Abstract
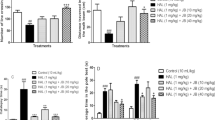
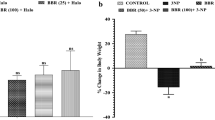
Haloperidol (HAL) is a widely used neuroleptic drug for the treatment of acute and chronic psychosis. Tardive dyskinesia (TD) is a complex hyperkinetic syndrome consisting of choreiform and athetoid movements, which persists for months or years after withdrawal. Increased levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive products are found in the cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of patients treated with neuroleptics, especially those with movement disorders. Alpha lipoic acid (ALA), a natural metabolic antioxidant, is effective in both prevention and treatment of numerous types of neurological disorders. It is proposed to study the effect of ALA on TD induced by HAL and to correlate it with oxidative stress by studying total antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation (LP). HAL (1 mg/kg/i.p.) was used to induce vacuous chewing movements in rats. ALA was suspended in 0.2% carboxy methyl cellulose at a dose of 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg and was administered orally by oral gavage 1 h before HAL on 21st day of treatment. ALA supplementation significantly decreased HAL-induced TD at a dose of 100 mg/kg and catalepsy dose dependently. ALA improved TD and catalepsy by decreasing HAL-induced LP. ALA and its metabolite dihydro lipoic acid protect against HAL-induced TD and catalepsy by scavenging reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler LA, Paselow E, Rotrosen J, Duncan E, Lee M, Rosenthal M, Angrist B (1993a) Vitamin E treatment of tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 150:1405–1407
Adler LA, Paselow E, Rotrosen J, Duncan E, Rosenthal M, Angrist B (1993b) Vitamin E in tardive dyskinesia: time course of effect placebo substitution. Psychopharmacol Bull 29:371–374
Adler LA, Edson R, Lavori P, Peselow E, Duncan E, Rosenthal M, Rotrosen J (1998) Long term effects of vitamin E for tardive dyskinesia. Biol Psychiatry 43:868–872
American Psychiatric Association (APA) (1992) Tardive dyskinesia: a task force report of the American Psychiatric Association. APA Press, Washington DC
Andreassen OA, Jorgensen HA (1995) The rat model of tardive dyskinesia: relationship between vacuous chewing movements and gross motor activity during acute and long term haloperidol treatment. Life Sci 57:2263–2272
Andreassen OA, Aam TO, Jorgensen HA (1996) Inhibition by memantine of the development of persistent oral dyskinesias induced by long term haloperidol treatment of rats. Br J Pharmacol 119:751–757
Arivazhagan P, Ayusawa D, Panneerselvam C (2006) Protective efficacy of alpha lipoic acid on acetyl choline esterase activity in aged rat brain regions. Rejuvenation Res 9(2):198–201
Barak Y, Swartz M, Shamir E, Stein D, Weizman A (1998) Vitamin E in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia: a statistical meta-analysis. Ann Clin Psychiatry 10:101–105
Behl C, Rupprecht R, Skutella T, Holsboer F (1995) Haloperidol-induced cell death-mechanism and protection with vitamin E in vitro. Neuroreport 7:360–364
Biewenga GP, Haenen GR, Bast A (1997) The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid. Gen Pharmacol 29(3):315–331
Blios MS (1958) Antioxidant determination by the use of stable free radical. Nature 26:1199
Burcham PC (1998) Genotoxic lipid peroxidation products: their DNA damaging properties and role in formation of endogenous and role in formation of endogenous DNA adducts. Mutagenesis 13:287–305
Cadenas E, Packer L (1996) Handbook of antioxidants. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 545–591
Cadet JL, Kahler LA (1994) Free radical mechanisms in schizophrenia and tardive dyskinesia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 18:457–467
