Abstract
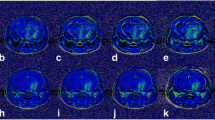
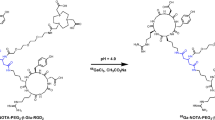
Gliomas are the most common type among all central nervous system tumors. The aggressiveness of gliomas is correlated with the level of angiogenesis and is often associated with prognosis. The aim of this study is to evaluate the novel GX1 peptide and the heterodimer RGD-GX1 radiolabeled with technetium-99m, for angiogenesis detection in glioma models. Radiolabeling and radiochemical controls were assessed for both radioconjugates. In vitro binding studies in glioma tumor cells were performed, as well as biodistribution in SCID mice bearing tumor cells, in order to evaluate the biological behavior and tumor uptake of the radiocomplexes. Blocking and imaging studies were also conducted. MicroSPECT/CT images were acquired in animals with experimentally implanted intracranial tumor. Open field activity was performed to evaluate behavior, as well as perfusion and histology analysis. The radiochemical purity of both radiotracers was greater than 96 %. In vitro binding studies revealed rather similar binding profi le for each molecule. The highest binding was for RGD-GX1 peptide at 120 min in U87MG cells (1.14 ± 0.35 %). Tumor uptake was also favorable for RGD-GX1 peptide in U87MG cells, reaching 2.96 ± 0.70 % at 1 h p.i. with 47 % of blocking. Imaging studies also indicated better visualization for RGD-GX1 peptide in U87MG cells. Behavior evaluation pointed brain damage and histology studies confirmed actual tumor in the uptake site. The results with the angiogenesis seeking molecule 99mTc-HYNIC-E-[c(RGDfk)-c(GX1)] were successful, and better than with 99mTc-HYNIC-PEG4-c(GX1). Future studies targeting angiogenesis in other glioma and nonglioma tumor models are recommended.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achilefu S (2004) Lighting up tumors with receptor-specific optical molecular probes. Technol Cancer Res Treat 3(4):393–409
Beekers N, Husson O, Mols F, van Eenbergen M, van de Poll-Franse LV (2014) Symptoms of anxiety and depression are associated with satisfaction with information provision and internet use among 3080 cancer survivors: results of the PROFILES Registry. Cancer Nurs. doi:10.1097/NCC.0000000000000184
Bello L, Giussani C, Carrabba G, Pluderi M, Costa F, Bikfalvi A (2004) Angiogenesis and invasion in gliomas. Cancer Treat Res 117:263–284
Campos AC, Fogaça MV, Aguiar DC, Guimarães FS (2013) Animal models of anxiety disorders and stress. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 35(Suppl. 2):S101–S111
Carmel JB, Martin JH (2014) Motor cortex electrical stimulation augments sprouting of the corticospinal tract and promotes recovery of motor function. Front Integr Neurosci 18:8–51
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407(6801):249–257
Chen K, Sun X, Niu G, Ma Y, Yap LP, Hui X, Wu K, Fan D, Conti PS, Chen X (2012) Evaluation of 64Cu labeled GX1: a phage display peptide probe for PET imaging of tumor vasculature. Mol Imaging Biol 14(1):96–105
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA (2010) Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 10:9–22
Durkan K, Lambrecht FY, Unak P (2007) Radiolabeling of bombesin-like peptide with 99mTc: 99mTc-litorin and biodistribution in rats. Bioconjug Chem 18:1516–1520
Fei XF, Zhang QB, Dong J, Diao Y, Wang ZM, Li RJ, Wu ZC, Wang AD, Lan Q, Zhang SM, Huang Q (2010) Development of clinically relevant orthotopic xenograft mouse model of metastatic lung cancer and glioblastoma through surgical tumor tissues injection with trocar. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29(1):84
Gautam A, Kapoor P, Chaudhary K, Kumar R, Raghava GP (2014) Tumor homing peptides as molecular probes for cancer therapeutics, diagnostics, and theranostics. Curr Med Chem 21:2367–2391
Guo W, Giancotti FG (2004) Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:816–826
Hou BL, Bradbury M, Peck KK, Petrovich NM, Gutin PH, Holodny AI (2006) Effect of brain tumor neovasculature defined by rCBV on BOLD fMRI activation volume in the primary motor cortex. Neuroimage 32(2):489–497
Hu H, Yin J, Wang M, Liang C, Song H, Wang J, Nie Y, Liang J, Wu K (2014) GX1 targeting delivery of rmhTNFα evaluated using multimodality imaging. Int J Pharm 461(1–2):181–191
Hua C, Zhao G, Li Y, Bie L (2014) Minichromosome maintenance (MCM) family as potential diagnostic and prognostic tumor markers for human gliomas. BMC Cancer 14(1):526
