Abstract
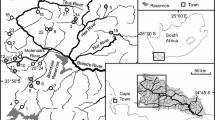
Non-native rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss have been widely introduced in the Cape Floristic Region (CFR) at the south-western tip of Africa and may pose a serious threat to endemic freshwater fishes in the region. Quantitative information about trout impacts in the CFR is scarce but is urgently needed to guide legislation and management efforts. We used a combination of comparative and experimental approaches to evaluate impacts of introduced trout on native fish populations in headwater streams draining the upper Breede River catchment in the CFR. Fish populations were surveyed, and 19 environmental variables measured, in 24 minimally-disturbed streams, half of which had been invaded by trout. The mean densities of native Breede River redfin Pseudobarbus burchelli, Cape kurper Sandelia capensis and Cape galaxias Galaxias zebratus, were 89–97 % lower in invaded streams than in streams without trout. Furthermore, while native fish were present at all 12 sites without trout, they were not recorded at seven of the 12 invaded sites. None of the measured environmental variables differed significantly between sites with and without trout, and distance-based linear models identified trout density as the best predictor of redfin and kurper density, while galaxias density was best predicted by other environmental variables (riparian vegetation, canopy cover, substrate length, site slope). Native fish ≤40 mm in length were largely absent from invaded streams, but generally abundant in streams without trout, and a field experiment confirmed that trout selectively consume small redfin. Taken together, these findings constitute evidence that trout have depleted the abundance of CFR-endemic fishes through size-selective predation. It is recommended that managers aim to prevent new trout introductions and consider eradicating trout populations where they pose a threat to highly threatened native species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MJ, Gorley RN, Clarke KR (2008) PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: guide to software and statistical methods. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Bovee KD (1982) A guide to stream habitat analysis using the instream flow incremental methodology. USDI Fish and Wildlife Service Instream Flow Information Paper #12, FWS/OBS-82/26, Colorado
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach, 2nd edn. Springer, Colorado
Cadwallader PL (1996) Overview of the impacts of introduced salmonids on Australian native fauna. Australian Nature Conservation Agency, Canberra
Cambray JA (2003) The global impact of alien trout species: a review; with reference to their impact in South Africa. Afr J Aquat Sci 28:61–67
Chakona A, Swartz ER (2012) Contrasting habitat associations of imperilled endemic stream fishes from a global biodiversity hot spot. BMC Ecol 12:19. doi:10.1186/1472-6785-12-19
Chakona A, Swartz ER (2013) A new redfin species, Pseudobarbus skeltoni (Cyprinidae, Teleostei), from the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. Zootaxa 3686:565–577
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER v6: user manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Cowling RM, Holmes PM (1992) Flora and vegetation. In: Cowling RM (ed) The ecology of fynbos: nutrients, fire and diversity. Oxford University Press, Cape Town
Cox JG, Lima SL (2006) Naiveté and an aquatic-terrestrial dichotomy in the effects of introduced predators. Trends Ecol Evol 21:674–680. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2006.07.011
Crawford SS, Muir AM (2008) Global introductions of salmon and trout in the genus Oncorhynchus: 1870–2007. Rev Fish Biol Fish 18:313–344. doi:10.1007/s11160-007-9079-1
Crowl TA, Townsend CR, McIntosh AR (1992) The impact of introduced brown and rainbow trout on native fish: the case of Australasia. Rev Fish Biol Fish 2:217–241
de Moor FC, Bruton MN (1988) Atlas of alien and translocated indigenous aquatic animals of southern Africa. S Afr Nat Sci Prog Rep No 144, CSIR, Pretoria, pp 78–133
de Moor FC, Day JA (2013) Aquatic biodiversity in the mediterranean region of South Africa. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1488-7
Dunham JB, Pilliod DS, Young MK (2004) Assessing the consequences of nonnative trout in headwater ecosystems in western North America. Fisheries 29:18–26
Ellender BR, Becker A, Weyl OLF, Swartz ER (2012) Underwater video analysis as an non-destructive alternative to electrofishing for sampling imperilled headwater stream fishes. Aquat Conserv 22:58–65. doi:10.1002/aqc.1236
Fausch KD (2007) Introduction, establishment and effects of non-native salmonids: considering the risk of rainbow trout invasion in the United Kingdom. J Fish Biol 71:1–32. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2007.01682.x
Fletcher AR (1979) Effects of Salmo trutta on Galaxias olidus and macroinvertebrates in stream communities. M.Sc. Dissertation, Monash University