Cadet JL, Lohr JB (1989) Possible involvement of free radicals in neuroleptic-induced movement disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 570:176–185
Cadet JL, Lohr JB, Jeste DV (1986) Free radicals and tardive dyskinesia. Trends Neurosci 9:107–108
Casey DE (1985a) Spontaneous and tardive dyskinesias: clinical and laboratory studies. J Clin Psychiatry 46:42–47
Casey DE (1985b) Tardive dyskinesia: reversible and irreversible. Psychopharmacology 2:88–97
Chartoff EH, Ward RP, Dorsa DM (1999) Role of adenosine and NMDA receptors in mediating haloperidol-induced gene expression and catalepsy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291(2):591–597
Chen YC, Shen SC, Lee WR, Hou WC, Yang LL, Lee TJ (2001) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and lipopolysaccharide induced inducible NOS and cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression by rutin, quercetin and quercetin penta acetate in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Cell Biochem 82:537–548
Clow A, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1979) Changes in dopamine mediated behaviour during one year’s neuroleptic administration. Eur J Pharmacol 57:365–375
Cohen G, Spina MB (1989) Deprenyl suppresses the oxidant stress associated with increased dopamine turnover. Ann Neurol 26:689–690
Creese I, Burt DR, Snyder SH (1976) Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science 192:481–483
Egan MT, Hyde TM, Albers GW, Elkashef A, Alexander RC, Reeve A, Blum A, Saez RE, Wyatt RJ (1992) Treatment of tardive dyskinesia with vitamin E. Am J Psychiatry 149:773–777
Egan MF, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Wyatt RJ (1995) Neuroleptic-induced vacuous chewing movements in rodents: incidence and effects of long term increases in haloperidol dose. Psychopharmacology 117:74–81
Elkashef AM, Wyatt RJ (1999) Tardive dyskinesia: possible involvement of free radical and treatment with vitamin E. Schizophr Bull 25:731–740
Elkashef AM, Ruskin PE, Bacher N, Barett D (1990) Vitamin E in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia. Am J Psychiatry 147:505–506
Esterbaur H, Zollner H, Schaur RJ (1990) Aldehydes formed by lipid peroxidation mechanism of formation, occurrence and determination. In: Vigopelfrey C (ed) Membrane lipid peroxidation. CRC, Baco Raton
Esterbauer H, Schaur RJ, Zollner H (1991) Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxy alkenal, malondialdehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic Biol Med 11:81–128
Faria RR, Abilio VC, Grassl C, Chinen CC, Negrao LTR, Castro JPMV, Fukshiro DF, Rodrigues MSD, Gomes PHZ, Registro S, Carvalho RCC, D’Almeida V, Silva RH, Ribeiro RA, Fussa-Filho R (2005) Beneficial effects of vitamin C and vitamin E on reserpine induced oral dyskinesia in rats: critical role of strital catalase activity. Neuropharmacology 48:993–1001
Freeman BA, Capro JD (1982) Biology of disease: free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest 47:412–425; Chem 243:5753–5756
Glazer WM, Morgenstern H, Schooler N, Berkman CS, Moore DC (1990) Predictors of improvement in tardive dyskinesia following discontinuation of neuroleptic medication. Br J Psychiatry 157:585–592
Goyal RK, Patel NM, Bhatt RV, Mehta AA, Prabhakhar MC (2006) Study of catalepsy in animals. In: Practicals in pharmacology, 5th edn. B S Shah Prakashan, Ahmedabad, pp 128
Gunne LM, Growdon J, Glaeser B (1982) Oral dyskinesia in rats following brain lesions and neuroleptic drug administration. Psychopharmacology 77:134–139
Gunne LM, Andersson U, Bondesson U, Johansson (1986) Spontaneous chewing movements in rats during acute and chronic antipsychotic drug administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:897–901
Gupta S, Monsik D, Black DW, Berry S, Masand PS (1999) Tardive dyskinesia; review of treatments past, present, and future. Ann Clin Psychiatry 11:257–266
