Abstract
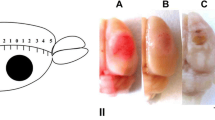
A traumatic brain injury or a focal brain lesion is followed by acute excitotoxicity caused by the presence of abnormally high glutamate (Glu) levels in the cerebrospinal and interstitial fluids. It has recently been demonstrated that this excess Glu in the brain can be eliminated into the blood following the intravenous administration of oxaloacetate (OxAc), which, by scavenging the blood Glu, induces an enhanced and neuroprotective brain-to-blood Glu efflux. In this study, we subjected rats to a photothrombotic lesion and treated them after the illumination with a single 30-min-long administration of OxAc (1.2 mg/100 g, i.v.). Following induction of the lesion, we measured the infarct size and the amplitudes of the somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs) as recorded from the skull surface. The photothrombotic lesion resulted in appreciably decreased amplitudes of the evoked potentials, but OxAc administration significantly attenuated this reduction, and also the infarct size assessed histologically. We suggest that the neuroprotective effects of OxAc are due to its blood Glu-scavenging activity, which, by increasing the brain-to-blood Glu efflux, reduces the excess Glu responsible for the anatomical and functional correlates of the ischemia, as evaluated by electrophysiological evoked potential (EP) measurements.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Glu:
-
Glutamate
- OxAc:
-
Oxaloacetate
- EP:
-
Evoked potential
- SEPs:
-
Somatosensory evoked potentials
- SSI:
-
Somatosensory cortex
- FJB:
-
Fluoro-Jade B
References
Back T, Hemmen T, Schuler OG (2004) Lesion evolution in cerebral ischemia. J Neurol 251:388–397. doi:10.1007/s00415-004-0399-y
Baik MW, Branston NM, Bentivoglio P, Symon L (1990) The effects of experimental brain-stem ischaemia on brain-stem auditory evoked potentials in primates. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 75:433–443. doi:10.1016/0013-4694(90)90088-2
Bordi F, Pietra C, Ziviani L, Reggiani A (1997) The glycine antagonist GV150526 protects somatosensory evoked potentials and reduces the infarct area in the MCAo model of focal ischemia in the rat. Exp Neurol 145:425–433. doi:10.1006/exnr.1997.6442
Bullock R, Zauner A, Woodward JJ, Myseros J, Choi SC, Ward JD, Marmarou A, Young HF (1998) Factors affecting excitatory amino acid release following severe human head injury. J Neurosurg 89:507–518
Castillo J, Davalos A, Naveiro J, Noya M (1996) Neuroexcitatory amino acids and their relation to infarct size and neurological deficit in ischemic stroke. Stroke 27:1060–1065
Castillo J, Davalos A, Noya M (1997) Progression of ischaemic stroke and excitotoxic aminoacids. Lancet 349:79–83. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(96)04453-4
Choi DW (1988) Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron 1:623–634. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(88)90162-6
Choi DW (1994) Glutamate receptors and the induction of excitotoxic neuronal death. Prog Brain Res 100:47–51. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60767-0
Choi DW, Rothman SM (1990) The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci 13:171–182. doi:10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.001131
Damjanac M, Rioux Bilan A, Barrier L, Pontcharraud R, Anne C, Hugon J, Page G (2007) Fluoro-Jade B staining as useful tool to identify activated microglia and astrocytes in a mouse transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1128:40–49. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.05.050
Ebisu T, Katsuta K, Fujikawa A, Aoki I, Umeda M, Naruse S, Tanaka C (2001) Early and delayed neuroprotective effects of FK506 on experimental focal ischemia quantitatively assessed by diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 19:153–160. doi:10.1016/S0730-725X(01)00233-8
el-Rahman A, Hammouda MA, Fakeir A (1995) Flow cytometric evaluation of erythrocyte response to oxidant stress. Cytometry 20:19–22
Farkas T, Perge J, Kis Z, Wolff JR, Toldi J (2000) Facial nerve injury-induced disinhibition in the primary motor cortices of both hemispheres. Eur J NeuroSci 12:2190–2194
Farkas T, Racekova E, Kis Z, Horvath S, Burda J, Galik J, Toldi J (2003) Peripheral nerve injury influences the disinhibition induced by focal ischaemia in the rat motor cortex. Neurosci Lett 342:49–52
Girotti AW, Thomas JP, Jordan JE (1985) Inhibitory effect of zinc(II) on free radical lipid peroxidation in erythrocyte membranes. J Free Radic Biol Med 1:395–401
Gottlieb M, Wang Y, Teichberg VI (2003) Blood-mediated scavenging of cerebrospinal fluid glutamate. J Neurochem 87:119–126
Hodgkins PS, Wu HQ, Zielke HR, Schwarcz R (1999) 2-Oxoacids regulate kynurenic acid production in the rat brain: studies in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem 72:643–651
Kharlamov A, Uz T, Joo JY, Manev H (1996) Pharmacological characterization of apoptotic cell death in a model of photothrombotic brain injury in rats. Brain Res 734:1–9
Ladds A, Branston NM, Vajda J, McGillicuddy JE, Symon L (1988) Changes in somatosensory evoked potentials following an experimental focal ischaemic lesion in thalamus. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 71:233–240