Hui X, Han Y, Liang S, Liu Z, Liu J, Hong L, Zhao L, He L, Cao S, Chen B, Yan K, Jin B, Chai N, Wang J, Wu K, Fan D (2008) Specific targeting of the vasculature of gastric cancer by a new tumor-homing peptide CGNSNPKSC. J Control Release 131:86–93
Hynes RO (1992) Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69(1):11–25
Jin ZH, Furukawa T, Waki A, Akaji K, Coll JL, Saga T, Fujibayashi Y (2010) Effect of multimerization of a linear Arg-Gly-Asp peptide on integrin binding affinity and specificity. Biol Pharm Bull 33(3):370–378
Koivunen E, Wang B, Ruoslahti E (1995) Phage libraries displaying cyclic peptides with different ring sizes: ligand specificities of the RGD-directed integrins. Biotechnology (NY) 13(3):265–270
Liu Z, Wang F (2010) Dual-targeted molecular probes for cancer imaging. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 11:610–619
Okarvi SM (2004) Peptide-based radiopharmaceuticals: future tools for diagnostic imaging of cancers and other diseases. Med Res Rev 24(3):357–397
Oliveira EA, Faintuch BL (2015) Radiolabeling and biological evaluation of the GX1 and RGD-GX1 peptide sequence for angiogenesis targeting. Nucl Med Biol 42(2):123–130
Ong BY, Ranganath SH, Lee LY, Lu F, Lee HS, Sahinidis NV, Wang CH (2009) Paclitaxel delivery from PLGA foams for controlled release in post-surgical chemotherapy against glioblastoma multiforme. Biomaterials 30:3189–3196
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Farah P, Ondracek A, Chen Y, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2013) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States 2006–2010. Neuro-Oncol 15(sup 2):ii1–ii56
Oyen WJG, Bodei L, Giammarile F, Maecke HR, Tennvall J, Luster M, Brans B (2007) Targeted therapy in nuclear medicine—current status and future prospects. Ann Oncol 18:1782–1792
Pasqualini R, Koivunen E, Ruoslahti E (1997) Alpha v integrins as receptors for tumor targeting by circulating ligands. Nat Biotechnol 15(6):542–546
Pasqualini R, Arap W, McDonald DM (2002) Probing the structural and molecular diversity of tumor vasculature. Trends Mol Med 8(12):563–571
Reubi JC (1997) Regulatory peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Q J Nucl Med 41:63–70
Reubi JC, Mäcke HR, Krenning EP (2005) Candidates for peptide receptor radiotherapy today and in the future. J Nucl Med 46(Suppl 1):67S–75S
Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD (1986) Arg-Gly-Asp: a versatile cell recognition signal. Cell 44(4):517–518
Skobe M, Rockwel LP, Goldstein N, Vosseler S, Fusenig NE (1997) Halting angiogenesis suppresses carcinoma cell invasion. Nat Med 3:1222–1227
Song KM, Lee S, Ban C (2012) Aptamers and their biological applications. Sensors (Basel) 12(1):612–631
Strijkers GJ, Kluza E, Van Tilborg GA, van der Schaft DW, Griffioen AW, Mulder WJ, Nicolay K (2010) Paramagnetic and fluorescent liposomes for target-specific imaging and therapy of tumor angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 13(2):161–173
Ueberberg S, Schneider S (2010) Phage library-screening: a powerful approach for generation of targeting-agents specific for normal pancreatic islet-cells and islet-cell carcinoma in vivo. Regul Pept 160(1–3):1–8
Wang ES, Zhang XP, Yao HB, Wang G, Chen SW, Gao WW, Yao HJ, Sun YR, Xi CH, Ji YD (2014) Tetranectin knockout mice develop features of Parkinson disease. Cell Physiol Biochem 34(2):277–287
Wu H, Chen H, Pan D, Ma Y, Liang S, Wan Y, Fang Y (2014) Imaging integrin αvβ 3 and NRP-1 positive gliomas with a novel fluorine-18 labeled RGD-ATWLPPR heterodimeric peptide probe. Mol Imaging Biol 16(6):781–792
Zhi M, Wu KC, Dong L, Hao ZM, Deng TZ, Hong L, Liang SH, Zhao PT, Qiao TD, Wang Y, Xu X, Fan DM (2004) Characterization of a specific phage-displayed peptide binding to vasculature of human gastric cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 3:1232–1235
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Ana Funari, Aryel Heitor and Daniele Seo for the assistance during some experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Brazil [Fapesp 2011/12405-0].
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, É.A., Faintuch, B.L., Targino, R.C. et al. Evaluation of GX1 and RGD-GX1 peptides as new radiotracers for angiogenesis evaluation in experimental glioma models. Amino Acids 48, 821–831 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2130-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2130-y