Abstract
Human serum albumin (HSA) is a biologically relevant protein that binds a variety of drugs and other small molecules. No less than 50 structures are deposited in the RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB). Based on these structures, we first performed a clustering analysis. Despite the diversity of ligands, only two well defined conformations are detected, with a deviation of 0.46 nm between the average structures of the two clusters, while deviations within each cluster are smaller than 0.08 nm. Those two conformations are representative of the apoprotein and the HSA-myristate complex already identified in previous literature. Considering the structures within each cluster as a representative sample of the dynamical states of the corresponding conformation, we scrutinize the structural and dynamical differences between both conformations. Analysis of the fluctuations within each cluster set reveals that domain II is the most rigid one and better matches both structures. Then, taking this domain as reference, we show that the structural difference between both conformations can be expressed in terms of twist and hinge motions of domains I and III, respectively. We also characterize the dynamical difference between conformations by computing correlations and principal components for each set of dynamical states. The two conformations display different collective motions. The results are compared with those obtained from the trajectories of short molecular dynamics simulations, giving consistent outcomes. Let us remark that, beyond the relevance of the results for the structural and dynamical characterization of HAS conformations, the present methodology could be extended to other proteins in the PDB archive.

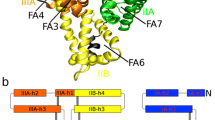
Two conformations of the human serum albumin were found in a cluster analysis of data available in the Protein Data Bank. X1 and X2 are structures representatives of each cluster. Both X1 and X2 represent the apo protein and the HSA-myristate conformations respectively. Two predominant motions of X2 with respect to X1 are observed, the first one shows a separation hinge motion (15°) of domain III, the second a twist motion of domain I (24°). A discussion of the residues involved in the conformational change as well a comparison between the experimental and theoretical (obtained from molecular dynamics) principal component analysis is performed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong F (2007) Drug insight: the role of albumin in the management of chronic liver disease. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:43–51
Divsalar A, Saboury AA, Ahadi L, Zemanatiyar E, Mansouri-Torshizi H, Ajloo A, Sarma RH (2011) Biological evaluation and interaction of a newly designed anti-cancer Pd(II) complex and human serum albumin. J Biomol Struct Dyn 29:283–296
Guizado TRC, Louro SRW, Pascutti PG, Anteneodo C (2010) Solvation of anionic water-soluble porphyrins: a computational study. Int J Quantum Chem 110:2094–2100
Guizado TC, Pita SR, Louro SRW, Pascutti PG (2008) Int J Quantum Chem 108:2603–2607
Guizado TRC, Louro SRW, Anteneodo C (2011) Hydration of hydrophobic biological porphyrins. J Chem Phys 134:055103,1–9
Wang RM, Komatsu T, Nakagawa A, Tsuchida E (2005) Human serum albumin bearing covalently attached iron(II) porphyrins as O2-coordination sites. Bioconjug Chem 16:23–26
Tominaga TT, Yushmanov VE, Borissevitch IE, Imasato H, Tabak M (1997) Aggregation phenomena in the complexes of iron tetraphenylporphine sulfonate with bovine serum albumin. J Inorg Biochem 65:235–244
Guizado TRC, Louro SRW, Anteneodo C (2012) Dynamics of heme complexed with human serum albumin: a theoretical approach. Eur Biophys J 41:1033–1042
Sudlow G, Birkett DJ, Wade DN (1975) The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol 11:824–832
Curry S, Mandelkow H, Brick P, Franks N (1998) Crystal structure of human serum albumin complexed with fatty acid reveals an asymmetric distribution of binding sites. Nat Struct Biol 5:827–835
Petitpas I, Grune T, Bhattacharya AA, Curry S (2001) Crystal structures of human serum albumin complexed with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Mol Biol 314:955–960
He XM, Carter DC (1992) Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 358:209–215
Bhattacharya AA, Curry S, Franks NP (2000) Binding of the general anesthetics propofol and halothane to human serum albumin: high-resolution crystal structures. J Biol Chem 275:38731–38738
Zunszain PA, Ghuman J, Komatsu T, Tsuchida E, Curry S (2003) Crystal structural analysis of human serum albumin complexed with hemin and fatty acid. BMC Struct Biol 3:6 available at http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6807/3/6
Ghuman J, Zunszain PA, Petitpas I, Bhattacharya AA, Otagiri M, Curry S (2005) Structural basis of the drug-binding specificity of human serum albumin. J Mol Biol 353:38–52