Liu X, Branston NM, Kawauchi M, Jellinek DA, Symon L (1992) Electrical stimulation of motor cortex in experimental cortical ischaemia: pyramidal responses at C5 and the surface EMG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85:209–214
Lye RH, Shrewsbury-Gee J, Slater P, Latham A (1987) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: use of evoked potentials and tetrazolium staining to assess chronic ischaemia. J Neurosci Methods 22:133–139
Mies G, Iijima T, Hossmann KA (1993) Correlation between peri-infarct DC shifts and ischaemic neuronal damage in rat. NeuroReport 4:709–711
Minamide H, Onishi H, Yamashita J, Ikeda K (1994) Reversibility of transient focal cerebral ischemia evaluated by somatosensory evoked potentials in cats. Surg Neurol 42:138–147
Molchanova S, Koobi P, Oja SS, Saransaari P (2004) Interstitial concentrations of amino acids in the rat striatum during global forebrain ischemia and potassium-evoked spreading depression. Neurochem Res 29:1519–1527
Muller TB, Haraldseth O, Jones RA, Sebastiani G, Lindboe CF, Unsgard G, Oksendal AN (1995) Perfusion and diffusion-weighted MR imaging for in vivo evaluation of treatment with U74389G in a rat stroke model. Stroke 26:1453–1458
Nagababu E, Rifkind JM (1998) Formation of fluorescent heme degradation products during the oxidation of hemoglobin by hydrogen peroxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247:592–596
Nagababu E, Rifkind JM (2004) Heme degradation by reactive oxygen species. Antioxid Redox Signal 6:967–978
Nistico R, Piccirilli S, Cucchiaroni ML, Armogida M, Guatteo E, Giampa C, Fusco FR, Bernardi G, Nistico G, Mercuri NB (2008) Neuroprotective effect of hydrogen peroxide on an in vitro model of brain ischaemia. Br J Pharmacol 153:1022–1029
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, London
Rozanowska M, Sarna T, Land EJ, Truscott TG (1999) Free radical scavenging properties of melanin interaction of eu- and pheo-melanin models with reducing and oxidising radicals. Free Radic Biol Med 26:518–525
Scheller D, Szathmary S, Kolb J, Tegtmeier F (2000) Observations on the relationship between the extracellular changes of taurine and glutamate during cortical spreading depression, during ischemia, and within the area surrounding a thrombotic infarct. Amino Acids 19:571–583
Shaw PJ, Forrest V, Ince PG, Richardson JP, Wastell HJ (1995) CSF and plasma amino acid levels in motor neuron disease: elevation of CSF glutamate in a subset of patients. Neurodegeneration 4:209–216
Spreux-Varoquaux O, Bensimon G, Lacomblez L, Salachas F, Pradat PF, Le Forestier N, Marouan A, Dib M, Meininger V (2002) Glutamate levels in cerebrospinal fluid in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a reappraisal using a new HPLC method with coulometric detection in a large cohort of patients. J Neurol Sci 193:73–78
Stieg PE, Sathi S, Warach S, Le DA, Lipton SA (1999) Neuroprotection by the NMDA receptor-associated open-channel blocker memantine in a photothrombotic model of cerebral focal ischemia in neonatal rat. Eur J Pharmacol 375:115–120
Stone TW (1993) Neuropharmacology of quinolinic and kynurenic acids. Pharmacol Rev 45:309–379
Teichberg VI, Cohen-Kashi-Malina K, Cooper I, Zlotnik A (2009) Homeostasis of glutamate in brain fluids: an accelerated brain-to-blood efflux of excess glutamate is produced by blood glutamate scavenging and offers protection from neuropathologies. Neuroscience. 158(1):301–308
Toldi J, Farkas T, Perge J, Wolff JR (1999) Facial nerve injury produces a latent somatosensory input through recruitment of the motor cortex in the rat. NeuroReport 10:2143–2147
Traystman RJ, Kirsch JR, Koehler RC (1991) Oxygen radical mechanisms of brain injury following ischemia and reperfusion. J Appl Physiol 71:1185–1195
Umemura K, Shimakura A, Nakashima M (1997) Neuroprotective effect of a novel AMPA receptor antagonist, YM90 K, in rat focal cerebral ischaemia. Brain Res 773:61–65
Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Wachtel MS, Ginsberg MD (1985) Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol 17:497–504
Wright A, Hawkins CL, Davies MJ (2003) Photo-oxidation of cells generates long-lived intracellular protein peroxides. Free Radic Biol Med 34:637–647
Zlotnik A, Gurevich B, Tkachov S, Maoz I, Shapira Y, Teichberg VI (2007) Brain neuroprotection by scavenging blood glutamate. Exp Neurol 203:213–220
Zlotnik A, Gurevich B, Cherniavsky E, Tkachov S, Matuzani-Ruban A, Leon A, Shapira Y, Teichberg VI (2008) The contribution of the blood glutamate scavenging activity of pyruvate to its neuroprotective properties in a rat model of closed head injury. Neurochem Res 33:1044–1050
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Bureau of Research and Development (NKTH RET 08/2004), OTKA K75628, TéT SK-26/200, and GVOP-3.2.1-2004-04-0357/3.0. T.F. is a Bolyai Fellow of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. V.I.T has received support from the Weizmann Institute Nella and Leon Benoziyo Center for Neurological Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagy, D., Marosi, M., Kis, Z. et al. Oxaloacetate Decreases the Infarct Size and Attenuates the Reduction in Evoked Responses after Photothrombotic Focal Ischemia in the Rat Cortex. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29, 827–835 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9364-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9364-8