Abstract
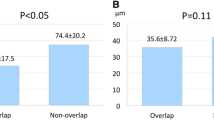
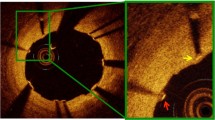
Minimal data exist regarding the use of optical coherence tomography (OCT) to evaluate malapposed strut coverage following implantation of drug-eluting stents (DESs). Follow-up OCT examination after DES implantation was performed in 368 patients with 406 lesions at our institute. We assessed the status of malapposed strut coverage that was identified via OCT in 92 (23 %) lesions. An absence of uncovered struts among malapposed struts was defined as completely covered (CC) malapposition; the presence of uncovered struts was defined as incompletely covered (IC) malapposition. Among the 92 lesions with malapposed DES struts, CC malapposition was detected in 47 lesions (51 %). Compared to lesions with IC malapposition (n = 45, 49 %), lesions with CC malapposition showed a significantly lower percentage of uncovered struts among all the struts (14.9 ± 14.5 vs. 4.4 ± 8.5 %, respectively, p < 0.001) and among the other well-apposed struts without malapposition (12.7 ± 12.8 vs. 4.5 ± 8.7 %, respectively, p = 0.001). The degree of malapposed strut coverage was significantly different according to the type of DES; new-generation DESs such as everolimus- or zotarolimus-eluting stents showed a higher incidence of CC malapposition, compared to first-generation DESs such as sirolimus- or paclitaxel-eluting stents (82 vs. 34 %, respectively, p < 0.001). This study showed the complete coverage in about 50 % of the lesions with malapposed DES struts on follow-up OCT. The degree of malapposed DES strut coverage was strongly affected by the type of implanted DESs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mintz GS, Weissman NJ (2006) Intravascular ultrasound in the drug-eluting stent era. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:421–429
Finn AV, Joner M, Nakazawa G, Kolodgie F, Newell J, John MC, Gold HK, Virmani R (2007) Pathological correlates of late drug-eluting stent thrombosis: strut coverage as a marker of endothelialization. Circulation 115:2435–2441
Cook S, Wenaweser P, Togni M, Billinger M, Morger C, Seiler C, Vogel R, Hess O, Meier B, Windecker S (2007) Incomplete stent apposition and very late stent thrombosis after drug-eluting stent implantation. Circulation 115:2426–2434
Siqueira DA, Abizaid AA, Costa Jde R, Feres F, Mattos LA, Staico R, Abizaid AA, Tanajura LF, Chaves A, Centemero M, Sousa AG, Sousa JE (2007) Late incomplete apposition after drug-eluting stent implantation: incidence and potential for adverse clinical outcomes. Eur Heart J 28:1304–1309
Hassan AK, Bergheanu SC, Stijnen T, van der Hoeven BL, Snoep JD, Plevier JW, Schalij MJ, WouterJukema J (2010) Late stent malapposition risk is higher after drug-eluting stent compared with bare-metal stent implantation and associates with late stent thrombosis. Eur Heart J 31:1172–1180
Guagliumi G, Sirbu V, Musumeci G, Gerber R, Biondi-Zoccai G, Ikejima H, Ladich E, Lortkipanidze N, Matiashvili A, Valsecchi O, Virmani R, Stone GW (2012) Examination of the in vivo mechanisms of late drug-eluting stent thrombosis. J Am Coll Cardiol Interv 1:12–20
Takano M, Inami S, Jang IK, Yamamoto M, Murakami D, Seimiya K, Ohba T, Mizuno K (2007) Evaluation by optical coherence tomography of neointimal coverage of sirolimus-eluting stent three months after implantation. Am J Cardiol 99:1033–1038
Prati F, Regar E, Mintz GS, Arbustini E, Di Mario C, Jang IK, Akasaka T, Costa M, Guagliumi G, Grube E, Ozaki Y, Pinto F, Serruys PW, for the expert’s OCT review document (2010) Expert review document on methodology, terminology, and clinical applications of optical coherence tomography: physical principles, methodology of image acquisition, and clinical application for assessment of coronary arteries and atherosclerosis. Eur Heart J 31:401–415
Kim JS, Hong MK, Fan C, Kim TH, Shim JM, Park SM, Ko YG, Choi D, Jang Y (2010) Intracoronary thrombus formation after drug-eluting stents implantation: optical coherence tomographic study. Am Heart J 159:278–283
Kim U, Kim JS, Kim JS, Lee JM, Son JW, Kim J, Ko YG, Choi D, Jang Y (2010) The initial extent of malapposition in ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated with drug-eluting stent: the usefulness of optical coherence tomography. Yonsei Med J 51:332–338
Tanigawa J, Barlis P, Di Mario C (2007) Intravascular optical coherence tomography: optimisation of image acquisition and quantitative assessment of stent strut apposition. EuroIntervention 3:128–136