Garcia de Leaniz C, Gajardo G, Consuegra S (2010) From best to pest: changing perspectives on the impact of exotic salmonids in the southern hemisphere. Syst Biodivers 8:447–459. doi:10.1080/14772000.2010.537706
Habit E, Piedra P, Ruzzante DE, Walde SJ, Belk MC, Cussac VE, Gonzalez J, Colin N (2010) Changes in the distribution of native fishes in response to introduced species and other anthropogenic effects. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 19:697–710. doi:10.1111/j.1466-8238.2010.00541.x
Hankin DG, Reeves GH (1988) Estimating total fish abundance and total habitat area in small streams based on visual estimation methods. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:834–844
Hardie SA, Barmuta LA, White RWG (2006) Comparison of day and night fyke netting, electrofishing and snorkelling for monitoring a population of the threatened golden galaxias (Galaxias auratus). Hydrobiologia 560:145–158. doi:10.1007/s10750-005-9509-9
Harrison AC (1950a) Introduction of exotic fishes to the Cape Province: the prelude. Piscator 16:125–128
Harrison AC (1950b) Trout and minnows. Piscator 13:2–6
Harrison AC (1952) Cape minnows. Piscator 24:117–128
Hey D (1926) Fisheries survey 1925–1926: inland waters. Department of Mines and Industries, Report No. 2. Cape Town
Impson ND (2001) Threatened fishes of the world: Barbus andrewi Barnard, 1937 (Cyprinidae). Environ Biol Fishes 61:212
IUCN (2013) IUCN red list of threatened species. Version 2013.2. http://www.iucnredlist.org. (Downloaded on 26 Feb 2014)
Januchowski-Hartley F, Graham N, Cinner J, Russ G (2013) Spillover of fish naivete from marine reserves. Ecol Lett 12:191–197
Kitano S (2004) Ecological impacts of rainbow, brown and brook trout in Japanese inland waters. Glob Environ Res 8:41–50
Lescak EA, von Hippel F (2011) Selective predation of threespine stickleback by rainbow trout. Ecol Freshw Fish 20:308–314. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0633.2011.00497
Linder HP, Johnson SD, Kuhlmann M, Matthee CA, Nyffeler R, Swartz ER (2010) Biotic diversity in the southern African winter-rainfall region. Environ Sustain 2:109–116. doi:10.1016/j.cosust.2010.02.001
Lintermans M (2000) Recolonization by the mountain galaxias Galaxias olidus of a montane stream after the eradication of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Mar Freshw Res 51:799–804
Lowe S, Browne M, Boudjelas S, De Poorter M (2000) 100 of the world’s worst invasive alien species: a selection from the global invasive species database. The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG), Aliens 12, Aukland
Macchi PJ, Cussac VE, Alonso MF, Denegri MA (1999) Predation relationships between introduced salmonids and the native fish fauna in lakes and reservoirs in northern Patagonia. Ecol Freshw Fish 8:227–236
Marr SM (2012) An assessment of a proposal to eradicate non-native fish from priority rivers in the Cape Floristic Region, South Africa. Afr J Aquat Sci 37:141–142. doi:10.2989/16085914.2012.666654
McDowall RM (2006) Crying wolf, crying foul, or crying shame: alien salmonids and a biodiversity crisis in the southern cool-temperate galaxioid fishes? Rev Fish Biol Fish 16:233–422. doi:10.1007/s11160-006-9017-7
McDowall RM, Allibone RM, Chadderton WL (2001) Issues for the conservation and management of Falkland Islands freshwater fishes. Mar Freshw Ecosyst 11:473–486
McIntosh AR (2000) Habitat- and size-related variations in exotic trout impacts on native galaxiid fishes in New Zealand streams. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57:2140–2151. doi:10.1139/cjfas-57-10-2140
McIntosh AR, McHugh PA, Dunn NR, Goodman JM, Howard SW, Jellyman PG, Brien LKO, Nyström P, Woodford DJ (2010) The impact of trout on galaxiid fishes in New Zealand. N Z J Ecol 34:195–206
McVeigh SJ (1977) Galaxias minnow: a trout food. Piscator 99:7
Mullner SA, Hubert WA, Weshe TA (1998) Snorkelling as an alternative to depletion electrofishing for estimating abundance and length class frequencies of trout in small streams. N Am J Fish Manag 18:947–953
Peterson DP, Fausch KD, White GC (2004) Population ecology of an invasion: effects of brook trout on native cutthroat trout. Ecol Appl 14:754–772
Quinn GP, Keough MJ (2002) Experimental design and data analysis for biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Raleigh RF, Hickman T, Solomon RC, Nelson PC (1984) Habitat suitability information: rainbow trout. US Fish and Wildlife Service, Report no. USFWS-BSP, Colorado, pp 1–39
Rebelo AG, Boucher C, Helme N, Mucina L, Rutherford MC (2006) Fynbos biome. In: Mucina L, Rutherford MC (eds) The vegetation of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland. Strelitzia 19. South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria
Reznick D, Endler J (1982) The impact of predation on life history evolution in Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Evolution 36:160–177
Reznick D, Butler M IV, Rodd F, Ross P (1996) Life-history evolution in guppies (Poecilia reticulata) 6. Differential mortality as a mechanism for natural selection. Evolution 50:1651–1660