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC, Carrol EC (1994) Free radicals, antioxidants and human disease: where are we now? J Lab Clin Med 119:598–619
Hyde TM, Egan MF, Wing LL, Wyatt RJ, Weinberger DR, Kleinman JE (1995) Persistent catalepsy associated with severe dyskinesias in rats treated with chronic injections of haloperidol decanoate. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 118:142–149
Iversen SD, Howells RB, Hughes RP (1980) Behavioral consequences of long-term treatment with neuroleptic drugs. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 24:305–313
Jeste DV, Potkin SG, Sinha S, Feder S, Wyatt RJ (1979) Tardive dyskinesia-reversible and persistent. Arch Gen Psychiatry 36:585–590
Kane JM, Smith JM (1982) Tardive dyskinesia: prevalence and risk factors, 1959 to 1979. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39:473–481
Kaneda H, Shirakawa O, Dale J, Goodman L, Bachus SE, Tamminga CA (1992) Co-administration of progabide inhibits haloperidol-induced oral dyskinesias in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 212:43–49
Keller JN, Mattson MP (1998) Roles of lipid peroxidation in modulation of cellular signaling pathways, cell dysfunction and death in the nervous system. Rev Neurosci 9:105–116
Kramer K, Packer L (2001) R-alpha lipoic acid. In: Kramer K, Hoppe P, Packer L (eds) Neutraceuticals in health and disease prevention. Marcel Dekker, New York
Lee MH, Lin RD, Shen LY, Yang YY, Yen KY, Hou WC (2001) Monoamino oxidase B and free radical scavenging activities of natural flavonoids in melastoma candidum D. Don J Argic Food Chem 49:5551–5555
Lohr JB, cadet JL, Lohr MA, Jeste DV, Wyatt RJ (1987) Alpha-tocopherol in tardive dyskinesia. Lancet 1:913–914
Lohr JB, Kuczenski R, Bracha HS, Moir M, Joste DV (1990) Increased indices of free radical activity in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tardive dyskinesia. Biol Psychiatry 28:533–539
Maddux BA, See W, Lawrence JC, Goldfine AL, Goldfine ID, Evans JL (2001) Protection against oxidative stress-induced insulin resistance in rat L6 muscle cells by micro molar concentrations of alpha-lipoic acid. Diabetes 50:404–410
Mahadik SP, Gowda S (1996) Antioxidants in the treatment of schizophrenia. Drugs Today 32:553–565
Mahadik SP, Scheffer RE (1996) Oxidative injury and potential use of antioxidants of schizophrenia. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 55:45–54
Mahadik SP, Sitasawad V, Mulchandani M (1999) Membrane peroxidation and the neuropathology of schizophrenia. In: Peet M, Glen I, Horrobin DF (eds) Phospholipids spectrum disorders in psychiatry. Marius Press, Lancashire
Mahadik SP, Evans D, Lal H (2001) Oxidative stress and role of antioxidant and ω-3 essential fatty acid supplementation in schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 25:463–493
Maritim AC, Sanders RA, Watkins JBIII (2003) The effect of α-lipoic acid on biomarkers of oxidative stress in streptozocin induced diabetic rats. J Nutr Biochem 14:88–294
Muthuswamy AD, Vedagiri K, Ganesan M, Chinnakannu P (2006) Oxidative stress mediated molecular damage and dwindle in antioxidant status in aged rat brain regions: role of l-carnitine and dl-alpha lipoic acid. Clin Chim Acta 368:84–92
Naidu PS, Kulkarni SK (2001a) Excitatory mechanisms in neuroleptic-induced vacuous chewing movements (VCMs): possible involvement of calcium and nitric oxide. Behav Pharmacol 12(3):209–216
Naidu PS, Kulkarni SK (2001b) Possible involvement of prostaglandins in haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 430:295–298
Naidu PS, Kulkarni SK (2004) Quercetin, a bioflavonoid, reverses haloperidol-induced catalepsy. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 26:323–326
Naidu PS, Singh A, Kaur P, Sandhir R, Kulkarni SK (2003a) Possible mechanism of action in melatonin attenuation of haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:641–648