Tanigawa J, Barlis P, Dimopoulos K, Dalby M, Moore P, Di Mario C (2009) The influence of strut thickness and cell design on immediate apposition of drug-eluting stents assessed by optical coherence tomography. Int J Cardiol 134:180–188
Barlis P, Dimopoulos K, Tanigawa J, Dzielicka E, Ferrante G, Del Furia F, Di Mario C (2010) Quantitative analysis of intracoronary optical coherence tomography measurements of stent strut apposition and tissue coverage. Int J Cardiol 141:151–156
Kim JS, Jang IK, Kim JS, Kim TH, Takano M, Kume T, Hur NW, Ko YG, Choi D, Hong MK, Jang Y (2009) Optical coherence tomography evaluation of zotarolimus-eluting stents at 9-month follow-up: comparison with sirolimus-eluting stents. Heart 95:1907–1912
Tanabe K, Serruys PW, Degertekin M, Grube E, Guagliumi G, Urbaszek W, Bonnier J, Lablanche JM, Siminiak T, Nordrehaug J, Figulla H, Drzewiecki J, Banning A, Hauptmann K, Dudek D, Bruining N, Hamers R, Hoye A, Ligthart JM, Disco C, Koglin J, Russell ME, Colombo A, TAXUS II Study Group (2005) Incomplete stent apposition after implantation of paclitaxel-eluting stents or bare metal stents: insights from the randomized TAXUS II trial. Circulation 111:900–905
Hong MK, Mintz GS, Lee CW, Park DW, Park KM, Lee BK, Kim YH, Song JM, Han KH, Kang DH, Cheong SS, Song JK, Kim JJ, Park SW, Park SJ (2006) Late stent malapposition after drug-eluting stent implantation: an intravascular ultrasound analysis with long-term follow-up. Circulation 113:414–419
Kim JS, Jang IK, Fan C, Kim TH, Kim JS, Park SM, Choi EY, Lee SH, Ko YG, Choi D, Hong MK, Jang Y (2009) Evaluation in 3 months duration of neointimal coverage after zotarolimus-eluting stent implantation by optical coherence tomography: the ENDEAVOR OCT trial. J Am Coll Cardiol Interv 2:1240–1247
Basalus MW, Ankone MJ, van Houwelingen GK, de Man FH, von Birgelen C (2009) Coating irregularities of durable polymer-based drug-eluting stents as assessed by scanning electron microscopy. EuroIntervention 5:157–165
Garg S, Serruys P, Onuma Y, Dorange C, Veldhof S, Miquel-Hébert K, Sudhir K, Boland J, Huber K, Garcia E, teRiele JA, SPIRIT II Investigators (2009) 3-year clinical follow-up of the XIENCE V everolimus-eluting coronary stent system in the treatment of patients with de novo coronary artery lesions: the SPIRIT II trial (clinical evaluation of the Xience V everolimus eluting coronary stent system in the treatment of patients with de novo native coronary artery lesions). J Am Coll Cardiol Interv 2:1190–1198
Leon MB, Nikolsky E, Cutlip DE, Mauri L, Liberman H, Wilson H, Patterson J, Moses J, Kandzari DE, ENDEAVOR IV Investigators (2010) Improved late clinical safety with zotarolimus-eluting stents compared with paclitaxel-eluting stents in patients with de novo coronary lesions: 3-year follow-up from the ENDEAVOR IV (randomized comparison of zotarolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents in patients with coronary artery disease) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol Interv 3:1043–1050
Ozaki Y, Okumura M, Ismail TF, Naruse H, Hattori K, Kan S, Ishikawa M, Kawai T, Takagi Y, Ishii J, Prati F, Serruys PW (2010) The fate of incomplete stent apposition with drug-eluting stents: an optical coherence tomography-based natural history study. Eur Heart J 31:1470–1476
Gutiérrez-Chico JL, Regar E, Nüesch E, Okamura T, Wykrzykowska J, di Mario C, Windecker S, van Es GA, Gobbens P, Jüni P, Serruys PW (2011) Delayed coverage in malapposed and side-branch struts with respect to well-apposed struts in drug-eluting stents: in vivo assessment with optical coherence tomography. Circulation 124:612–623
Mehanna EA, Attizzani GF, Kyono H, Hake M, Bezerra HG (2011) Review assessment of coronary stent by optical coherence tomography, methodology and definitions. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 27:259–269
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by grants from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (No. A085012 and A102064), the Korea Health 21 R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (No. A085136), and the Cardiovascular Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, BK., Shin, DH., Kim, JS. et al. Optical coherence tomography-based evaluation of malapposed strut coverage after drug-eluting stent implantation. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 28, 1887–1894 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-012-0039-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-012-0039-z