Abstract
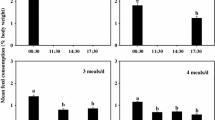
An experiment was conducted to determine the effects of optimal feeding frequency on growth performance, feed efficiency, nutrient utilization and body composition in juvenile flounder. Four feeding frequencies of one (F1), two (F2), three (F3) and four (F4) times a day were evaluated as treatments in triplicate for a period of 60 days. Forty-seven hatchery produced juveniles (2.5 ± 0.7 g) were stocked into 160-L rectangular fiberglass tanks and fed with a commercial diet containing 54 % protein to satiation. At the end of the experiment, the final weight of F1, F2, F3 and F4 were 5.06 ± 0.29, 5.91 ± 0.42, 6.24 ± 0.42 and 6.16 ± 0.46 g, respectively. Growth rates and feed consumption were highest in F3 and lowest in F1. Feed conversion ratios ranged between 0.83 ± 0.04 and 0.90 ± 0.03. There were no significant differences in either moisture or ash content of the fish groups. Protein content decreased with increasing feeding frequency, while lipid content partly increased with increasing feeding frequency. Nitrogen intake and lipid intake were significantly higher in fish fed under F3 and F4 treatment, whereas the nitrogen gain decreased and lipid gain increased with increasing feeding frequency. It is concluded that the flounder juveniles can achieve maximum growth performance and better nutrient utilization when they are fed a given ration two times a day. The findings have practical significance toward establishing an appropriate flounder nursery rearing and will directly benefit the nursery operations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews JW, Page JW (1975) The effects of frequency of feeding on culture of catfish. Trans Am Fish Soc 104:317–321
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis of the Association of Analytical Chemists. Arlington, VA, USA
Aydın İ (2012) The external abnormalities of hatchery-reared Black Sea flounder (Platichthys flesus luscus Pallas, 1814) in Turkey. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 12:127–133
Aydın İ, Ak O, Küçük E, Polat H, Ceylan B (2011a) Optimum temperature and growth performance of hatchery reared Black Sea flounder (Platichthys flesus luscus Pallas, 1814). Turk J Vet Anim Sci 36:101–106
Aydın İ, Küçük E, Şahin T, Kolotoğlu L (2011b) The effect of feeding frequency and feeding rate on growth performance of juvenile Black Sea Turbot (Psetta maxima Linneaus, 1758). J Fishscicom 5:35–42
Aydın İ, Şahin T, Polat H, Güneş E (2011c) Reproductive performance of wild and hatchery-reared flounder, Platichthys flesus luscus, in the Southern Black Sea Coast. Turk J Zool 35:811–817
Biswas G, Thirunavukkarasu AR, Sundaray JK, Kailasam M (2010) Optimization of feeding frequency of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) fry reared in net cages under brackishwater environment. Aquaculture 305:26–31
Brown N (2010) Halibut aquaculture in North America. In: Daniels HV, Watanabe WO (eds) Practical flatfish culture and stock enhancement. Wiley-Blackwell, Ames, pp 3–29
Carter CG, Bransden MP (2001) Relationships between protein-nitrogen flux and feeding regime in greenback flounder, Rhombosolea tapirina (Günther). Comp Biochem Phys A 130:799–807
Chua TE, Teng SK (1978) Effects of feeding frequency on the growth of young estuary grouper, Epinephelus tauvina (Forskål), cultured in floating net-cages. Aquaculture 14:31–47
Dwyer KS, Brown JA, Parrish C, Lall SP (2002) Feeding frequency affects food consumption, feeding pattern and growth of juvenile yellowtail flounder (Limanda ferruginea). Aquaculture 213:279–292
Goddard S (1996) Feed management in intensive aquaculture. Chapman and Hall, New York, p 194
Guinea J, Fernandez F (1997) Effect of feeding frequency, feeding level and temperature on energy metabolism in Sparus aurata. Aquaculture 148:125–142
Jobling M (1982) Some observations on the effects of feeding frequency on the food intake and growth of plaice, Pleuronectes platessa L. J Fish Biol 20:431–444
Jobling M (1983) Effect of feeding frequency on food intake and growth of Arctic charr, Salvelinus alpinus L. J Fish Biol 23:177–185