RHP (2011) River health programme state of rivers report: rivers of the Breede water management area. Institute for Water Quality Studies, Pretoria
Rowntree KM, Wadeson RA (1999) A hierarchical geomorphological model for the classification of selected South African rivers. Water Research Commission, Report No. 497/1/99, Pretoria
Skelton PH (1987) South African red data book: fishes. Afr Nat Sci Prog Rep No 137, CSIR, Pretoria, pp 60–62
Skelton PH (2001) A complete guide to the freshwater fishes of Southern Africa, 2nd edn. Struik, Cape Town
SPSS (2011) IBM SPSS statistics, version 20.0. SPSS Inc., Chicago
Steynor AC, Hewitson BC, Tadross MA (2009) Projected future runoff of the Breede River under climate change. Water SA 35:433–440
Swartz ER, Flemming AF, Mouton P (2004) Contrasting genetic patterns and population histories in three threatened redfin species (Cyprinidae) from the Olifants River system, western South Africa. J Fish Biol 64:1153–1167. doi:10.1046/j.1095-8649.2004.00375.x
Tankard AJ, Jackson MPA, Eriksson KA, Hobday DK, Hunter WEL, Minter DR (1982) The Cape trough: an aborted rift. In: Tankard AJ, Jackson MPA, Eriksson KA, Hobday DK, Hunter WEL, Minter DR (eds) Crustal evolution of Southern Africa: 3.8 billion years of earth history. Springer, New York, pp 333–335
Thurow RF (1994) Underwater methods for study of salmonids in the Intermountain West. General Technical Report INT-GTR-307, Ogden
Tweddle D, Bills R, Swartz ER, Coetzer W, Da Costa L, Engelbrecht J, Cambray JA, Marshall B, Impson ND, Skelton PH, Darwall WRT, Smith KG (2009) The status and distribution of freshwater fishes. In: Darwall WRT, Smith KG, Tweddle D, Skelton P (eds) The status and distribution of freshwater biodiversity in South Africa. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland and SAIAB (South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity), Information Press, Oxford, pp 21–37
van Rensburg BJ, Weyl OLF, Davies SJ, van Wilgen LJ, Peacock DS, Spear D, Chimimba CT (2011) Chapter 15: invasive vertebrates of South Africa. In: Pimentel D (ed) Biological invasions: economic and environmental costs of alien plant, animal, and microbe species, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 326–378
Weyl OLF, Ellender BR, Woodford DJ, Jordaan MS (2013) Fish distributions in the Rondegat River, Cape Floristic Region, South Africa, and the immediate impact of rotenone treatment in an invaded reach. Afr J Aquat Sci 38:201–209. doi:10.2989/16085914.2012.753401
White JL, Harvey BC (2001) Effects of an introduced piscivorous fish on native benthic fishes in a coastal river. Freshw Biol 46:987–995. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.2001.00724.x
Woodford DJ (2009) Riverscape-mediated effects of introduced trout on non-diadromous galaxiid fishes in New Zealand. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Cantebury
Woodford DJ, Impson ND (2004) Preliminary assessment of the impact of alien rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) on indigenous fishes of the upper Berg River, Western Cape Province, South Africa. Afr J Aquat Sci 29:107–111
Woodford DJ, Impson ND, Day JA, Bills IR (2005) The predatory impact of invasive alien smallmouth bass, Micropterus dolomieu (Teleostei: Centrarchidae), on indigenous fishes in a Cape Floristic Region mountain stream. Afr J Aquat Sci 30:167–173. doi:10.2989/16085910509503852
Young KA, Dunham JB, Stephenson JF, Terreau A, Thailly AF, Gajardo G, Garcia de Leaniz C (2010) A trial of two trouts: comparing the impacts of rainbow and brown trout on a native galaxiid. Anim Conserv 13:399–410. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1795.2010.00354.x
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Acknowledgments
Financial support was from the DST-NRF Centre of Excellence for Invasion Biology (CIB), the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD), the University of Cape Town (UCT) and the Cape Tercentenary Foundation. JMS also acknowledges a UCT Postgraduate Publication Incentive Bursary. This research was conducted under permit 0035-AAA 007-00057 issued from CapeNature, and animal ethics clearance for the study was obtained from the University of Cape Town. We thank K Tilanus and MS Bird for field assistance, and ND Impson, SM Marr and SR Lowe for constructive discussions. H Waldron of the UCT Marine Research Institute at UCT conducted the nutrient analysis. We thank CL Moloney and D Pillay for analytical advice and I Hampton, OLF Weyl and two anonymous reviewers who provided valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shelton, J.M., Samways, M.J. & Day, J.A. Predatory impact of non-native rainbow trout on endemic fish populations in headwater streams in the Cape Floristic Region of South Africa. Biol Invasions 17, 365–379 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-014-0735-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-014-0735-9