Naidu PS, Singh A, Kulkarni SK (2003b) Quercetin, a bioflavonoid, attenuates haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia. Neuropharmacology 44:1100–1106
Nichans WG, Samuelson D (1968) Formation of malondialdehyde from phospholipids arachidonate during microsomal lipid peroxidation. Eur J Biochem 6:126–130
Nielson EB, Lyon M (1978) Evidence for cell loss in corpus striatum after long term treatment with a neuroleptic drug (flupenthixol) in rats. Psychopharmacology 59:85–89
Obrosova IG, Fathallah L, Edwin L, Nourooz-Zadeh J (2003a) Early changes oxidative stress in the diabetic kidney: effect of dl-α-lipoic acid. Free Radic Boil Med 34(20):186–195
Obrosova IG, Fathallah L, Greene DA (2003b) Early changes in lipid peroxidation and antioxidative defense in diabetic rat retina: effect of dl-α-lipoic acid. Eur J Pharmacol 398:139–146
Packer L, Witt KH, Tristschler HJ (1995) Alpha-lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radic Biol Med 19:227–250
Packer L, Kraemer K, Rimbach G (2001) Molecular aspects of lipoic acid in the prevention of diabetes complications. Nutrition 17:888–895
Pall HS, Williams AC, Blake DR, Lunec J (1987) Evidence of enhanced lipid peroxidation in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients taking phenothiazines. Lancet 2:596–599
Parikh V, Mohammad Khan M, Sahebarao Mahadik P (2003) Differential effects of antipsychotics on expression of antioxidant enzymes and membrane lipid peroxidation in rat brain. J Psychiatr Res 37:43–51
Pascand M (1993) The essential polyunsaturated fatty acids of spirulina and our immune response. Bull Inst Oceanogr 12:49–57
Peet M, Langharne J, Rangarajan N, Renolds GP (1993) Tardive dyskinesia, lipid peroxidation and sustained amelioration with vitamin E treatment. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 8:151–153
Pires JG, Bonikovski V, Furturo-Neto HA (2005) Acute effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on neuroleptic-induced catalepsy in mice. Braz J Med Biol Res 38:1867–1872
Post A, Holsboer F, Behl C (1998) Induction of NF-kappaB activity during haloperidol-induced oxidative toxicity in clonal hippocampal cells: suppression of NF-kappaB and neuroprotection by antioxidants. J Neurosci 18:8236–8246
Raso GM, Meli R, Di Carlo R (2001) Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase expression by flavonoids in macrophage J773A.I. Life Sci 12:921–931
Ravindranath V, Reed DJ (1990) Glutathione depletion and formation of glutathione protein mixed disulfide following exposure of brain mitochondria to oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 169:150–158
Reddy R, Yao JK (1996) Free radical pathology in schizophrenia: a review. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 55:33–43
Roy S, Packer L (1998) Redox regulation of cell function by alpha-lipoate: biochemical and molecular aspects. Biofactors 7:263–267
Sagara Y (1998) Induction of reactive oxygen species in neurons by haloperidol. J Neurochem 71:1002–1012
Sahin M, Sagdic G, Elmas O, Akpinar D, Derin N, Asian M, Agar A, Aliciguzel Y, Yargicoglu P (2006) Effect of chronic resistant stress and alpha lipoic acid on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activity in rat peripheral organs. Pharmacol Res 54(3):247–252
Sanberg PR, Bunsey MD, Giordano M et al (1988) The catalepsy test: its ups and downs. Behav Neurosci 102:748–759
Sasaki H, Hashimoto K, Maeda Y, Inada T, Kitao Y, Fukui S, Iyo M (1995) Rolipram, a selective c-AMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor suppresses oro-facial dyskinetic movements in rats. Life Sci 56:443–447
Scapicchio P, Decina P, Mukherjee S, Caracci G (1991) Effects of α-tocopherol on persistent tardive dyskinesia in elderly schizophrenic patients. Ital J Psychiatry Behav Sci 1:111–114
Scholich H, Murphy ME, Sies H (1989) Antioxidant activity of dihydrolipoate against microsomal lipid peroxidation and its dependence on alpha-tocopherol. Biochem Biophys Acta 1001:256–261
