64(4):712–720
Zhao Q, Liu S, Deng L, Yang Z, Dong S, Wang C, Zhang Z (2012) Spatio-temporal variation of heavy metals in fresh water after dam construction: a case study of the Manwan Reservoir, Lancang river. Environ Monit Assess 184(7):4253–4266
Zheng N, Wang Q, Liang Z, Zheng D (2008) Characterization of heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, Northeast China. Environ Pollut 154(1):135–142
Zhu HN, Yuan XZ, Zeng GM, Jiang M, Liang J, Zhang C, Yin J, Huang HJ, Liu ZF, Jiang HW (2012) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Xiawan Port based on modified potential ecological risk index. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 22(6):1470–1477
Acknowledgments
This project was supported in part by Open Funding Project of the Key Laboratory of Aquatic Botany and Watershed Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (NO. 2012FFB07301) and the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NO. Y329671K01).
Conflict of interest
All authors have read and approve this version of the article, and due care has been taken to ensure the integrity of the work. No part of this paper has published or submitted elsewhere. No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Yang, Y., Yun, X. et al. Distribution and ecological assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the East Lake, China. Ecotoxicology 23, 92–101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1154-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-013-1154-x