Available at http://www.pdb.org/
Ascenzi P, Fasano M (2010) Allostery in a monomeric protein: the case of human serum albumin. Biophys Chem 148:16–22
Ascenzi P, di Masi A, De Sanctis G, Coleta M, Fasano M (2009) Ibuprofen modulates allosterically NO dissociation from ferrous nitrosylated human serum albumin by binding to three sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:83–86
Ascenzi P, di Masi A, Coletta M, Ciaccio C, Fanali G, Nicoletti FP, Smulevich G, Fasano M (2009) Ibuprofen impairs allosterically peroxynitrite isomerization by ferric HAS. J Biol Chem 284:31006–31017
Artali R, Bombieri G, Calabi L, Del Pra A (2005) A molecular dynamics study of human serum albumin binding sites. Il Farmacol 60:485–495
Fujiwara S, Amisaki T (2006) Molecular dynamics study of conformational changes in human serum albumin by binding of fatty acids. Proteins 64:730–739
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18:2714–2723
Szekely GJ, Rizzo ML (2005) Hierarchical clustering via join between-within distances: extending ward’s minimum variance method. J Classif 22:151–183
van der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, van Buuren AR, Apol E, Meulenhoff PJ et al. (2010) Gromacs user manual version 4.5 www.gromacs.org
Oostenbrink C, Villa A, Mark AE, Van Gunsteren EF (2004) A biomolecular force field based on the free enthalpy of hydration and solvation: the GROMOS force-field parameter sets 53A5 and 53A6. J Comput Chem 25:1656–1676
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, Hermans J (1981) In: Pullman B (ed) Intermolecular forces. Reidel, Dordrech
Essmann U, Pereira L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577–8593
Bussi G, Donadio D, Parrinello M (2007) Canonical sampling through velocity-rescaling. J Chem Phys 126:014101, FALTA
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, DiNola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81:3684–3690
Scheer A, Cotecchia S (1997) J Recept Signal Transduct Res 17:57–73
Lee AL, Wand AJ (2001) Microscopic origins of entropy, heat capacity and the glass transition in proteins. Nature 411:501–504
Pasi M, Tiberti M, Arrigoni A, Papaleo E (2012) xPyder: a PyMOL plugin to analyze coupled residues and their networks in protein structures. J Chem Inf Model 52(7):1865–1874
DeLano WL (2002) The PyMOL molecular graphics system. http://www.pymol.org
de Groot BL, van Aalten DMF, Amadei A, Berendsen HJC (1996) The consistency of large concerted motions in proteins in molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J 71:1707–1713
Paris G, Ramseyer C, Enescu M (2014) A principal component analysis of the dynamics of subdomains and binding sites in human serum albumin. Biopolymers 101:561–572
Available at http://fizz.cmp.uea.ac.uk/dyndom/
Hayward S, Berendsen HJC (1998) Systematic analysis of domain motions in proteins from conformational change: new results on citrate synthase and T4 Lysozyme. Proteins 30:144–154
Hayward S, Kitao A, Berendsen HJC (1997) Model-Free methods of analyzin domains motions in proteins from simulation: a comparison of normal model analysis and molecular dynamics simulation of Lyysozome. Proteins 22:425–437
Wardell M, Wang Z, Ho JX, Justin R, Ruker F, Ruble J, Carter C (2002) The atomic structure of human serum albumin at 1.9 C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291:813–819
Lehninger AL, Nelson DL, Cox MM (1982) Principles of biochemistry. Worth, New York, p 145
Bocedi A, Notari S, Menegatti E, Fanali G, Fasano M, Ascenzi P (2002) Allosteric modulation of anti-HIV drug and ferric heme binding to human serum albumin. FEBS J 272:6287–6296
Fanali G, Bocedi A, Ascenzi P, Fasano M (2007) Modulation of heme and myristate binding to human serum albumin by anti-HIV drugs. An optical and NMR spectroscopic study. FEBS J 274:4491–4502
Ascenzi P, Bocedi A, Notari S, Fanali G, Fesce R, Fasano M (2006) Allosteric modulation of drug binding to human serum albumin. Mini Rev Med Chem 6:483–489
Fanali G, Fesce R, Agrati C, Ascenzi P, Fasano M (2005) Allosteric modulation of myristate and Mn(III)heme binding to human serum albumin. Opt NMR Spectrosc Charact FEBS J 272:4672–4683
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge CAPES/Brazil (under the project “Integrated Action on Chemical Nanotechnology” No. 02559/09-9), Faperj (Foundation for Research Support, State of Rio de Janeiro) and CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development) for partial financial support. We also acknowledge the developers of the free software Gromacs [24].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper belongs to Topical Collection Brazilian Symposium of Theoretical Chemistry (SBQT2013)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guizado, T.R.C. Analysis of the structure and dynamics of human serum albumin. J Mol Model 20, 2450 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-014-2450-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-014-2450-y