Johansen SJS, Jobling M (1998) The influence of feeding regime on growth and slaughter traits of cage-reared Atlantic salmon. Aquac Int 6:1–17
Kim KD, Kim KM, Kang YJ (2007) Influences of feeding frequency of extruded pellet and moist pellet on growth and body composition of juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus in suboptimal water temperatures. Fish Sci 73:745–749
Kubitza F, Lovshin LL (1999) Formulated diets, feeding strategies, and cannibalism control during intensive culture of juvenile carnivorous fishes. Rev Fish Sci 7:1–22
Lee SM, Pham MA (2010) Effects of feeding frequency and feed type on the growth, feed utilization and body composition of juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceu. Aquac Res 41:166–171
Lee SM, Cho SH, Kim DJ (2000a) Effects of feeding frequency and dietary energy level on growth and body composition of juvenile flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck and Schlegel). Aquac Res 31:917–921
Lee SM, Hwang UG, Cho SH (2000b) Effects of feeding frequency and dietary moisture content on growth, body composition and gastric evacuation of juvenile Korean rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Aquaculture 187:399–409
Liu FG, Liao IC (1999) Effect of feeding regimen on the food consumption, growth, and body composition in hybrid striped bass Morone saxatilis × Morone chrysops. Fish Sci 65:513–519
Riche M, Oetker M, Haley DI, Smith T, Garling DL (2004) Effect of feeding frequency on consumption, growth, and efficiency in juvenile Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Isr J Aquacult-Bamid 56(4):247–255
Şahin T (2000) Larval rearing of flounder, Pleuronectes flesus luscus, under laboratory conditions. Turk J Mar Sci 6:263–270
Şahin T, Güneş E, Aydın İ, Polat H (2008) Reproductive characteristics and egg development in flounder (Pleuronectes flesus luscus) in the southern Black Sea. Isr J Aquacult-Bamid 60:20–26
Schnaittacher G, King WV, Berlins LD (2005) The effects of feeding frequency on growth of juvenile Atlantic halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus L. Aquac Res 36:370–377
Sunde LM, Imsland AK, Folkvord A, Stefansson SO (1998) Effects of size grading on growth and survival of juvenile turbot at two temperatures. Aquac Int 6:19–32
Thompson KR, Webster CD, Morgan AM, Grisby EJ (2000) Effects of different feeding frequencies on growth, body composition, and fillet composition of juvenile sunshine bass, Morone chrysops × M. saxatilis. Grown Indoors. J Appl Aquac 10:55–65
Türker A (2006) Effect of feeding frequency on growth, feed consumption, and body composition in juvenile turbot (Psetta maxima Linaeus, 1758) at low temperature. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 30:251–256
Wang N, Hayward RS, Noltie DB (1998) Effect of feeding frequency on food consumption, growth, size variation and feeding pattern of age-0 hybrid sunfish. Aquaculture 165:261–265
Wang Y, Kong L, Li K, Bureau DP (2007) Effects of feeding frequency and ration level on growth, feed utilization and nitrogen waste output of cuneate drum (Nibea miichthioides) reared in net pens. Aquaculture 271:350–356
Webster CD, Tidwell JH, Yancey DH (1992) Effect of protein level and feeding frequency on growth and body composition of cage-reared channel catfish. Prog Fish Cult 54:92–96
Xie F, Ai Q, Mai K, Xu W, Ma H (2011) The optimal feeding frequency of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea Richardson) larvae. Aquaculture 311:162–167
Zar JH (1999) Biostatistical analysis, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, the Central Fisheries Research Institute, with project entitled “Research on Rearing Possibilities of Flounder (Platichthys flesus luscus L.)”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Küçük, E., Aydın, İ., Polat, H. et al. Effect of feeding frequency on growth, feed efficiency and nutrient utilization of juvenile flounder (Platichthys flesus luscus). Aquacult Int 22, 723–732 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9701-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9701-2