See RE (1991) Striatal dopamine metabolism increases during long-term haloperidol administration in rats but shows tolerance in response to acute challenge with raclopride. Neurosci Lett 129:265–268
Sethumadhavan S, Chinnakannu P (2006) l-Carnitine and alpha lipoic acid improve age associated decline in mitochondrial respiratory activity of rat heart muscle. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 61(7):650–659
Sies H (1985) Oxidative stress: introductory remarks. In: Sies H (ed) Oxidative stress. Academic, London, pp 1–5
Shamir E, Barak Y, Plopsky I, Zisapel N, Elizur A, Weizman A (2000) Is melatonin treatment effective for tardive dyskinesia? J Clin Psychiatry 61:556–558
Shamir E, Barak Y, Shalman I, Laudon M, Zisapel N (2001) Melatonin treatment for tardive dyskinesia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:1049–1052
Sharma S, Paladino P, Gabriele J, Saeedi H, Henry P, Chang M, Mishra RK, Johnson RL (2003) Pro-Leu-glycinamide and its peptidomimetic, PAOPA, attenuate haloperidol induced vacuous chewing movements in rat: a model of human tardive dyskinesia. Peptides 2:313–319
Shirakawa O, Tamminga CA (1994) Basal ganglia GABA and dopamine D1 binding site correlates of haloperidol-induced oral dyskinesias in rat. Exp Neurol 127:62–69
Shivakumar BR, Ravindranath V (1993) Oxidative stress and thiol modification induced by chronic administration of haloperidol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265:1137–1141
Skoblenick KJ, Castellano JM, Rogoza RM, Dyck BA, Thomas N, Gabriele JP, Chong VZ, Mishra RK (2006) Translocation of AIF in the human and rat striatum following protracted haloperidol, but not clozapine treatment. Apoptosis 11(5):663–672
Soares KV, McGrath JJ (2000) Vitamin E for neuroleptic-induced tardive dyskinesia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2:CD000209
Subramaniam B, Rollema H, Woolf T, Castagnoli NG (1990) Identification of a potentially neurotoxic pyridinium metabolite of haloperidol in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 166:238–244
Sugioka K, Shimosegawa Y, Nakano M (1987) Estrogens as natural antioxidants of membrane phospholipids peroxidation. FEBS Lett 210:37–39
Thaakur SR, Jyothi B (2007) Effect of spirulina maxima on the tardive dyskinesia and oxidative stress induced by haloperidol in rats. J Neural Transm. doi:10.1007/S00702-007-0744
Ukai W, Ozawa H, Tateno M, Hashimoto E, Saito T (2004) Neurotoxic potential of haloperidol in comparison with risperidone: implication of Akt-mediated signal changes by haloperidol. J Neural Transm 111:667–681
Verma A, Kulkarni SK (1992) D1/D2 dopamine and NMDA receptor participation in experimental catalepsy in rats. Psychopharmacology 109(4):477–483
Von Voigtlander PF, Burian MA, Althaus JS, Willams LR (1990) Effects of chronic haloperidol on vitamin E levels and monoamine metabolism in rats fed normal and vitamin E deficient diets. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 68(3):343–352
Waddington JL (1990) Spontaneous orofacial movements induced in rodents by very long-term neuroleptic drug administration. Phenomenology, pathophysiology and putative relationship to tardive dyskinesia. Psychopharmacology 101:431–447
Yao JK, Reddy R, Elhinny LG, Vankammen DP (1998) Effects of haloperidol on antioxidant defense system enzymes in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 32:385–391
Zhang WJ, Frei B (2001) Alpha lipoic acid inhibits TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells. FASEB J 15(13):2423–2432
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thaakur, S., Himabindhu, G. Effect of alpha lipoic acid on the tardive dyskinesia and oxidative stress induced by haloperidol in rats. J Neural Transm 116, 807–814 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0232-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0232-y